How to Achieve Efficiency with Business Process Improvement Methodologies

Achieving efficiency in business operations demands the strategic application of business process improvement methodologies. These methodologies enable organizations to streamline workflows, reduce waste, and enhance productivity. For instance, businesses that prioritize process improvement often see a 20% increase in operational efficiency within the first year. Over time, they experience a 40% reduction in production defects and a 30% decrease in operational costs. Continuous improvement, a core principle of Total Quality Management, ensures long-term success by fostering innovation and refining systems like hiring systems and optimization steps. Companies that embrace these practices gain a competitive edge in their industries.
Key Takeaways
Improving business processes can make work 20% faster in a year.
Using these methods can cut costs by 30% in five years.
Always improving helps businesses stay creative and handle market changes.
Six Sigma and Lean Manufacturing help reduce mistakes and save resources.
Involving workers in improvements boosts their mood and gives better results.
Checking processes often keeps them useful and meeting company goals.
Using tools like automation makes tasks easier and reduces mistakes.
Picking the best method means looking at needs and resources.
Understanding Business Process Improvement Methodologies
What Are Business Process Improvement Methodologies?
Business Process Improvement Methodologies refer to structured approaches designed to analyze, optimize, and enhance business processes. These methodologies aim to eliminate inefficiencies, reduce errors, and improve overall performance. By focusing on continuous improvement, organizations can adapt to changing market demands and maintain a competitive edge. For example, Six Sigma and Lean Manufacturing are widely recognized methodologies that help businesses achieve operational excellence.
A study by industry experts highlights the impact of these methodologies on key metrics:
Metric | Value |
|---|---|
20% | |
Reduction in production defects (5 years) | 40% |
Decrease in operational costs (5 years) | 30% |
Boost in customer satisfaction (5 years) | 25% |
These figures demonstrate the tangible benefits of adopting Business Process Improvement Methodologies.
Why Are They Essential for Efficiency?
Efficiency is the backbone of any successful organization. Business Process Improvement Methodologies play a crucial role in achieving this by streamlining workflows and eliminating waste. For instance, Lean Manufacturing focuses on reducing non-value-adding activities, while Agile promotes adaptability and faster delivery of results.
Organizations that implement these methodologies report significant improvements in operational efficiency and cost savings. A bar chart below illustrates the percentage improvements achieved through process optimization:
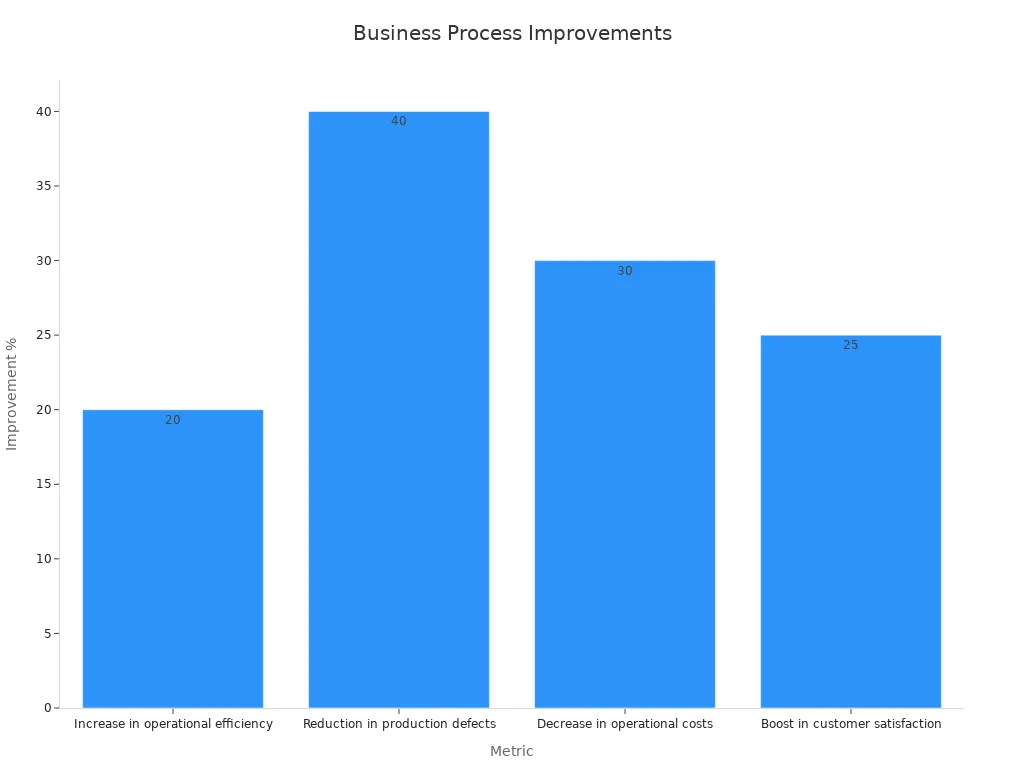
These methodologies not only enhance productivity but also foster a culture of continuous improvement, ensuring long-term success.
Key Benefits of Implementing These Methodologies
Adopting Business Process Improvement Methodologies offers numerous advantages. Some of the key benefits include:
Increased Operational Efficiency: Streamlined processes lead to faster and more effective operations.
Reduced Costs: Companies like Motorola saved over $16 billion by implementing Six Sigma.
Improved Customer Satisfaction: Research shows that 90% of consumers prefer businesses that use modern and efficient processes.
Enhanced Employee Satisfaction: Clear and efficient workflows reduce frustration and boost morale among team members.
These benefits highlight the transformative potential of Business Process Improvement Methodologies. By focusing on optimization, organizations can achieve sustainable growth and maintain a competitive advantage.
Key Business Process Improvement Methodologies

Six Sigma
Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology that aims to improve processes by identifying and eliminating defects. It uses statistical tools and techniques to achieve near-perfect quality. This approach focuses on reducing variability in processes, which leads to consistent and predictable outcomes. Six Sigma is widely adopted in both manufacturing and service industries due to its proven effectiveness.
For example, in the manufacturing sector, Six Sigma implementation improved yield by 18%, saving millions in costs. In the healthcare industry, it reduced emergency room wait times by 28%. The table below highlights additional outcomes achieved through Six Sigma across various industries:
Industry | Outcome Description |
|---|---|
Automated Systems | Reduced order processing time by 50% with 99.9% accuracy. |
Medical Devices | Customer complaints dropped by 45% after SPC implementation. |
Automotive | Defect rates reduced by 37% within six months. |
Electronics | Throughput increased by 22% after adopting SPC techniques. |
Finance | Trading efficiency improved by 50%, operational errors reduced by 65%. |
These results demonstrate the versatility and impact of Six Sigma in achieving operational excellence.
Lean Manufacturing
Lean Manufacturing focuses on minimizing waste while maximizing value. This methodology emphasizes identifying non-value-adding activities and eliminating them to streamline processes. By doing so, organizations can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Lean Manufacturing operates on five core principles: defining value, mapping the value stream, creating flow, establishing pull, and pursuing perfection. These principles ensure that every step in the process adds value to the final product or service. For instance, companies using Lean Manufacturing often experience faster production cycles and lower inventory costs. This methodology also fosters a culture of continuous improvement, encouraging teams to regularly evaluate and refine their workflows.
Comparative analysis of business process improvement methodologies shows that Lean Manufacturing excels in reducing waste and improving productivity. Its focus on efficiency makes it a popular choice for industries seeking to optimize their operations.
Kaizen
Kaizen, a Japanese term meaning "continuous improvement," is a methodology that encourages small, incremental changes to improve processes. Unlike other methodologies that focus on large-scale transformations, Kaizen emphasizes daily improvements involving all employees. This approach fosters a culture of collaboration and innovation within organizations.
Kaizen has been successfully implemented in various industries. Toyota, a pioneer of Kaizen, achieved significant improvements in quality, efficiency, and waste reduction. Similarly, the Virginia Mason Medical Center used Kaizen to enhance patient care and operational efficiency. The table below provides a summary of these achievements:
Case Study | Improvements Achieved |
|---|---|
Toyota | Reduced waste, improved quality, increased efficiency |
Virginia Mason Medical Center | Significant improvements in patient care and operational efficiency |
Kaizen's focus on teamwork and employee involvement makes it a powerful tool for driving sustainable improvements. Organizations that adopt Kaizen often see enhanced morale and a stronger commitment to achieving shared goals.
Kanban
Kanban is a visual workflow management methodology that helps teams optimize their processes and improve efficiency. Originating from Toyota's production system, Kanban uses visual boards to represent tasks, enabling teams to track progress and identify bottlenecks. This approach emphasizes limiting work in progress (WIP) to ensure that teams focus on completing tasks before starting new ones.
Organizations across industries have achieved remarkable results by implementing Kanban. For instance, Vanguard reported a fourfold increase in delivery throughput and reduced lead time to one-quarter of the average compared to their previous Scrum baseline. Similarly, Microsoft’s XIT team transformed from having the worst service record to the best by adopting Kanban, proving its effectiveness even for geographically dispersed teams. Blizzard Sport also leveraged Kanban to foster a culture of continuous improvement and employee empowerment, which was critical for its survival after an acquisition.
Key benefits of Kanban include:
Improved Workflow Efficiency: Visualizing tasks helps teams identify and address inefficiencies.
Enhanced Agility: Teams can adapt quickly to changing priorities.
Employee Empowerment: Encouraging team members to take ownership of their tasks fosters accountability.
Kanban's flexibility makes it a valuable tool for organizations seeking to enhance their business process improvement methodologies.
Agile
Agile is a dynamic methodology that focuses on iterative development and collaboration. It enables teams to deliver value incrementally, ensuring that processes remain adaptable to changing requirements. Agile is particularly effective in environments where customer needs evolve rapidly, such as software development and product design.
Several industries have successfully applied Agile to improve their processes. For example, Spotify restructured its engineering teams using Agile, resulting in accelerated feature releases and enhanced collaboration. In the healthcare sector, Cleveland Clinic redesigned its patient intake and care delivery processes, reducing wait times and improving patient experiences. Similarly, Domino’s revolutionized its food delivery operations by introducing the Pizza Tracker, which enhanced customer satisfaction and accountability.
Industry | Example Description | Measurable Benefits |
|---|---|---|
Fashion Retail | Zara transformed its supply chain and product development processes. | Faster product design and distribution, reduced inventory waste, competitive edge. |
Food Delivery | Domino’s introduced the Pizza Tracker for real-time order updates. | Improved customer satisfaction, reduced errors, enhanced internal accountability. |
Healthcare | Cleveland Clinic redesigned patient intake and care delivery processes. | Reduced patient wait times, increased staff productivity, improved patient experience. |
Agile's focus on collaboration and adaptability makes it a cornerstone of modern business process improvement methodologies.
Total Quality Management (TQM)
Total Quality Management (TQM) is a comprehensive approach that emphasizes continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. It involves all employees in the process of enhancing quality and streamlining operations. TQM focuses on preventing defects rather than correcting them, ensuring that products and services meet or exceed customer expectations.
Organizations implementing TQM often experience significant improvements in operational quality. For example, companies that prioritize TQM report higher employee morale due to active involvement in decision-making processes. Additionally, streamlined operations reduce waste and lower costs, enhancing market competitiveness. The table below highlights key performance metrics associated with TQM:
Performance Metric | Description |
|---|---|
Improved Quality of Products and Services | Focus on customer satisfaction leads to reduced defects and higher quality outputs. |
Operational Efficiency | Streamlined operations through process optimization reduce waste and lower costs. |
Employee Morale and Engagement | Active employee involvement fosters a sense of ownership and accountability, enhancing morale. |
Market Competitiveness | Consistent delivery of high-quality products builds a strong reputation and attracts customers. |
Enhanced Customer Loyalty and Retention | Prioritizing customer needs strengthens relationships, leading to higher retention rates. |
TQM's holistic approach ensures that quality improvement becomes an integral part of an organization's culture, driving long-term success.
Business Process Management (BPM)
Business Process Management (BPM) is a systematic approach to improving an organization's workflows. It focuses on analyzing, designing, and optimizing processes to achieve better efficiency and adaptability. BPM ensures that business operations align with organizational goals, enabling teams to deliver consistent results.
One of the key strengths of BPM lies in its ability to streamline complex processes. By mapping out workflows, organizations can identify inefficiencies and implement solutions to address them. For instance, automating repetitive tasks reduces manual errors and accelerates turnaround times. BPM also enhances collaboration by providing clear visibility into each step of a process, ensuring that teams work cohesively toward shared objectives.
The impact of BPM is evident in various industries. A study highlights the following benefits achieved through BPM solutions:
Benefit | Result |
|---|---|
Faster Business Process Turnaround | |
Cost Savings | 80% cost reduction |
Improved Compliance | Enhanced regulatory adherence |
These results demonstrate how BPM can transform operations, making it an essential tool for organizations seeking to optimize their workflows.
BPM also fosters a culture of continuous improvement. By regularly reviewing and refining processes, businesses can adapt to changing market demands and maintain a competitive edge. This methodology empowers teams to focus on value-adding activities, ultimately driving growth and innovation.
Theory of Constraints
The Theory of Constraints (TOC) is a methodology that identifies and addresses the most significant bottleneck in a process. By focusing on the constraint, organizations can optimize their workflows and achieve substantial improvements in efficiency and output. TOC operates on the principle that every system has at least one limiting factor, and improving this constraint leads to overall process enhancement.
TOC has proven effective across various industries. For example, Bajaj Electricals Ltd optimized its internal processes, resulting in a 20-25% growth in segment revenue. Similarly, Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories improved supply chain management and supplier ratings, enhancing operational performance. The table below highlights additional success stories:
Organization | Impact Description | Quantifiable Metrics |
|---|---|---|
Morphy Richards | Addressed stock outs and excess inventory, optimizing working capital. | 40% optimization of working capital. |
Lithuania | Nationwide TOC implementation leading to improvements in various sectors. | Significant improvements in lead times and operational efficiency. |
Mazda | Enhanced product development cycles, contributing to turnaround. | Halved development durations. |
TOC's focus on constraints ensures that resources are allocated effectively, maximizing productivity. However, its success depends on continuous monitoring and adjustment. Once a bottleneck is resolved, another constraint may emerge, requiring further optimization.
Organizations that adopt TOC often experience faster project delivery, reduced costs, and improved customer satisfaction. By addressing the weakest link in their processes, they can unlock their full potential and achieve sustainable growth.
How to Choose the Right Methodology
Assessing Organizational Needs
Selecting the right methodology begins with a thorough assessment of organizational needs. Every business has unique goals, challenges, and resources that influence its approach to process improvement. To start, organizations should evaluate their objectives, such as reducing defects, improving customer satisfaction, or increasing operational efficiency. For example, manufacturing teams often benefit from Lean or Six Sigma, while service-based industries may find Agile or Kaizen more suitable.
Assessment tools can provide valuable insights during this phase. Performance evaluation tools measure individual and team productivity, offering data to guide decisions. Process mapping visually represents workflows, helping organizations identify inefficiencies. Skill and competency assessments highlight employee strengths and areas for improvement, ensuring the chosen methodology aligns with available expertise.
Tip: Organizations should also consider their financial, human, and technological resources. A methodology that requires extensive training or advanced tools may not be feasible for all businesses.
Identifying Process Pain Points
Understanding process pain points is critical for effective improvement. These pain points often manifest as bottlenecks, inefficiencies, or recurring errors that hinder productivity. Organizations can use various data collection methods to uncover these issues. Process mapping, for instance, provides a clear visualization of workflows, revealing areas where delays or redundancies occur. Feedback from employees through surveys, interviews, or focus groups offers qualitative insights into operational challenges.
Operational data analysis is another powerful tool. By examining metrics such as cycle times, error rates, or customer complaints, businesses can pinpoint inefficiencies and prioritize areas for improvement. Once identified, these pain points serve as a foundation for selecting a methodology tailored to address specific challenges.
Note: Regularly reviewing processes ensures that new pain points are identified as they arise, maintaining a cycle of continuous improvement.
Matching Methodologies to Challenges
Matching the right methodology to organizational challenges requires a strategic approach. Each methodology has strengths suited to specific scenarios. For instance, Lean Manufacturing excels at eliminating waste and streamlining production, making it ideal for industries focused on efficiency. Six Sigma, with its data-driven approach, is effective for reducing defects and improving quality. On the other hand, Agile thrives in dynamic environments where adaptability and collaboration are essential.
Case studies provide valuable examples of successful matches. Toyota’s adoption of Lean Manufacturing reduced production costs and improved product quality. Motorola’s implementation of Six Sigma minimized process variation, leading to significant cost savings. These examples highlight the importance of aligning methodologies with organizational goals and challenges.
Decision matrices can further aid in this process. By evaluating factors such as resource availability, expected outcomes, and industry-specific needs, organizations can make informed choices. Leadership commitment and employee involvement also play a crucial role in ensuring the success of the chosen methodology.
Tip: Businesses should revisit their methodology periodically to ensure it continues to meet evolving needs and challenges.
Considering Resources and Expertise
Selecting the right business process improvement methodology requires a careful evaluation of available resources and expertise. Organizations must assess their financial, technological, and operational capabilities to ensure successful implementation. This evaluation helps align the chosen methodology with the organization’s goals and constraints.
Financial resources play a critical role in determining the feasibility of a methodology. Some frameworks, such as Lean, often require minimal financial investment, making them accessible to smaller organizations. In contrast, methodologies like Total Quality Management (TQM) may demand significant financial commitments due to their comprehensive nature. Businesses must analyze their budgets to identify the level of investment they can sustain without compromising other operations.
Technological capabilities also influence the selection process. Organizations should evaluate their existing infrastructure to ensure compatibility with the chosen methodology. For instance, implementing Kanban may require digital tools to visualize workflows effectively. Without the necessary technology, teams may struggle to achieve the desired outcomes. Upgrading systems or investing in new tools might be necessary to support the methodology.
Operational constraints, such as time limitations and regulatory requirements, further shape the decision-making process. Industries with strict compliance standards, like healthcare, often need tailored frameworks to meet regulatory demands. Additionally, organizations operating under tight deadlines may benefit from methodologies that prioritize speed and adaptability, such as Agile. Understanding these constraints helps businesses select a framework that aligns with their operational realities.
Tip: Conducting a resource audit can provide valuable insights into an organization’s readiness for process improvement. This audit should include financial assessments, technology evaluations, and a review of operational constraints.
Organizations must also consider the expertise of their teams. Some methodologies, like Six Sigma, require specialized training and certifications. Without skilled personnel, implementing such frameworks may prove challenging. Investing in employee training ensures that teams possess the knowledge and skills needed to execute the methodology effectively. Cross-functional collaboration further enhances the implementation process by leveraging diverse perspectives and expertise.
By thoroughly evaluating resources and expertise, organizations can make informed decisions about which methodology to adopt. This strategic approach increases the likelihood of successful implementation and long-term benefits. Businesses that align their resources with their chosen framework often achieve greater efficiency, reduced costs, and improved outcomes.
Steps to Implement Business Process Improvement Methodologies
Building a Cross-Functional Team
A cross-functional team is essential for implementing Business Process Improvement Methodologies effectively. These teams bring together individuals from different departments, ensuring diverse perspectives and expertise. Collaboration across functions helps identify inefficiencies and develop innovative solutions.
To build an effective cross-functional team, organizations should follow these best practices:
Recognition and Reward Systems: Align rewards with team goals to motivate members and enhance productivity.
Time Management Practices: Use prioritization tools and set clear deadlines to optimize workflows.
Regular Team-Building Activities: Foster unity and trust through activities that improve communication.
Cross-Training Opportunities: Train team members in multiple roles to enhance adaptability.
Leadership Support: Provide clear direction and resources to empower the team.
Best Practice | Description |
|---|---|
Recognition and reward systems | Align rewards with team goals to motivate and enhance productivity. |
Time management practices | Use prioritization tools and set clear deadlines to optimize work processes. |
Regular team-building activities | Foster unity and collaboration through diverse activities that enhance communication and trust. |
Cross-training opportunities | Enhance team versatility by training members in multiple roles, allowing for adaptability. |
Leadership support and involvement | Provide clear direction and resources, empowering teams to thrive and innovate. |
Cross-functional teams thrive when they have clear goals and strong leadership. By fostering collaboration, organizations can ensure successful implementation of process improvement initiatives.
Setting Clear Objectives and KPIs
Clear objectives and measurable Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are critical for tracking progress and ensuring success. Objectives provide direction, while KPIs offer a way to measure performance against goals. Together, they create a roadmap for implementing Business Process Improvement Methodologies.
Organizations should follow these steps to set effective objectives and KPIs:
Define specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives.
Align KPIs with overall business goals to ensure relevance.
Choose metrics that reflect critical success factors, such as cycle time, defect rates, or customer satisfaction.
Implement a rigorous tracking process to monitor progress and make adjustments as needed.
Tip: Regularly review KPIs to ensure they remain aligned with evolving business needs.
Case studies highlight the importance of clear objectives and KPIs. For example, organizations that implemented KPI management strategies achieved significant improvements in efficiency and customer satisfaction. These strategies included designing relevant KPIs, tracking them rigorously, and adjusting them over time to maintain alignment with business goals.
Training and Educating Employees
Employee training is a cornerstone of successful process improvement. Well-trained employees understand the methodologies and can apply them effectively. Training also fosters a culture of continuous improvement, empowering employees to contribute to organizational success.
Organizations can use various training frameworks to enhance employee skills:
Training Framework | Focus Area |
|---|---|
Data-driven problem-solving techniques | |
Lean Training | Waste reduction and value creation |
TQM Workshops | Company-wide commitment to quality |
Training programs should focus on practical applications, enabling employees to implement methodologies in real-world scenarios. For example, Six Sigma certification equips employees with data-driven problem-solving skills, while Lean training emphasizes waste reduction and value creation. TQM workshops instill a company-wide commitment to quality.
Note: Creating a realistic training timeline ensures employees can balance learning with their regular responsibilities.
By investing in employee education, organizations can build a skilled workforce capable of driving process improvement. This investment not only enhances operational efficiency but also boosts employee morale and engagement.
Monitoring and Adjusting Processes
Monitoring and adjusting processes is a critical step in achieving sustainable business process improvement. Organizations must continuously evaluate their workflows to ensure they align with objectives and deliver optimal results. This step involves tracking performance, identifying inefficiencies, and implementing corrective actions to maintain progress.
The Role of Monitoring Systems
Monitoring systems, such as performance dashboards, play a vital role in tracking the effectiveness of process improvements. These tools provide real-time data that helps organizations measure key performance indicators (KPIs) and assess the impact of their actions. By visualizing metrics, teams can identify trends, pinpoint bottlenecks, and make informed decisions.
Benefit/Functionality | Description |
|---|---|
Dashboards track key performance indicators over time, enabling evaluation of actions and adjustments. | |
Accountability | Real-time data fosters accountability, motivating employees to meet and exceed targets. |
Identifying Issues | Dashboards highlight inefficiencies and resource underutilization, guiding targeted improvements. |
Performance dashboards also encourage transparency within teams. Employees gain visibility into their contributions, fostering a sense of ownership and accountability. This culture of responsibility drives continuous improvement and ensures alignment with organizational goals.
Steps for Effective Process Adjustment
Adjusting processes requires a systematic approach to ensure changes yield positive outcomes. Organizations can follow these steps to refine workflows:
Analyze Data: Teams should review metrics from monitoring systems to identify areas needing improvement. For example, a spike in defect rates may signal a need for process redesign.
Engage Teams: Cross-functional collaboration ensures diverse perspectives contribute to solutions. Employees closest to the process often provide valuable insights.
Implement Changes: Organizations should prioritize small, incremental adjustments to minimize disruption. Testing changes on a smaller scale allows teams to evaluate their effectiveness before full implementation.
Track Results: After adjustments, teams must monitor outcomes to ensure improvements align with objectives. If results fall short, further refinements may be necessary.
Tip: Regularly scheduled reviews of processes help organizations stay proactive in addressing inefficiencies and adapting to evolving needs.
Building a Feedback Loop
A feedback loop is essential for maintaining continuous improvement. Teams should establish mechanisms for collecting input from employees, customers, and stakeholders. Surveys, focus groups, and performance reviews provide valuable insights into process effectiveness. Incorporating this feedback ensures adjustments address real-world challenges and opportunities.
Organizations that prioritize monitoring and adjusting processes often achieve greater efficiency and adaptability. By leveraging tools like performance dashboards and fostering a culture of accountability, they can optimize workflows and sustain long-term success.
Leveraging Technology for Process Improvement

Automation Tools and Software
Automation tools and software play a pivotal role in streamlining workflows and enhancing efficiency. These tools reduce manual intervention, minimize errors, and accelerate task completion. For instance, platforms like Whatfix offer features such as process analytics and automation, enabling organizations to analyze and improve their workflows effectively. Similarly, Q-optimize from Qmarkets centralizes workflow tracking and management, ensuring the success of continuous improvement initiatives.
Visualization tools also contribute significantly to process improvement. Applications like Lucidchart, Microsoft Visio, and Bizagi help teams map and analyze workflows, making inefficiencies easier to identify and address. By leveraging these tools, organizations can create clear, actionable plans for optimization.
The impact of automation can be measured through various metrics. For example:
Metric | Definition | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|
Productivity per Engineer | Measures work completed with automation | Quantifies productivity improvements |
Managed Service Cost Reduction | Reduction in costs by automating network orchestration | Lowers operational expenses |
Average Time for End-to-End Process Execution | Time taken to complete a process | Demonstrates efficiency gains from faster execution |
These metrics highlight the tangible benefits of automation tools in improving business processes.
Data Analytics for Optimization
Data analytics serves as a cornerstone for optimizing business processes. By analyzing large datasets, organizations can uncover patterns, predict outcomes, and make informed decisions. For example, integrating data analytics into supply chain management has helped companies achieve a 20% reduction in operational costs. Similarly, merging CRM and social media data has led to a 15% increase in customer satisfaction.
Case studies further illustrate the power of data analytics:
Organization | Improvement Achieved |
|---|---|
Mayo Clinic | 35% reduction in wait times and 28% increase in patient satisfaction |
JPMorgan Chase | 35% improvement in fraud detection accuracy |
Amazon | 50% reduction in order processing time with 99.9% accuracy |
These examples demonstrate how data analytics can transform operations across industries. By leveraging insights from data, organizations can refine their processes, enhance customer experiences, and achieve measurable improvements.
Integrating Technology with Methodologies
Integrating modern technology with established Business Process Improvement Methodologies amplifies their effectiveness. Business Process Automation (BPA) eliminates repetitive tasks, increasing efficiency and reducing errors. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) takes this a step further by automating rule-based tasks, allowing employees to focus on higher-value activities. Intelligent Process Automation (IPA) combines artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance decision-making and data analysis.
This integration offers several advantages:
Improves product quality and customer satisfaction.
Boosts competitiveness and profitability.
For example, technology supports methodologies like Lean and Six Sigma by providing tools for process mapping, data analysis, and workflow automation. These tools enable teams to implement improvements more effectively, ensuring better outcomes. Organizations that embrace this integration often experience faster project delivery, reduced costs, and improved operational performance.
Tip: Regularly updating technology ensures compatibility with evolving methodologies, maximizing the benefits of integration.
The Importance of Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement is a fundamental principle for organizations aiming to sustain efficiency and remain competitive. By fostering innovation, engaging employees, and regularly refining processes, businesses can adapt to evolving challenges and seize new opportunities.
Fostering a Culture of Innovation
A culture of innovation drives continuous improvement by encouraging creativity and adaptability. Organizations that prioritize innovation empower teams to explore new ideas and implement transformative solutions. For example, a nonmetallic mineral product manufacturer adopted a Corporate Entrepreneurship framework to address a 20% decline in market share. This strategy stimulated innovation, enabling the company to capture new opportunities and achieve long-term growth.
Similarly, a mid-size logistics firm enhanced operational efficiency by integrating innovative technologies. This approach reversed a 12% decline in efficiency and restored market competitiveness. These examples highlight the importance of fostering innovation to overcome challenges and drive progress.
To cultivate innovation, organizations should:
Encourage open communication and idea-sharing across teams.
Provide resources and training to support creative problem-solving.
Recognize and reward innovative contributions to reinforce positive behaviors.
By embedding innovation into their culture, businesses can unlock new potential and sustain continuous improvement.
Encouraging Employee Participation
Employee participation is a cornerstone of successful process improvement. Engaged employees contribute valuable insights and take ownership of their roles, leading to practical and sustainable changes. Toyota exemplifies this approach through its suggestion system and Gemba walks, which involve employees in identifying inefficiencies. These practices have increased efficiency, boosted morale, and reduced turnover rates.
Starbucks also demonstrates the power of employee engagement. Its "My Starbucks Idea" portal allows employees to submit suggestions, fostering a sense of community and shared purpose. This initiative has led to innovative contributions that enhance customer experiences and operational success.
Organizations can encourage participation by:
Establishing platforms for employees to share ideas.
Involving teams in decision-making processes.
Providing feedback and recognition for contributions.
When employees feel valued and empowered, they become active participants in driving continuous improvement.
Regularly Reviewing and Updating Processes
Regular reviews and updates ensure that business processes remain effective and aligned with organizational goals. Establishing Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) helps evaluate the success of implemented frameworks. Periodic audits identify areas for improvement, enabling organizations to adapt to changing demands.
For instance, Toyota's commitment to continuous improvement has minimized defects and enhanced product reliability. Amazon's focus on operational excellence has optimized processes, resulting in significant efficiency gains and customer loyalty. These examples demonstrate the long-term benefits of regularly refining workflows.
To maintain progress, organizations should:
Conduct routine process audits to identify inefficiencies.
Use performance dashboards to monitor KPIs and track improvements.
Implement feedback loops to incorporate insights from employees and stakeholders.
By prioritizing regular updates, businesses can sustain the momentum of continuous improvement and achieve lasting success.
Business process improvement methodologies provide organizations with the tools to enhance efficiency and remain competitive. By evaluating their unique needs, businesses can select the most suitable approach to optimize workflows and achieve measurable results. Continuous improvement ensures that systems and teams adapt to evolving challenges, fostering sustainable success. Organizations seeking to refine their processes and drive innovation should explore these methodologies further. For tailored guidance, they can reach out to experts for support.
FAQ
What is the primary goal of business process improvement methodologies?
The primary goal is to enhance efficiency by streamlining workflows, reducing waste, and improving productivity. These methodologies help systems and teams achieve measurable results, such as cost savings and higher customer satisfaction.
How do organizations know which methodology to choose?
Organizations should assess their needs, identify pain points, and match methodologies to specific challenges. Evaluating available resources and expertise ensures the chosen approach aligns with organizational goals.
Can small businesses benefit from these methodologies?
Yes, small businesses can benefit significantly. Methodologies like Lean or Kaizen require minimal investment and focus on incremental improvements, making them accessible for smaller teams and systems.
How do these methodologies impact employee satisfaction?
Improved workflows reduce frustration and create clarity, boosting employee morale. Engaging employees in the process fosters a sense of ownership and accountability, leading to higher satisfaction levels.
Are these methodologies applicable across industries?
Yes, they are versatile and adaptable. Industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and finance have successfully implemented methodologies like Six Sigma, Agile, and BPM to optimize their processes.
What role does technology play in process improvement?
Technology enhances methodologies by automating tasks, analyzing data, and visualizing workflows. Tools like automation software and performance dashboards help systems and teams achieve faster and more accurate results.
How can organizations sustain continuous improvement?
Organizations can sustain improvement by fostering innovation, encouraging employee participation, and regularly reviewing processes. Establishing feedback loops ensures systems and teams adapt to evolving challenges.
Where can businesses learn more about implementing these methodologies?
Businesses can reach out to experts for tailored guidance. Systems and teams seeking to refine their processes and achieve measurable results should contact us for support.



