Essential Tips for Streamlining Business Management Systems

Imagine a manager struggling with delayed orders, high costs, and frustrated employees. Streamlining Business Management Systems can transform these challenges into opportunities. Companies that optimize their process see real results:
Metric | Improvement/Benefit |
|---|---|
Reduction in production delays | |
Invoice processing efficiency | |
On-time payments improvement | 25% increase |
Employee productivity | Increased |
Average annual savings | $51,000 |
Modern Hiring Systems and integrated Business Management save time, cut costs, and boost satisfaction for both staff and customers.
Key Takeaways
Simplify business processes by removing redundant steps and standardizing workflows to save time and reduce errors.
Automate repetitive tasks like data entry and scheduling to boost efficiency, accuracy, and employee satisfaction.
Integrate systems to enable smooth data flow, improve communication, and support better decision-making across teams.
Regularly assess your systems through audits and user feedback to identify bottlenecks and address pain points effectively.
Design user-friendly interfaces with custom dashboards and fewer features to increase adoption and reduce training time.
Provide ongoing training and easy-to-access help resources to empower employees and improve system use.
Use automation tools to monitor performance and quickly adjust workflows for continuous improvement and higher quality.
Engage teams in change management by communicating benefits, involving stakeholders, and recognizing achievements to overcome resistance and ensure successful adoption.
Core Principles
Business Management Systems rely on three foundational strategies: simplification, automation, and integration. These principles help organizations optimize operations by combining policies, practices, and procedures into a unified framework.
Simplification
Remove Redundancies
Redundant steps slow down processes and create confusion. Teams should review workflows and identify duplicate tasks or unnecessary approvals. Removing these redundancies saves time and reduces errors. For example, eliminating repeated data entry or overlapping approval chains can speed up decision-making and improve accuracy.
Standardize Processes
Standardization ensures consistency across departments. When everyone follows the same procedures, training becomes easier and results become more predictable. Teams can use checklists, templates, and clear guidelines to support standardization. This approach also makes it easier to measure performance and spot areas for improvement.
Automation
Identify Tasks
Automation transforms routine work and boosts efficiency. Organizations should start by listing repetitive tasks that take up valuable time. Common candidates include data entry, invoice processing, and scheduling. Automating these tasks frees employees to focus on higher-value activities.
73% of IT leaders report automation cuts manual task time by 50%.
51% of IT leaders say automation reduces costs by 10% to 50%.
78% of business leaders believe automation enhances overall productivity.
42% of business leaders agree workflow automation saves time and frees employees for strategic tasks.
85% of business leaders state automation allows employees to focus on important strategic goals.
Automation also improves accuracy. Companies have seen error rates drop by up to 70% after automating workflows. Many employees trust automation tools for their reliability and report higher job satisfaction.
Balance Oversight
While automation streamlines operations, oversight remains essential. Managers should monitor automated processes to ensure they work as intended. Regular reviews help catch issues early and maintain quality. Setting clear rules and alerts can prevent mistakes and keep processes aligned with business goals.
Integration
Connect Systems
Integration links different tools and platforms within Business Management Systems. When systems connect, information flows smoothly between departments. This reduces manual data transfers and minimizes the risk of errors. Integration also supports better communication and collaboration across teams.
Alignment with strategic objectives ensures all activities contribute to organizational goals, reducing confusion and duplication.
Accountability is established through clear roles and responsibilities, making tasks traceable and driving performance.
Progress tracking via Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) such as throughput, lead times, cost per unit, labor efficiency, and quality enables data-driven decision-making and continuous improvement.
Integration of technology automates workflows, streamlines communication, and centralizes data, freeing resources for strategic tasks.
Data Flow
A smooth data flow is critical for effective management. Integrated systems allow real-time updates and accurate reporting. Teams can track progress, measure results, and make informed decisions quickly. Continuous review and updating of management systems keep operations efficient and adaptable. Enhanced customer satisfaction and sustainable growth often follow when integration supports a high-performance culture.
Assessing Systems
System Audit
Map Processes
A thorough system audit starts with mapping out every process in the business management system. Teams create visual diagrams or flowcharts to show each step from start to finish. This mapping helps everyone see how information moves and where tasks overlap. Auditors often use interviews and direct observation to understand how employees complete their work. They may also review documents and electronic records to confirm that processes match what is described. By combining these methods, teams gain a clear picture of daily operations.
Tip: Using data analytics tools can help spot patterns or irregularities in large datasets. For example, a retail company once used real-time inventory monitoring to find mismatches between recorded and actual stock. This approach uncovered a system integration error that could have caused financial mistakes.
Find Bottlenecks
After mapping, the next step is to identify bottlenecks. These are points where work slows down or stops. Auditors look for repeated delays, high error rates, or tasks that require too many approvals. They may use sampling to check a subset of transactions or apply a risk-based approach to focus on areas with the highest impact. Auditors gather different types of evidence, such as physical counts, document reviews, and electronic logs, to verify where problems occur. Maintaining auditor independence and ethical standards ensures that findings remain objective and reliable.
Innovative technologies like artificial intelligence and robotic process automation can also help detect bottlenecks. These tools analyze workflows and highlight steps that need improvement. Regular training and collaboration between departments support ongoing audit quality and adaptability.
User Feedback
Surveys
User feedback plays a critical role in assessing business management systems. Teams often use surveys to collect opinions from employees and customers. These surveys ask about ease of use, satisfaction, and any challenges faced. Segmenting survey data by user group helps identify which teams or customers experience the most issues. Tracking feedback over time shows whether changes lead to better results.
Key metrics to monitor include Net Promoter Score (NPS), Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT), and Customer Effort Score (CES). Statistical analysis, such as regression or correlation, can reveal links between feedback and system performance. Benchmarking against industry standards provides context for these results.
Pain Points
Analyzing feedback uncovers common pain points. These might include confusing interfaces, slow response times, or frequent errors. Addressing these issues leads to measurable improvements:
Performance Metric | Improvement Range |
|---|---|
Productivity | |
Defect Reduction | Up to 40% decrease |
Operational Cost Reduction | 15-25% decrease |
Resource Utilization | 30-40% improvement |
Waste Reduction | 20-30% decrease |
Customer Satisfaction Scores | Increased |
Customer Loyalty | Increased |
Teams that act on user feedback often see higher productivity, fewer defects, and lower costs. Customer satisfaction and loyalty also rise, showing the value of listening to users and making targeted improvements.
Business Management Systems & User Experience

A well-designed user experience stands at the heart of effective Business Management Systems. When employees find systems easy to use, they work faster and make fewer mistakes. A user-friendly interface also helps teams coordinate and control tasks across departments.
Interface Design
Custom Dashboards
Custom dashboards give users quick access to the information they need most. Each team can see relevant data, such as sales numbers or project deadlines, without searching through menus. This approach saves time and reduces frustration. Companies that improve their dashboards often see higher adoption rates and better performance.
Metric | Improvement After UI Changes |
|---|---|
App Registrations (Costa Coffee) | |
App Ratings (JobNimbus) | Increased from 2.5 to 4.8 |
Support Tickets (Recora) | Reduced by 142% |
In-App Sales (PlaceMakers) | Doubled |
Feature Adoption (Housing.com) | Increased by 20% |
These results show that better dashboards and interfaces lead to more users, higher satisfaction, and fewer support issues.
Feature Reduction
Too many features can overwhelm users. By focusing on the most important tools, companies make systems easier to learn and use. A simple interface reduces training time by up to 80%. Employees feel more confident and complete tasks with fewer errors. Good design uses clear labels, consistent layouts, and options for customization. When users only see what they need, they stay engaged and productive.
A user-friendly and intuitive interface encourages employees to use the system daily. Poor design causes frustration and leads to abandonment, even if the system has strong features.
Training
Ongoing Support
Continuous training helps employees keep up with system updates and new features. Regular learning sessions boost confidence and job satisfaction. In fact, 80% of employees say learning adds purpose to their work, and 70% feel more connected to their organization. Companies that invest in training see a 17% increase in productivity and a 21% rise in profitability. Ongoing support also prepares teams for changes, such as automation or new compliance rules.
Help Resources
Easy-to-access help resources, like guides and video tutorials, support users when they face challenges. Employees who can quickly find answers stay productive and avoid costly mistakes. Companies that offer strong learning resources report higher job satisfaction and lower turnover. In fact, 94% of employees would stay longer at a company that invests in their career development. Help resources also reduce the number of support tickets, freeing up IT staff for other tasks.
Well-designed Business Management Systems, paired with strong training and support, create a workplace where employees feel empowered and customers receive better service.
Automation

Automation stands as a powerful tool for streamlining business management systems. Companies use automation to handle routine tasks, improve accuracy, and optimize performance. By reducing manual work, teams can focus on more valuable activities and achieve better results.
Routine Tasks
Workflow Tools
Workflow tools automate repetitive steps in daily operations. These tools eliminate manual data entry, which often leads to typographical and numerical errors. Standardized processes ensure that every task follows the same steps, reducing the chance of mistakes. Real-time validation checks data as it enters the system, flagging any issues before they cause bigger problems. Automated scheduling tools remind teams of important deadlines and trigger actions based on set rules. For example, inventory systems can automatically create purchase orders when stock runs low, improving both speed and accuracy.
Automation eliminates manual data entry, reducing errors.
Standardized workflows ensure consistent execution.
Real-time validation flags incorrect or incomplete data.
Automated scheduling reduces reliance on memory.
Automated purchase orders improve accuracy and speed.
Workflow automation coordinates complex processes and reduces miscommunication.
Audit trails and role-based access controls enhance accountability.
Manufacturing and HR departments report fewer errors and higher efficiency after automation.
Nearly all workers in small and medium businesses perform tasks that automation can handle. Most knowledge workers say automation makes their jobs easier and boosts productivity. Many businesses also find that technology helps them compete with larger companies.
Scheduling
Automated scheduling tools help teams manage time and resources more effectively. These tools assign tasks, send reminders, and adjust plans as needed. Manufacturing companies use advanced scheduling to reduce manual errors and keep production on track. HR departments rely on AI-driven workflows to automate approvals and update records, which lowers mistakes and saves time. Finance teams use automation to improve loan approvals, detect fraud, and reduce invoicing errors. Across industries, workflow automation leads to fewer mistakes, better compliance, and improved efficiency.
Optimization
Performance Review
Optimization strategies rely on regular performance reviews. Automated systems track key metrics and provide real-time analytics through dashboards. These dashboards help managers spot trends, identify issues, and make data-driven decisions. Companies like General Electric use Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) to cut manufacturing costs and boost efficiency. Toyota applies lean manufacturing and cycle time reduction to minimize downtime and increase flexibility. Amazon uses throughput and lead time metrics, along with robotics and AI, to speed up order fulfillment and increase capacity.
Metric | Description | Benefit Confirmed by Metric |
|---|---|---|
Efficiency | Maximum output with minimum input | Improved resource utilization |
Effectiveness | Achievement of intended goals | Validates goal attainment |
Quality | Degree of excellence and defect reduction | Improved product/service quality |
Productivity | Output per unit input | Increased work volume |
Profitability | Financial gain after expenses | Financial benefits from optimization |
Customer Satisfaction | Meeting or exceeding customer expectations | Enhanced customer experience |
Cycle Time | Total time to complete a process | Reduced process duration and bottlenecks |
Lead Time | Time from order receipt to delivery | Faster delivery and supply chain efficiency |
Throughput | Number of units processed in a timeframe | Increased processing capacity and revenue potential |
OEE | Measures manufacturing performance | Improved equipment utilization and reduced downtime |
Defect Rate | Percentage of defective units | Quality improvements and reduced errors |
Rework Rate | Percentage of items requiring rework | Reduced waste and improved process accuracy |
Changeover Time | Time to switch production processes | Enhanced flexibility and reduced downtime |
Inventory Turnover | Frequency of inventory replacement | Efficient inventory management |
Order Accuracy | Percentage of correctly fulfilled orders | Improved order fulfillment and customer satisfaction |
MTBF | Average time between equipment failures | Increased reliability and reduced breakdowns |
MTTR | Average time to repair equipment | Faster recovery and minimized disruption |
On-Time Delivery (OTD) | Percentage of orders delivered on time | Improved delivery performance and customer trust |
Adjust Rules
Automated systems allow managers to adjust rules and workflows quickly. When performance metrics reveal a problem, teams can update processes without major disruptions. Automation tools like Cflow help by sending alerts for performance deviations and integrating with other business systems. This flexibility supports continuous improvement and ensures that business management systems stay aligned with company goals. As a result, organizations see higher efficiency, better quality, and greater customer satisfaction.
Integration
Integration connects all parts of a business. When systems work together, teams share information quickly and make better decisions. Companies that use integrated solutions see big improvements in cost, quality, and growth.
Compatible Solutions
Evaluate Options
Choosing the right tools is the first step. Teams should look for software that fits their needs and works well with other systems. They can compare features, pricing, and support. Many companies use a checklist to score each option. This helps them pick the best fit for their Business Management Systems.
Tip: Involve both IT staff and end users in the evaluation process. Their feedback helps avoid problems later.
APIs
APIs, or Application Programming Interfaces, let different programs talk to each other. With APIs, companies connect sales, inventory, and finance tools. This connection means data moves automatically between systems. Teams do not need to enter the same information twice. APIs also make it easier to add new features or switch to better tools in the future.
Data Sync
Real-Time Updates
Real-time updates keep everyone on the same page. When one team changes a record, others see the update right away. This reduces mistakes and speeds up work. For example, sales teams know when inventory changes, so they avoid selling out-of-stock items. Real-time data also helps managers spot trends and act fast.
Avoid Silos
Silos happen when departments do not share information. This leads to errors, delays, and higher costs. Integrated systems break down these barriers. Teams work together and share data easily. Companies that avoid silos see better results across the board.
Metric | Integrated Solutions Impact | Non-Integrated Solutions Impact |
|---|---|---|
Operational Cost Reduction | Costs up to 40% higher than integrated firms | |
Labor Productivity Increase | 30-50% increase in labor productivity | Baseline productivity without integration |
Defect Rate Reduction | Over 40% reduction in defects | Higher defect rates due to fragmented processes |
Revenue Growth Post-Integration | 20-30% increase in revenue | Lower or stagnant revenue growth |
Return on Investment (ROI) | Multiple times the initial investment | ROI figures below industry averages |
This table shows that integrated solutions help companies save money, boost productivity, and grow faster. Business Management Systems that focus on integration give organizations a strong advantage in today’s market.
Data Accuracy
Ensuring data accuracy stands as a top priority for any business management system. Accurate data supports better decisions, reduces costly mistakes, and builds trust across teams.
Validation
Error Checks
Error checks form the first line of defense against inaccurate data. Automated validation processes catch mistakes as soon as data enters the system. These checks include type, range, and format validation, which help spot errors before they spread. Businesses often use statistical methods like regression analysis and chi-square testing to identify inconsistencies and validate data quality.
Robust data validation detects and corrects errors early, significantly reducing inaccurate data risks.
Automated validation processes reduce human error and improve operational efficiency.
Continuous monitoring and auditing detect anomalies early, maintaining data accuracy.
Data profiling techniques reveal inconsistencies and missing data, strengthening validation.
Documenting validation processes and using advanced tools like machine learning sustain high data quality.
Organizations that use multi-stage validation, such as outlier detection and cross-validation, achieve up to 99% data accuracy. For example, a financial institution improved its market data accuracy to 99% and reduced financial risks by applying these methods. In healthcare, similar techniques ensured reliable clinical conclusions despite missing or inconsistent data.
Manual Review
While automation handles most errors, manual review remains essential for complex or unusual cases. Analysts and engineers collaborate to review flagged data, ensuring accuracy and reliability. They check for issues that automated tools might miss, such as context-specific errors or subtle inconsistencies. Regular documentation of validation rules and error handling keeps the process transparent and adaptable.
Tip: Combining automated checks with manual review creates a strong safety net for data quality. This approach supports confident decision-making and regulatory compliance.
Security
Access Control
Access control protects data from unauthorized changes. By defining who can view or edit information, businesses limit the risk of data tampering. Data governance policies set clear standards for data ownership and access. These measures ensure that only trusted users handle sensitive information, preserving data integrity.
Enhanced security enables detection of unauthorized changes and suspicious activities.
Controlled data access limits exposure if credentials are compromised.
Employee training reduces human errors in data entry and modification.
A financial services firm that implemented strict access controls and audit trails improved the accuracy and reliability of its financial reports. This approach also helped the company comply with regulations like GDPR and SOX.
Audits
Regular audits play a key role in maintaining data accuracy. Auditors review system logs, track changes, and verify that data matches original records. Automated validation tools and AI-powered anomaly detection help spot errors quickly. For example, AI tools can reduce false positives by 60% and speed up threat detection by 85%. These audits not only catch mistakes but also support continuous improvement.
Security Measure | Business Impact |
|---|---|
AI-powered anomaly detection | 60% fewer false positives, 85% faster threat response |
Mature data integrity practices | 29% more accurate forecasting, 26% lower costs |
Strategic security integration | 28% faster product cycles, 23% higher satisfaction |
Cross-department collaboration | 42% more effective risk management |
Strong security and regular audits ensure that business management systems deliver reliable, accurate data. This foundation supports better business outcomes and long-term success.
Team Adoption
Change Management
Communicate Benefits
Clear communication helps teams understand why changes matter. Leaders who explain the benefits of new business management systems build trust and reduce resistance. When employees see how changes improve their daily work, they feel more motivated to participate. Companies that share success stories and real-life examples help teams visualize positive outcomes.
Teams respond better when leaders highlight how new systems save time, reduce errors, and make jobs easier.
Stakeholder Involvement
Involving stakeholders early leads to higher adoption rates. When employees, managers, and executives take part in planning and decision-making, they feel valued and invested. Dedicated change management teams guide the process, provide training, and collect feedback. Regular monitoring of key performance indicators (KPIs) ensures progress stays on track.
Evidence Aspect | Description & Impact | Supporting Data / Outcome |
|---|---|---|
Strong executive support aligns teams with change vision and improves success likelihood. | Organizations with strong leadership support are 1.7 times more likely to succeed (McKinsey & Company). | |
Comprehensive Change Plans | Detailed roadmaps covering all phases reduce failure risk. | Missing key activities can reduce success rates by up to 50% (Prosci Benchmarking Report). |
Employee Engagement | Early and continuous involvement increases profitability and reduces resistance. | Highly engaged teams see a 21% increase in profitability (Gallup). |
Training & Support | Allocating significant budget to training triples chances of meeting change goals. | Organizations spending >20% of project budget on training are 3x more likely to succeed (PMI). |
Monitoring & KPIs | Regular tracking of adoption rates and system performance improves outcomes. | Continuous KPI monitoring leads to 37% improvement in adoption rates (Microsoft study). |
Dedicated Change Management | Specialized teams improve planning, communication, training, and feedback processes. | Companies with excellent change management are 3.5x more likely to outperform peers (Harvard Business Review). |
Case Study: Microsoft | Initial 20% productivity dip due to resistance; post-training, 45% productivity boost in 6 months. | Demonstrates impact of structured change management and training (CIO report). |
Case Study: Airbnb | Employee involvement and transparent communication led to 95% user adoption in 3 months. | Highlights importance of engagement and dedicated teams (Airbnb internal report). |
Digital Adoption Platforms | Use of tools like Giva and Jira Service Management facilitates smoother transitions and real-time support. | Companies using DAPs see ~30% increase in software usage (Airbnb study). |
Incentives
Recognition
Recognition programs encourage employees to embrace new systems. When leaders celebrate achievements, teams feel appreciated and motivated. Regular recognition strengthens company values and builds a positive culture.
83% of HR leaders say employee recognition strengthens organizational values.
Employees who strongly agree recognition is important are 3.8 times more likely to feel connected to their culture.
51% of employees receiving regular recognition are highly likely to recommend their company.
Recognized employees are 2.5 times more likely to be happy with their jobs.
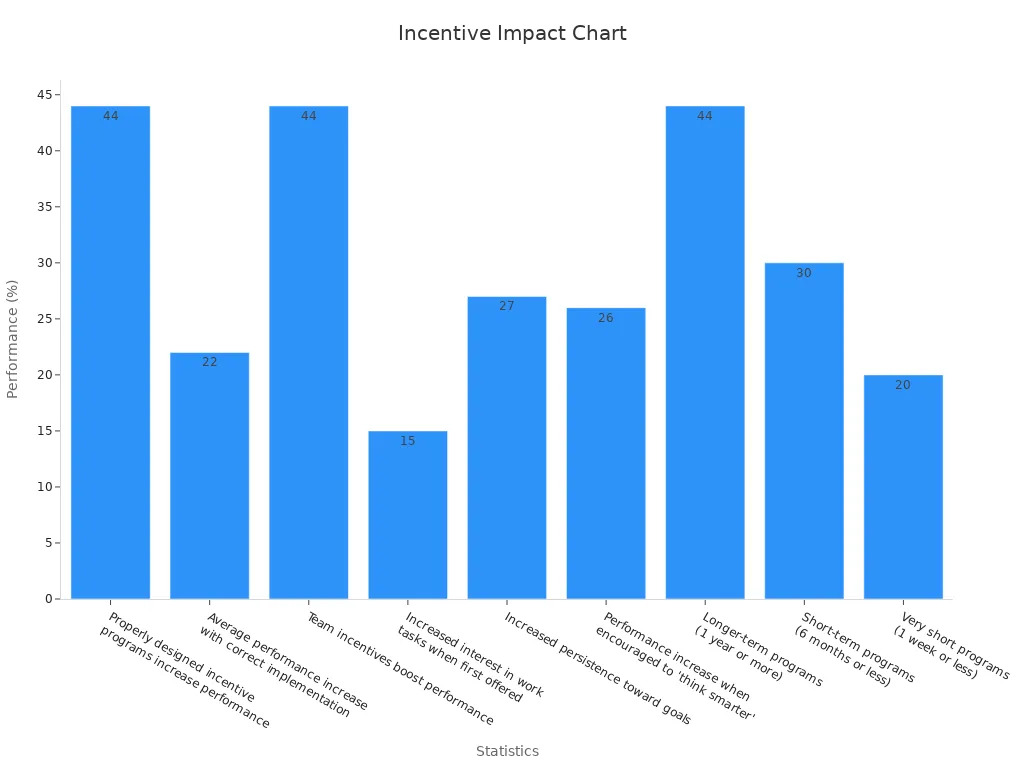
Statistic Description | Performance Impact / Result |
|---|---|
Properly designed incentive programs increase performance | |
Average performance increase with correct implementation | 22% increase |
Team incentives boost performance | Up to 44% increase |
Increased interest in work tasks when first offered | 15% increase |
Increased persistence toward goals | 27% increase |
Performance increase when encouraged to "think smarter" | 26% increase |
Longer-term programs (1 year or more) | 44% performance increase |
Short-term programs (6 months or less) | 30% performance increase |
Very short programs (1 week or less) | 20% performance increase |
Employee and manager valuation of incentive programs | Highly valued, though 98% report implementation issues |
Quota-based incentive measures | Most positive results |
Piece-rate programs | Positive results |
Tournament-based programs | Least effective |
Feedback
Feedback helps teams improve and adapt. Leaders who ask for input show respect for employee opinions. Regular feedback sessions identify challenges and highlight what works well. Companies that listen and respond to feedback see higher engagement and faster adoption of new systems.
Open communication and recognition create a supportive environment where teams feel confident to embrace change and strive for success.
Overcoming Challenges
Implementing or upgrading a Business Management System often brings challenges. Two of the most common issues are resistance to change and system complexity. Addressing these challenges with proven strategies helps organizations achieve smoother transitions and better results.
Resistance
Build Trust
Employees may resist new systems because they feel uncertain or fear disruption. Building trust starts with open and transparent communication. Leaders should explain the reasons for change clearly and use multiple channels to reach everyone. They can involve employees in workshops and feedback sessions, which increases ownership and reduces anxiety. Training tailored to employee needs helps build confidence. Leaders who model the desired behaviors and attitudes set a positive example for others.
Leaders who celebrate early successes and recognize contributions create momentum and foster a supportive environment.
A step-by-step approach to overcoming resistance includes:
Involve employees in the process through workshops and feedback.
Provide training and support that matches employee needs.
Address concerns directly with open dialogue.
Celebrate successes and recognize contributions.
Lead by example and model positive behaviors.
Use participative strategies, such as involving resistant employees in change roles.
Reserve coercion for urgent situations, acknowledging its drawbacks.
Clear Roadmap
A clear roadmap guides everyone through the change. Leaders should define and communicate the reasons for change, targeting messages to different groups. Building excitement and aligning incentives with employee interests help create positive sentiment. Delegating change to natural leaders within teams spreads enthusiasm and trust. Using data to support decisions and sharing facts builds credibility. Leaders should anticipate resistance and empathize with concerns, making employees feel heard and valued.
Complexity
Phased Rollout
Complex systems can overwhelm users. A phased rollout allows gradual adaptation. Organizations can start with pilot programs, set clear timelines, and include reflection points to adjust the pace based on feedback. This approach gives teams time to learn and adapt, reducing confusion and mistakes. Leaders should address different types of resistance with targeted strategies, such as using data for logical concerns and emotional support for psychological barriers.
Continuous Improvement
Managing complexity requires ongoing effort. Teams should define stakeholders and understand their perceptions of complexity. Adopting the customer’s perspective helps identify problem points. Data from customer questions, website analytics, and social media feedback reveal where users struggle. Applying systematic changes, such as simplifying software interfaces or improving user manuals, reduces complexity and improves performance.
Metric Category | Description / Example |
|---|---|
Time to perform operations; number of components; number of connections; number of levels; shortest message length | |
Quick Estimation Metrics | Number of support specialists per number of clients or product implementations (shows maintenance effort and product complexity) |
Stakeholder-Specific Indicators | Insights from interviews and observations, such as confusion in specific system areas |
Four-Step Management Approach | Define stakeholders, adopt customer perspective, identify problem points with data, apply systematic changes |
Practical Example | Simplifying software interfaces by reducing duplicate tabs and improving user manuals |
Continuous improvement and regular feedback help organizations keep complexity under control and ensure long-term success with their business management systems.
Business Management Systems work best when teams simplify processes, automate routine tasks, and connect their tools. Leaders should align these systems with company goals for better results. A system assessment helps spot weak areas, while a focus on user experience keeps teams engaged.
Start today by reviewing your current setup. Continuous improvement leads to lasting success.
FAQ
What is a Business Management System (BMS)?
A Business Management System (BMS) helps companies organize, control, and improve their daily operations. It combines tools, processes, and policies to make work easier and more efficient.
How can a company identify if its BMS needs improvement?
Teams should look for signs like frequent errors, slow processes, or employee complaints. Regular audits and user feedback help spot weak areas that need attention.
What are the main benefits of streamlining a BMS?
Streamlining a BMS leads to faster workflows, fewer mistakes, and lower costs. Employees feel less stressed, and customers receive better service.
How does automation improve business management systems?
Automation handles repetitive tasks, such as data entry or scheduling. This reduces human error and saves time. Employees can focus on more important work.
Why is user experience important in a BMS?
A user-friendly system helps employees work faster and with fewer mistakes. Good design encourages daily use and increases overall productivity.
What steps help teams adopt new business management systems?
Teams succeed by communicating benefits, involving stakeholders, offering training, and recognizing achievements. Regular feedback sessions help address concerns and improve adoption rates.
How can companies keep their BMS secure?
Companies use access controls, regular audits, and employee training. These steps protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized changes.
Can small businesses benefit from streamlining their BMS?
Yes. Small businesses often see big gains in efficiency and cost savings. Streamlined systems help them compete with larger companies.



