How to Streamline Business Operations with Process Improvement Methodology

Operational efficiency remains the cornerstone of competitive business management. Companies that optimize their processes often achieve measurable improvements in performance. For instance, leveraging data analytics can lead to significant cost savings, enhanced customer satisfaction, and a stronger market position. By identifying inefficiencies within their processes and addressing them strategically, businesses not only improve current operations but also enhance their long-term resilience.
Implementing a methodology for process improvement provides a structured approach to streamlining operations. Techniques like Lean Manufacturing have demonstrated their ability to reduce costs, maximize value, and improve overall efficiency. In one example, organizations reported up to a 20% boost in operational efficiency within the first year of adopting such methodologies. These transformations highlight the undeniable role of process optimization in fostering growth and maintaining a competitive edge, particularly in the context of hiring systems that support effective business management.
Key Takeaways
Making operations simpler saves money and makes work faster for businesses.
Using methods like Lean and Six Sigma finds problems and improves tasks.
Checking processes often can show hidden problems and help use resources better.
Involving workers in improvements creates a habit of always getting better and being creative.
Automation tools help by doing repetitive tasks, so workers can focus on important work.
Watching key performance indicators (KPIs) ensures changes match business goals and show clear results.
Picking the right improvement method is key to meeting specific business needs.
Updating processes regularly helps businesses keep up with changes and stay successful.
Understanding the Methodology for Process Improvement
Definition and Core Principles
Process improvement methodologies provide structured frameworks for enhancing operational efficiency. These methodologies aim to identify inefficiencies, eliminate waste, and optimize workflows. At their core, they rely on principles rooted in operational excellence, such as respect for individuals, scientific thinking, and a focus on creating value for customers.
Operational excellence draws inspiration from historical management theories, including Adam Smith's division of labor and Frederick Winslow Taylor's scientific management. Henry Ford's assembly line innovation further shaped modern process improvement practices. These foundational ideas have evolved into methodologies like Lean Manufacturing, Six Sigma, and Agile, which prioritize continuous improvement and adaptability.
A closer look at the principles reveals their alignment with cultural enablers, drivers of improvement, and systemic thinking. For example:
Principle Area | Core Principles |
|---|---|
Cultural Enablers | Respect every individual, Lead with humility |
Drivers of Continuous Improvement | Seek Perfection, Assure Quality at the Source, Flow and Pull Value, Embrace Scientific Thinking, Focus on Process |
Alignment Factors | Think Systemically, Create Constancy of Purpose |
Results | Create Value for the Customer |
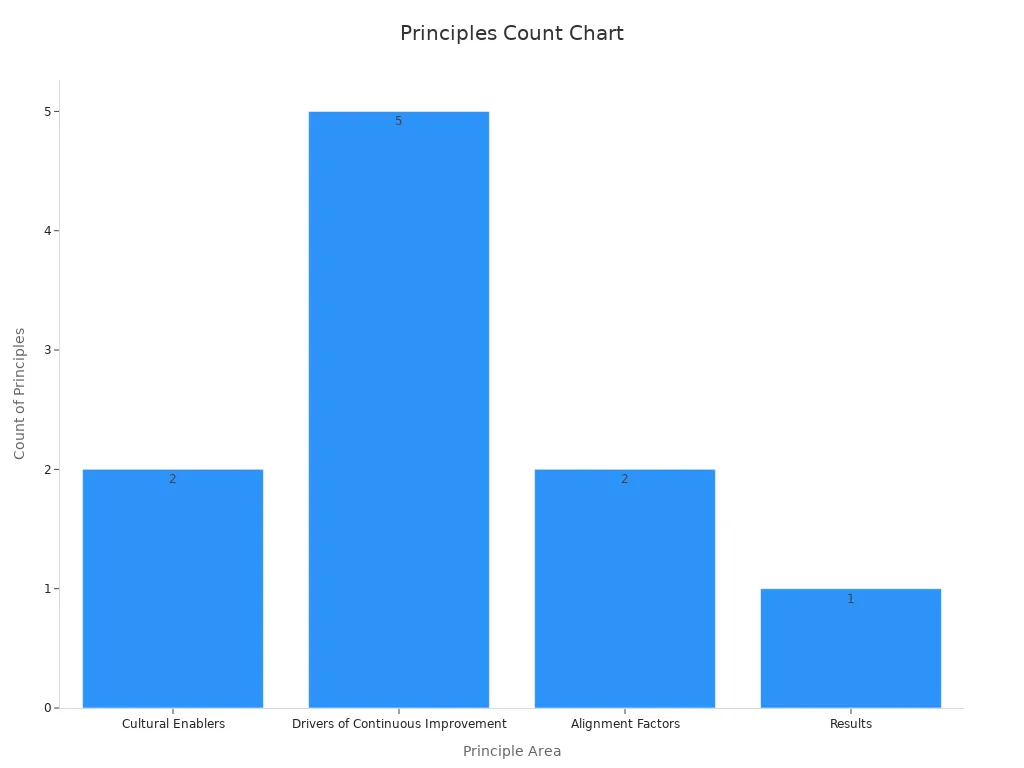
These principles serve as the foundation for methodologies that drive operational excellence across industries.
Why Process Improvement is Crucial for Business Success
Process improvement methodologies play a pivotal role in helping businesses achieve sustainable growth. By streamlining operations, organizations can reduce costs, enhance productivity, and improve customer satisfaction. For instance, Toyota's Just-In-Time manufacturing system led to a 30% reduction in costs within a few years, demonstrating the tangible benefits of adopting these methodologies.
Empirical research validates the effectiveness of process improvement methodologies across industries:
Methodology | Description | Empirical Evaluation |
|---|---|---|
Six Sigma | Aims to eliminate errors in manufacturing processes using quantitative tools. | Focuses on step-by-step optimization through experimental changes, validated through various case studies. |
Business Process Reengineering (BPR) | Optimizes processes on a large scale rather than incrementally. | Empirical evaluations indicate a high risk of project failure, suggesting a cautious approach to implementation. |
Process Improvement Patterns (PIPs) | Framework for assessing and implementing process improvements. | Validated through scenario-specific assessments, but generalizability remains a challenge. |
These methodologies enable businesses to adapt to market changes, address bottlenecks, and foster innovation. Companies like Siemens and Harley-Davidson have leveraged process improvement to achieve remarkable results, including productivity gains and cost reductions.
Company | Industry | Key Results |
|---|---|---|
Siemens | Technology/Manufacturing | 99.9989% quality rate, 140% productivity improvement, 17% energy reduction, 50% change time reduction, 99.7% on-time delivery |
Harley-Davidson | Automotive | 21 days to 6 hours lead time, 75% inventory reduction, 80% productivity improvement, 70% warranty claims reduction, 62% market share recovery |
These examples highlight the transformative impact of process improvement methodologies on business performance.
Characteristics of Effective Process Improvement Methodologies
Effective process improvement methodologies share several key characteristics that make them adaptable and impactful across industries. They emphasize data-driven decision-making, continuous improvement, and collaboration. For example, Six Sigma uses quantitative tools to reduce anomalies, while Lean Manufacturing focuses on eliminating waste and enhancing workflow efficiency.
Methodology | Key Characteristics | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
Kanban | Visual workflow management system to enhance efficiency and eliminate bottlenecks. | Improves workflow visibility, minimizes task overload, promotes consistency and adaptability. |
Six Sigma | Data-driven decision-making to reduce anomalies and enhance quality. | Cuts back errors, enhances product quality, promotes customer satisfaction. |
Total Quality Management (TQM) | Continuous improvement efforts engaging employees at all levels. | Sustains a culture of quality improvement, eliminates waste, promotes customer trust. |
Lean Manufacturing | Focuses on eliminating waste and enhancing workflow efficiency. | Cuts costs, champions operational speed, promotes customer value. |
These methodologies also prioritize adaptability, enabling organizations to respond to changing market demands. Agile methodology, for instance, fosters collaboration and responsiveness, while Kaizen promotes a culture of incremental improvements.
By aligning people, processes, and technology, businesses can achieve operational efficiency and long-term success. Systems and teams that adopt these methodologies often report significant improvements in productivity, cost savings, and customer satisfaction. Organizations interested in learning more about these methodologies can reach out to explore tailored solutions for their unique needs.
Benefits of Streamlining Business Operations
Reducing Costs and Optimizing Resources
Streamlining business operations directly impacts cost reduction and resource optimization. By eliminating inefficiencies, organizations can significantly lower operational expenses. For example, methodologies like Business Process Reengineering (BPR) have demonstrated a 75% decrease in process costs and a 65% reduction in process cycle times. Similarly, Kaizen has been shown to reduce operational costs by 30%.
Methodology | Cost Reduction | Resource Optimization |
|---|---|---|
BPR | 75% decrease | 65% reduction in cycle times |
Kaizen | 30% decrease | N/A |
TQM | N/A | 40% fewer complaints, 35% higher satisfaction |
General | 15-25% reduction | 30-40% improvement in resource utilization, 20-30% waste reduction |
Inefficiencies cost businesses 20–30% of their revenue annually. Employees often spend 36% of their workweek searching for information or clarifying tasks. By addressing these inefficiencies, companies can reallocate resources to high-value activities, ensuring better utilization and reducing waste.
Tip: Regular process audits can help identify areas where resources are underutilized, enabling businesses to make data-driven decisions for optimization.
Boosting Productivity and Workflow Efficiency
Streamlined processes enhance productivity by eliminating redundant tasks and improving workflow speed. Research shows that businesses focusing on process improvement can achieve up to 30% higher productivity gains. Integrated processes also allow employees to focus on higher-value tasks, leading to labor productivity increases of 30–50%.
Evidence Type | Description |
|---|---|
Improvements in Workflow Speed | Businesses report measurable increases in workflow speed due to the elimination of redundant tasks. |
Labor Productivity Gains | Productivity can increase by 30-50% with integrated processes, allowing employees to focus on higher-value tasks. |
Link Between Productivity and Process Integration | Fewer interruptions and bottlenecks lead to faster project throughput and higher profitability. |
Efficient workflows reduce interruptions and bottlenecks, enabling teams to complete projects faster and with greater accuracy. This not only improves operational efficiency but also fosters a more collaborative and productive work environment.
Note: Implementing tools like Kanban boards or workflow management software can further enhance visibility and efficiency across teams.
Enhancing Customer Experience and Satisfaction
Streamlined operations improve customer experiences by ensuring faster service delivery and higher-quality outcomes. Metrics such as Net Promoter Score (NPS), Customer Satisfaction (CSAT), and Customer Effort Score (CES) highlight the impact of process optimization on customer loyalty and satisfaction.
Metric | Purpose | Impact on Customer Experience |
|---|---|---|
NPS | Long-term strategy | Measures customer loyalty and likelihood to recommend |
CSAT | Specific touchpoints | Evaluates satisfaction at various interaction points |
CES | Process optimization | Assesses ease of customer interactions and identifies pain points |
Customers value seamless interactions and quick resolutions. By optimizing processes, businesses can reduce friction points, leading to higher satisfaction rates and stronger customer relationships. For instance, Total Quality Management (TQM) has been associated with a 40% reduction in customer complaints and a 35% increase in satisfaction.
Callout: Happy customers are more likely to become repeat buyers and brand advocates, driving long-term business success.
Gaining a Competitive Advantage in the Market
Streamlined business operations provide organizations with a significant edge in competitive markets. By optimizing processes, companies can deliver better products and services, respond faster to market demands, and allocate resources more effectively. These improvements not only enhance internal efficiency but also strengthen a company’s position in the marketplace.
One of the most critical indicators of competitive advantage is market share growth. Businesses that streamline their operations often gain a larger share of their industry by outperforming competitors in cost efficiency and service delivery. For example, companies that reduce production cycle times can bring products to market faster, capturing customer interest before competitors. This agility allows businesses to stay ahead in industries where speed and innovation are key.
KPI | Description | Importance for Competitive Advantage |
|---|---|---|
Market Share Growth | Measures the percentage of an industry that a company controls. | Indicates overall competitiveness and market position. |
Customer Satisfaction | Assesses how products or services meet customer expectations. | High satisfaction can lead to customer loyalty and retention. |
Return on Investment (ROI) | Evaluates the profitability of investments relative to their costs. | Essential for understanding the financial impact of operations. |
Customer satisfaction also plays a pivotal role in gaining a competitive edge. Streamlined operations ensure consistent quality and faster service delivery, which directly impacts customer loyalty. Satisfied customers are more likely to recommend a business, increasing its reputation and market reach. Metrics like Net Promoter Score (NPS) and Customer Effort Score (CES) help businesses measure these outcomes and refine their strategies.
Tip: Businesses can use systematic data collection and analysis to monitor performance and identify areas for improvement. Transforming unstructured information into actionable insights enables better decision-making and operational optimization.
Return on Investment (ROI) is another key metric that highlights the financial benefits of streamlined operations. Companies that optimize workflows and reduce waste often see higher profitability. For instance, investing in automation tools may initially require capital, but the long-term savings and productivity gains far outweigh the costs. This financial efficiency not only boosts ROI but also frees up resources for innovation and growth.
Benefits of streamlined operations for competitive advantage include:
Faster response to market changes.
Improved product and service quality.
Enhanced customer loyalty and retention.
Higher profitability and resource optimization.
Streamlining operations equips businesses with the tools to adapt quickly to evolving market conditions. By focusing on efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction, companies can secure a stronger foothold in their industries and achieve sustainable growth.
Steps to Apply the Methodology for Process Improvement
Identifying Bottlenecks and Areas for Improvement
The first step in applying a methodology for process improvement involves identifying bottlenecks and areas that hinder efficiency. Bottlenecks are points in a process where delays occur, causing disruptions in workflow and reducing overall productivity. Recognizing these problem areas allows organizations to focus their efforts on the most critical issues.
Several tools and techniques can help identify bottlenecks effectively. For example, value stream mapping provides a visual representation of workflows, highlighting inefficiencies and areas of waste. Gemba walks, where managers observe processes directly on the work floor, offer valuable insights into real-time challenges. These methods have proven successful across industries. A pharmaceutical company, for instance, used Gemba walks to identify a bottleneck in tablet coating. By implementing quick changeover techniques, the company achieved a 25% increase in overall equipment effectiveness.
Continuous improvement plays a vital role in addressing bottlenecks. Toyota’s production system demonstrates this through takt time calculations, which align production rates with customer demand. Similarly, an automotive parts manufacturer applied the theory of constraints to increase throughput by 30% and reduce work-in-process inventory by 20%.
Tip: Regularly reviewing processes and involving employees in identifying inefficiencies can lead to more accurate and actionable insights.
Choosing the Right Methodology for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate methodology for process improvement is crucial for achieving desired outcomes. Different methodologies offer unique approaches, and the choice depends on the specific needs and goals of the organization. For example, Lean focuses on eliminating waste, while Six Sigma emphasizes reducing variability and defects. Agile prioritizes adaptability, making it ideal for dynamic environments.
Research shows that choosing the right methodology can significantly enhance operational success. Companies that effectively reduce process time cycles experience a 20-50% boost in efficiency and are 2.5 times more likely to lead their industry. Streamlined workflows save an average of 270 hours per employee in the first year, translating into financial benefits of approximately $7,924 per process improvement.
Organizations should evaluate their current challenges and objectives before deciding on a methodology. For instance, a manufacturing company aiming to improve quality might benefit from Six Sigma, while a service-based organization seeking flexibility could adopt Agile. Aligning the methodology with organizational goals ensures a higher likelihood of success.
Callout: Systems and teams that tailor their approach to their unique needs often achieve better results. For more guidance, reach out to explore tailored solutions.
Implementing Changes and Solutions Effectively
Once a methodology is selected, implementing changes requires careful planning and execution. Organizations should start by developing a clear action plan that outlines specific steps, timelines, and responsibilities. Communication is key during this phase to ensure all stakeholders understand the changes and their roles in the process.
Case studies highlight the importance of effective implementation. In healthcare, reengineering product screening and development processes streamlined operations and eliminated low-value projects, leading to improved efficiency and profitability. Similarly, a manufacturing company used process mining software to analyze procure-to-pay processes. This approach reduced maverick buying and rework costs, resulting in significant operational improvements.
Industry | Approach | Results |
|---|---|---|
Healthcare | Streamlined operations, eliminated low-value projects, improved efficiency and profitability. | |
Manufacturing | Analyzed procure-to-pay processes using process mining software. | Reduced maverick buying and rework costs, improved operational efficiency, and cost savings. |
Financial Services | Automated account opening processes to increase customer engagement. | Increased customer engagement and profitability, allowing more valuable interactions. |
Intergovernmental Org | Implemented comprehensive business process redesign methodology. | Achieved over two dozen process improvements, realizing annual cost savings exceeding $5 million. |
Monitoring progress is equally important. Organizations should track key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the impact of changes. Metrics such as cycle time, defect rates, and customer satisfaction provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of the improvements. Regular reviews and adjustments ensure that the changes remain aligned with organizational goals.
Note: Effective implementation requires collaboration across all levels of the organization. Engaging employees and providing training can foster a culture of continuous improvement.
Monitoring Progress and Measuring Outcomes
Monitoring progress ensures that process improvement initiatives achieve their intended outcomes. Organizations must track key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the effectiveness of changes. Metrics such as cycle time, defect rates, and customer satisfaction provide valuable insights into operational performance. Regular monitoring helps identify whether adjustments are needed to stay aligned with business goals.
A structured approach to monitoring involves setting clear benchmarks. For example, a company implementing Lean methodology might track waste reduction percentages or production cycle times. These benchmarks act as reference points to evaluate success. Tools like dashboards and analytics software simplify the process by offering real-time data visualization. This allows decision-makers to respond quickly to deviations.
Tip: Use visual tools like Gantt charts or Kanban boards to track progress and maintain transparency across teams.
Measuring outcomes also involves gathering feedback from employees and customers. Employee feedback highlights internal challenges, while customer feedback reveals the impact of changes on service quality. For instance, a higher Net Promoter Score (NPS) indicates improved customer satisfaction, which often correlates with streamlined operations.
Continuous monitoring fosters accountability. Teams remain focused on achieving measurable results, and leaders can make informed decisions based on data. This proactive approach minimizes risks and ensures that process improvements deliver long-term benefits.
Refining and Optimizing Processes Continuously
Refining processes is not a one-time effort. Continuous optimization ensures that businesses adapt to changing market conditions and maintain efficiency. Methodologies like Kaizen emphasize small, incremental changes that eliminate waste and improve workflows. This approach creates a culture of ongoing improvement, where employees actively seek ways to enhance processes.
Business Process Management (BPM) provides a structured framework for continuous refinement. It involves five phases: Design, Model, Implement, Monitor, and Optimize. Each phase builds on the previous one, ensuring that processes evolve to meet organizational goals. For example, during the "Optimize" phase, businesses analyze performance data to identify areas for further improvement.
Benefits of continuous refinement include:
Enhanced adaptability to market changes.
Improved resource utilization.
Sustained operational efficiency.
Digital transformation initiatives often rely on process optimization. Automation tools, for instance, streamline repetitive tasks, freeing employees to focus on strategic activities. A financial services firm that automated its account opening process reported increased customer engagement and profitability. This demonstrates how optimization supports broader business objectives.
Callout: Encourage employees to participate in improvement initiatives. Their insights often lead to innovative solutions that drive efficiency.
Refinement also involves revisiting methodologies. Businesses should periodically assess whether their chosen methodology for process improvement aligns with current needs. Adjusting strategies ensures that processes remain relevant and effective. For instance, a company using Six Sigma might integrate Agile principles to enhance flexibility in dynamic environments.
By fostering a mindset of continuous improvement, organizations can achieve sustained growth and resilience. This approach not only enhances operational efficiency but also positions businesses to thrive in competitive markets.
Comparing Popular Process Improvement Methodologies
Lean Methodology: Eliminating Waste for Maximum Value
Lean methodology focuses on eliminating waste to maximize value for customers. It emphasizes efficiency by identifying and removing non-value-added activities from workflows. Businesses that adopt Lean often experience significant improvements in productivity, cost reduction, and quality.
A study by the Lean Enterprise Research Centre revealed that organizations implementing Lean reduced lead times by 70–90%. McKinsey & Company reported a 25–30% decrease in manufacturing costs, while the Aberdeen Group noted an 80% improvement in quality. These statistics highlight Lean’s effectiveness in transforming operations.
Statistic | Improvement Percentage/Value | Source |
|---|---|---|
Reduction in Lead Time | 70-90% | Lean Enterprise Research Centre |
Decrease in Manufacturing Costs | 25-30% | McKinsey & Company |
Improvement in Quality | 80% | Aberdeen Group |
Increase in Labor Productivity | 35% | Boston Consulting Group |
Return on Investment | 200% | Industry Week |
Lean methodology also fosters a culture of continuous improvement. Employees actively participate in identifying inefficiencies and proposing solutions. This collaborative approach ensures sustained operational excellence and adaptability to market demands.
Tip: Businesses can use tools like value stream mapping to visualize workflows and pinpoint areas for improvement.
Six Sigma: Reducing Variability and Defects
Six Sigma aims to minimize process variability and defects by using data-driven techniques. It relies on statistical analysis to identify and eliminate errors, ensuring consistent quality. Organizations that implement Six Sigma often achieve higher efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Lower Defects Per Million Opportunities (DPMO) values demonstrate Six Sigma’s impact. Automated manufacturing lines typically achieve DPMO rates of 30,000, compared to manual processes with rates as high as 90,000. This reduction in defects highlights the methodology’s ability to enhance precision and reliability.
Six Sigma focuses on reducing variability to improve quality.
Automated processes often achieve lower DPMO values, reflecting fewer defects.
A DPMO of zero signifies perfection, while higher values indicate increased variability.
Six Sigma also promotes a structured approach to problem-solving through its DMAIC framework (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control). This systematic process ensures that improvements are sustainable and aligned with organizational goals.
Callout: Businesses seeking to enhance product quality and reduce waste can benefit significantly from Six Sigma’s data-driven approach.
Agile: Adapting Quickly to Change
Agile methodology prioritizes adaptability and responsiveness to changing market conditions. It enables teams to refine products iteratively based on user feedback and evolving customer needs. This approach ensures businesses remain competitive in dynamic environments.
Agile practices support shorter development cycles, allowing teams to prototype and test rapidly. Regular feedback loops help validate goals and adjust strategies. Close collaboration between teams ensures alignment with business objectives, enhancing overall adaptability.
Agile promotes iterative development for rapid prototyping and testing.
Teams validate goals frequently and make necessary adjustments.
Faster learning cycles improve responsiveness to market dynamics.
By embracing Agile, organizations can respond quickly to customer demands and market shifts. This flexibility fosters innovation and accelerates time-to-market for new products.
Note: Agile is particularly effective in industries where speed and adaptability are critical, such as technology and software development.
Kaizen: Fostering a Culture of Continuous Improvement
Kaizen, a Japanese term meaning "change for the better," emphasizes small, incremental improvements to achieve long-term operational excellence. This methodology fosters a culture where employees actively participate in identifying inefficiencies and proposing solutions. By focusing on continuous improvement, Kaizen helps organizations enhance productivity, reduce waste, and improve overall quality.
One of Kaizen's key strengths lies in its ability to engage employees at all levels. Participation in Kaizen activities encourages collaboration and innovation, creating a workplace culture that values improvement. For example, employees often suggest practical changes during Kaizen events, leading to measurable outcomes such as reduced defect rates and increased efficiency.
Metric | Description |
|---|---|
Output per Labor Hour | Indicates increased productivity post-Kaizen, showing more output per labor hour. |
Defect Rate Reduction | Measures quality improvements by tracking the percentage of defects in total output. |
Rework and Scrap Reduction | Reflects process efficiency by reducing rework and scrap, improving first-pass yield. |
Customer Complaints Rate | Fewer complaints post-Kaizen indicate enhanced customer satisfaction. |
Direct Cost Savings | Tracks measurable cost reductions achieved through Kaizen events. |
Inventory Cost Reduction | Measures improvements in flow and reduced holding costs due to better inventory management. |
Waste Elimination | Assesses the reduction of non-value-added activities, leading to cost savings. |
Participation Rates in Kaizen | Indicates employee engagement in Kaizen activities, reflecting a strong continuous improvement culture. |
Employee Suggestions Implemented | Shows the effectiveness of employee ideas generated during Kaizen events. |
Employee Satisfaction Surveys | Evaluates the impact of Kaizen on team morale and workplace culture through pre- and post-event surveys. |
Rate of Sustained Improvements | Tracks the longevity of changes made during Kaizen events over time. |
Follow-up Audits | Verifies adherence to new standards post-Kaizen, ensuring improvements are maintained. |
Standardized Work Adoption Rates | Measures the percentage of employees trained on new standards, ensuring consistency in application. |
Kaizen’s emphasis on small changes ensures that improvements are sustainable. Organizations that adopt this methodology often report higher employee satisfaction and stronger customer relationships. By eliminating waste and optimizing workflows, Kaizen creates a foundation for continuous growth and adaptability.
Tip: Encourage employees to share ideas during Kaizen events. Their insights often lead to innovative solutions that drive efficiency and quality.
Business Process Reengineering (BPR): Rethinking Processes for Radical Change
Business Process Reengineering (BPR) takes a bold approach to process improvement by rethinking and redesigning workflows from the ground up. Unlike incremental methodologies, BPR focuses on achieving dramatic improvements in efficiency, cost reduction, and quality. This methodology is ideal for organizations seeking transformative change rather than gradual enhancements.
BPR often involves analyzing existing processes to identify inefficiencies and redundancies. Once problem areas are identified, organizations redesign workflows to eliminate bottlenecks and optimize resource utilization. For example, a company implementing BPR might restructure its supply chain to reduce delivery times and improve customer satisfaction.
Outcome Type | Description |
|---|---|
Cost Reduction | |
Time Savings | Faster product delivery and shorter cycle times. |
Quality Improvements | Higher consistency and reliability in outputs. |
ROI | ROI of several hundred percent over time. |
Organizations that successfully implement BPR often achieve significant cost savings and efficiency gains. However, this methodology requires careful planning and execution to minimize risks. Employee training and stakeholder engagement play a crucial role in ensuring the success of BPR initiatives.
Callout: BPR is best suited for businesses facing major challenges or seeking to overhaul outdated processes.
PDCA Cycle: A Systematic Approach to Iterative Improvement
The PDCA cycle, also known as Plan-Do-Check-Act, provides a structured framework for iterative process improvement. This methodology emphasizes continuous learning and adaptation, making it ideal for organizations aiming to refine workflows over time.
Continuous Improvement: The iterative nature of the PDCA cycle fosters a culture of continuous learning and improvement.
Data-Driven Decision Making: Emphasizes the collection and analysis of data throughout the cycle.
Customer-Centric Focus: Ensures customer feedback and satisfaction levels are consistently evaluated.
Organizations using the PDCA cycle often report measurable improvements in key performance indicators. Metrics such as defect rates, process cycle times, and employee productivity highlight the effectiveness of this approach. For example, a company might use the PDCA cycle to reduce production defects by analyzing root causes and implementing corrective actions.
To assess the effectiveness of the PDCA cycle, businesses should consider both quantitative measures, such as cost savings, and qualitative measures, like employee satisfaction. Regular feedback loops ensure that improvements align with organizational goals and customer expectations.
Note: The PDCA cycle is particularly effective in industries where adaptability and precision are critical, such as manufacturing and healthcare.
Practical Tips and Tools for Getting Started
Conducting a Comprehensive Process Audit
A comprehensive process audit serves as the foundation for identifying inefficiencies and opportunities for improvement. This step involves analyzing workflows, pinpointing bottlenecks, and understanding user behavior. By conducting a detailed audit, businesses can streamline operations and enhance overall performance.
Key metrics validate the importance of process audits in improving business outcomes:
Metric | Description |
|---|---|
Improve User Flow | Streamline the user's journey by understanding where and why users abandon tasks or get stuck. |
Enhance User Engagement | Increase user satisfaction and retention by understanding their behavior and pain points. |
Boost Conversion Rates | Track metrics that directly contribute to revenue, such as form completions, purchases, or subscription sign-ups. |
Time on Task | Track the amount of time users spend on specific tasks, indicating whether redesigns improve efficiency. |
User Engagement | Evaluate user feedback through surveys, qualitative interviews, or user testing to measure satisfaction. |
Process audits also uncover hidden inefficiencies that may not be immediately apparent. For example, systems and teams that regularly audit their workflows often discover opportunities to reduce redundant tasks and improve resource allocation. This proactive approach ensures that businesses remain agile and responsive to changing market demands.
Tip: Use tools like value stream mapping or process mining software to visualize workflows and identify areas for improvement.
Leveraging Technology and Automation Tools
Technology and automation tools play a pivotal role in streamlining business operations. These tools reduce manual effort, enhance accuracy, and free up employees to focus on strategic tasks. Organizations that embrace automation often report significant improvements in productivity and decision-making.
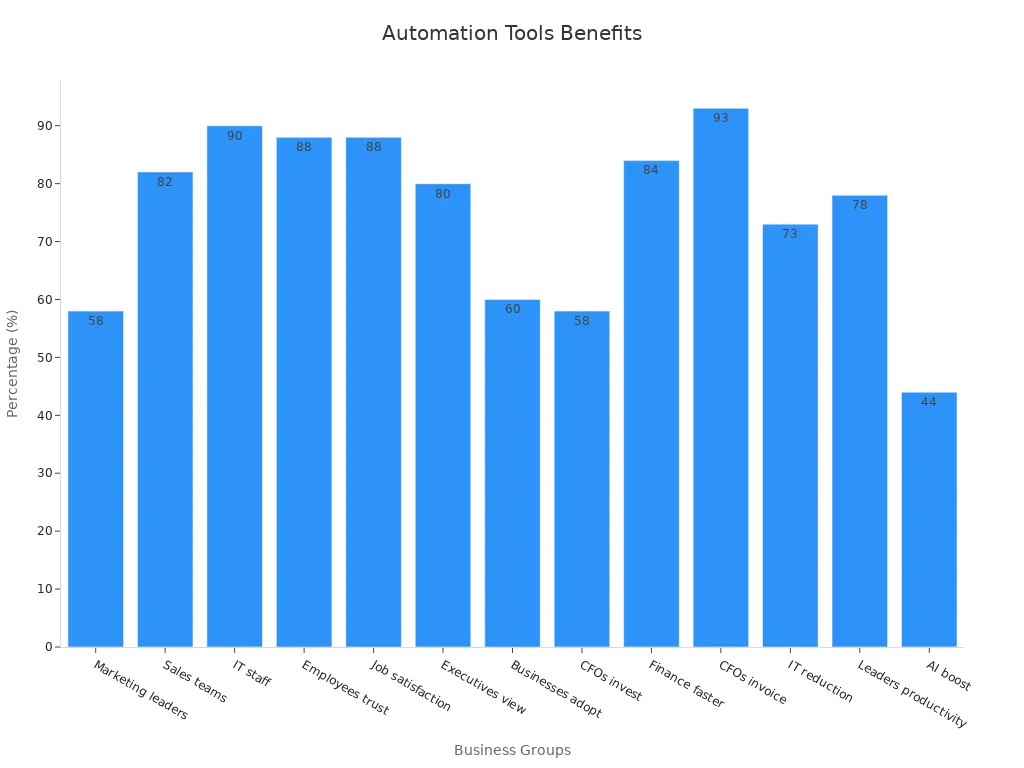
The following statistics highlight the benefits of automation:
Statistic | Source |
|---|---|
58% of marketing leaders automated email processes in 2024. | Statista |
82% of sales teams can focus on client relationships due to automation. | Salesforce |
90% of IT staff credit automation for improved collaboration. | Salesforce |
88% of employees trust the accuracy of automation tools. | Salesforce |
88% report higher job satisfaction due to automation. | Salesforce |
80% of executives believe automation is useful for business decisions. | N/A |
60% of businesses have implemented automation solutions. | Duke University |
84% of finance staff make faster decisions thanks to automation. | N/A |
93% of CFOs have shorter invoice processing times due to automation. | N/A |
73% of IT leaders report a 50% reduction in manual task time. | N/A |
78% of business leaders see a positive impact on productivity from automation. | N/A |
44% increase in productivity from AI adoption. | N/A |
Automation tools also enhance collaboration across departments. For instance, systems and teams that implement automated workflows often experience faster decision-making and improved communication. These tools not only optimize operations but also empower employees to achieve better results.
Callout: Businesses can explore automation solutions tailored to their unique needs. Reach out to learn how systems and teams can help implement these tools effectively.
Building a Culture of Continuous Improvement
A culture of continuous improvement ensures that organizations remain adaptable and innovative. This culture relies on well-trained employees who actively identify problems and propose solutions. By fostering this mindset, businesses can achieve sustained operational benefits.
Key benefits of a continuous improvement culture include:
Boosts Employee Engagement and Retention
Enhances Customer Satisfaction
Improves Efficiency and Productivity
Encourages Innovation
Promotes Learning and Development
Fosters a Culture of Transparency and Accountability
Facilitates Change Management
A continuous improvement culture thrives when employees feel empowered to contribute. Training programs play a crucial role in equipping teams with the skills needed to drive change. For example, systems and teams that prioritize employee development often report higher engagement and productivity levels.
Block Quote: Continuous improvement needs to be driven by the frontline or your employees in the field. They are the ones who should be identifying the problems, and developing and implementing the improvements.
Organizations that embrace continuous improvement also benefit from enhanced customer satisfaction. By consistently refining processes, businesses can deliver better products and services, strengthening customer loyalty and trust.
Tip: Encourage employees to participate in improvement initiatives. Their insights often lead to innovative solutions that drive efficiency and quality.
Training and Empowering Employees for Success
Training employees equips them with the skills needed to implement process improvement methodologies effectively. Empowered employees contribute to smoother workflows and higher productivity. Organizations that prioritize training often see better engagement and improved outcomes.
A structured training program ensures employees understand the tools and techniques required for process optimization. For example, workshops on Lean or Six Sigma methodologies provide practical knowledge. Employees learn to identify inefficiencies, analyze data, and implement solutions. These skills enable them to take ownership of their roles and drive continuous improvement.
Tip: Use role-specific training to address the unique needs of different departments. Tailored programs ensure employees gain relevant skills.
Empowerment goes beyond training. It involves giving employees the authority to make decisions and solve problems. When employees feel trusted, they take initiative and contribute innovative ideas. For instance, Kaizen events encourage team members to suggest small, incremental changes. These contributions often lead to significant improvements over time.
Key Benefits of Training and Empowerment | Impact on Business |
|---|---|
Enhanced Skill Development | Employees perform tasks more efficiently. |
Increased Engagement | Teams feel motivated and valued. |
Better Decision-Making | Employees solve problems independently. |
Higher Productivity | Processes run smoothly with fewer delays. |
Regular feedback and recognition also play a vital role. Managers should acknowledge employee efforts and provide constructive input. This approach fosters a positive work environment and encourages continuous learning.
Callout: Empowered employees are more likely to embrace change and adapt to new methodologies. Their involvement ensures the success of process improvement initiatives.
Using Process Mapping and Analysis Tools Effectively
Process mapping tools provide a visual representation of workflows, helping organizations identify inefficiencies. These tools highlight bottlenecks, redundancies, and areas for improvement. By analyzing these maps, businesses can streamline operations and enhance productivity.
Flowcharts, value stream maps, and swimlane diagrams are popular tools for process mapping. Each tool serves a specific purpose. For instance, flowcharts outline the sequence of steps in a process, while swimlane diagrams show responsibilities across departments. Value stream maps focus on identifying waste and optimizing value delivery.
Example: A manufacturing company used value stream mapping to reduce production cycle times by 20%. The map revealed unnecessary steps, which the team eliminated to improve efficiency.
Tool | Purpose | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
Flowchart | Visualizes step-by-step processes. | Simplifies complex workflows. |
Value Stream Map | Identifies waste and optimizes value delivery. | Improves efficiency and reduces costs. |
Swimlane Diagram | Clarifies roles and responsibilities. | Enhances cross-department collaboration. |
Analysis tools complement process mapping by providing data-driven insights. Tools like process mining software analyze workflows to uncover hidden inefficiencies. These insights guide decision-makers in implementing targeted improvements.
Tip: Combine process mapping with data analysis for a comprehensive understanding of workflows. This approach ensures more effective solutions.
Effective use of these tools requires collaboration. Teams should work together to create accurate maps and analyze data. Regular reviews ensure that processes remain aligned with organizational goals. By leveraging these tools, businesses can achieve sustained operational excellence.
Real-World Examples of Process Improvement Success

Case Study 1: Lean Implementation in Toyota’s Manufacturing Process
Toyota revolutionized its manufacturing process by adopting Lean methodology. This approach focused on eliminating waste and optimizing workflows to deliver maximum value to customers. The company introduced the Toyota Production System (TPS), which emphasized principles like Just-In-Time (JIT) production and continuous improvement (Kaizen).
One of the most notable achievements of TPS was the reduction of inventory waste. By producing only what was needed, when it was needed, Toyota minimized excess stock and storage costs. The company also implemented standardized work processes, which improved efficiency and reduced errors. For example, assembly line workers followed detailed instructions, ensuring consistent quality across all vehicles.
The results of Lean implementation were remarkable. Toyota reduced production lead times by 50% and increased labor productivity by 25%. The company also achieved higher customer satisfaction due to faster delivery times and improved product quality. These outcomes solidified Toyota’s position as a global leader in the automotive industry.
Tip: Businesses can adopt Lean principles like JIT and Kaizen to reduce waste and enhance operational efficiency.
Case Study 2: Six Sigma in General Electric’s Operational Strategy
General Electric (GE) embraced Six Sigma to improve its operational strategy and achieve higher quality standards. The methodology focused on reducing process variability and eliminating defects through data-driven decision-making. GE trained thousands of employees as Six Sigma Green Belts and Black Belts, equipping them with the skills to identify and solve problems.
One of GE’s key initiatives involved optimizing its billing process. The company used the DMAIC framework (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) to identify inefficiencies and implement solutions. By analyzing data, GE discovered that errors in billing caused delays and customer dissatisfaction. The team streamlined the process, reducing defects by 98%.
The impact of Six Sigma on GE’s operations was significant. The company saved over $1 billion in its first five years of implementation. Customer satisfaction scores improved, and operational costs decreased. These successes demonstrated the power of Six Sigma in driving measurable results.
Callout: Six Sigma’s structured approach makes it ideal for organizations aiming to enhance quality and reduce costs.
Lessons Learned from Successful Process Improvement Initiatives
Real-world examples like Toyota and GE highlight valuable lessons for businesses. First, adopting a structured methodology ensures consistent results. Lean and Six Sigma provided clear frameworks for identifying inefficiencies and implementing changes. Second, employee involvement is crucial. Both companies empowered their teams to contribute ideas and drive improvements.
Another key takeaway is the importance of data. GE’s success with Six Sigma relied on analyzing metrics to make informed decisions. Similarly, Toyota used performance data to refine its processes continuously. Finally, businesses must focus on customer value. Streamlined operations not only reduce costs but also enhance customer satisfaction.
Note: Organizations should prioritize training and data analysis to maximize the benefits of process improvement methodologies.
Adopting a methodology for process improvement is essential for achieving operational efficiency. Businesses that streamline their processes often experience cost savings, productivity gains, and improved customer satisfaction. These benefits not only enhance internal operations but also strengthen market competitiveness.
The first step toward improvement involves evaluating current workflows and identifying inefficiencies. By exploring the methodologies discussed, organizations can implement tailored solutions that drive long-term success. Taking action today ensures a more efficient and resilient future.
FAQ
What is process improvement methodology?
Process improvement methodology refers to structured frameworks designed to enhance business operations. These methodologies identify inefficiencies, eliminate waste, and optimize workflows. Popular examples include Lean, Six Sigma, and Agile. They aim to improve productivity, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.
How do businesses identify inefficiencies in their processes?
Businesses use tools like value stream mapping, Gemba walks, and process mining software to identify inefficiencies. These tools visually represent workflows, highlight bottlenecks, and uncover areas of waste. Regular audits and employee feedback also provide valuable insights into operational challenges.
Which industries benefit most from process improvement methodologies?
Industries like manufacturing, healthcare, technology, and financial services benefit significantly. For example, manufacturing uses Lean to reduce waste, while healthcare applies Six Sigma to improve patient care. Any industry seeking efficiency and quality improvements can adopt these methodologies.
How does automation support process improvement?
Automation reduces manual tasks, enhances accuracy, and speeds up workflows. Tools like robotic process automation (RPA) streamline repetitive processes, allowing employees to focus on strategic activities. Businesses often report higher productivity and cost savings after implementing automation solutions.
What is the role of employees in process improvement?
Employees play a crucial role by identifying inefficiencies and suggesting solutions. Their involvement fosters a culture of continuous improvement. Training programs equip them with the skills needed to implement methodologies like Kaizen or Six Sigma effectively.
How can businesses measure the success of process improvement initiatives?
Businesses track key performance indicators (KPIs) like cycle time, defect rates, and customer satisfaction. Tools like dashboards and analytics software provide real-time data. Regular reviews ensure that improvements align with organizational goals and deliver measurable results.
What challenges do businesses face when implementing process improvement?
Common challenges include resistance to change, lack of employee training, and unclear objectives. Effective communication, leadership support, and structured action plans help overcome these obstacles. Businesses must also monitor progress to ensure sustained success.
Can small businesses adopt process improvement methodologies?
Yes, small businesses can benefit from methodologies like Lean or Agile. These frameworks are scalable and adaptable to different organizational sizes. Small businesses often achieve significant cost savings and efficiency gains by streamlining their operations.
Tip: Start small by focusing on one process and gradually expand improvements across the organization.



