Unlock the Benefits of Automating Your Business Processes
Automating business processes unlocks measurable improvements in productivity, efficiency, and profitability. Studies show that organizations often achieve 30–50% productivity gains for back office work and see significant boosts in knowledge worker output. Many leaders report that automation enhances workflow efficiency and reduces costly errors. When companies automate business processes, they streamline sales, improve business management, and empower teams to focus on high-value activities. These changes help organizations make smarter decisions and drive growth.
Key Takeaways
Automating business processes boosts productivity by saving time and reducing errors, helping teams focus on important work.
Automation cuts costs significantly, often paying for itself within months through savings in labor and error reduction.
Clear documentation and well-defined roles are essential for smooth automation and ongoing success.
Starting with small, repetitive tasks allows organizations to learn and build confidence before scaling automation.
Involving employees and stakeholders early reduces resistance and ensures automation meets real business needs.
Regularly reviewing automated processes helps keep them efficient, secure, and aligned with company goals.
Automation improves customer experience by providing faster, accurate, and personalized service around the clock.
Choosing the right tools and integrating them carefully with existing systems prevents delays and maximizes benefits.
Why Automate Business Processes

Efficiency Gains
Automating business processes delivers significant efficiency gains for organizations of all sizes. Many companies report that automation reduces manual tasks, saving employees up to 50% of their time. This allows teams to focus on higher-value work and strategic goals. Automation streamlines operations, helping businesses meet deadlines and maintain high availability. Technologies such as robotic process automation (RPA), artificial intelligence, and machine learning further enhance these capabilities, driving measurable improvements in productivity and operational precision.
Faster Response
Automated systems enable organizations to respond to tasks and customer requests much faster than manual processes. For example, automated workflows can send instant notifications, process approvals in real time, and provide immediate updates to stakeholders. This speed helps businesses stay competitive and meet customer expectations. A recent survey found that 90% of customers feel satisfied with the speed of automated responses, which boosts organizational reputation and customer loyalty.
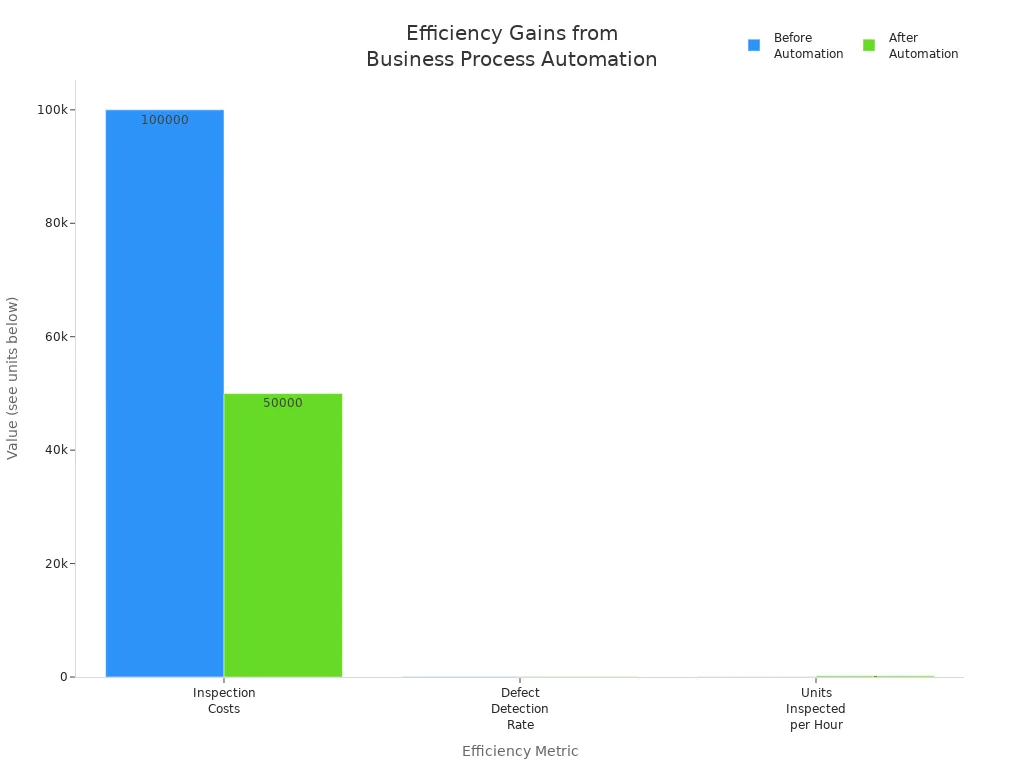
The following chart highlights measurable efficiency gains after automation:
Reduced Errors
Manual processes often lead to mistakes that can cost businesses both time and money. Automation minimizes human intervention, which reduces the risk of errors. Studies show that automation can cut error rates by up to 70%. This improvement leads to more reliable processes and higher customer satisfaction. For example, organizations that automate business processes often see a 13% improvement in quality and a 4x increase in throughput. These gains help companies avoid costly rework and lost revenue.
Cost Savings
Cost savings represent one of the most compelling reasons to automate business processes. Companies typically achieve an average return on investment (ROI) of 240%, with many recouping their investment within six to nine months. Automation reduces the need for manual labor, lowers operational costs, and eliminates expenses related to error correction. For instance, businesses can save about $10 or more per invoice processed automatically. A company processing 1,000 invoices each month could save around $120,000 annually.
Large enterprises using business process management and automation have reported a 20% reduction in operational costs. In the financial sector, over half of firms save at least $100,000 each year through robotic process automation.
Key areas where automation drives cost savings include:
Recruitment and onboarding
Customer relationship management
Inventory monitoring and reordering
These savings allow organizations to reinvest in growth and innovation.
Improved Accuracy
Automation greatly improves accuracy in data entry and processing. Automated systems follow strict algorithms, which reduces the chance of human error. The table below compares manual and automated data entry:
Aspect | Manual Data Entry | Automated Data Entry |
|---|---|---|
Error Rate | High due to human mistakes | Significantly lower |
Consistency | Variable | Consistent across all entries |
Speed | Slower | Faster, handles large volumes |
Data Validation | Manual, prone to oversight | Automated, reduces inaccuracies |
Fatigue Impact | Errors increase with fatigue | No fatigue, accuracy maintained |
Scalability | Limited by workforce | Easily scalable |
Automated systems also support continuous improvement. Some organizations use a hybrid approach, combining automation with human review for complex cases. This method ensures high data integrity and allows the system to learn and improve over time.
Organizations that automate business processes benefit from fewer mistakes, more reliable data, and better decision-making. These improvements support business growth and help maintain a competitive edge.
Better Customer Experience
Automating business processes transforms the way companies interact with their customers. Customers expect quick, accurate, and personalized service. Automation helps businesses meet these expectations by improving every step of the customer journey.
Many organizations see higher customer satisfaction when they automate business processes. Automated systems can provide instant replies to common questions through chatbots or self-service portals. These tools work around the clock, so customers get help any time of day. When a customer submits a request, automation routes it to the right team member, which speeds up resolution and reduces wait times.
Automation also ensures that every customer receives consistent and accurate information. By following set rules, automated systems minimize human error and maintain high service standards. This consistency builds trust and encourages customers to return.
Personalization is another key benefit. Automated tools powered by artificial intelligence analyze customer data to tailor responses and recommendations. Customers feel valued when they receive relevant information or offers based on their preferences.
Companies that automate business processes often see improvements in first contact resolution rates, faster order processing, and real-time updates for customers. These changes lead to higher satisfaction and loyalty.
Automation supports customer service teams by handling routine tasks. This allows employees to focus on complex issues that require a human touch. As a result, customers receive better support for both simple and challenging problems.
Key ways automation enhances customer experience include:
Faster response times and instant replies to inquiries
24/7 availability through chatbots and self-service options
Consistent and accurate information in every interaction
Personalized communication based on customer data
Efficient handling of high volumes during busy periods
Automated follow-ups that show customers their opinions matter
When companies automate business processes, they create a smoother, more reliable experience for every customer. This approach leads to higher engagement, stronger loyalty, and better business outcomes.
What Is Business Process Automation
Definition
Business process automation (BPA) uses computer systems and software to automate business processes and the tasks within them. Companies apply BPA to individual tasks or to multiple steps in a process. This approach uses tools such as artificial intelligence, robotic process automation (RPA), business process management (BPM), and data management. BPA aims to improve efficiency, reduce errors, and free human resources for higher-level decision-making. Unlike RPA, which focuses on specific tasks, BPA orchestrates complex end-to-end business processes. Mike Cichy, Area VP at Appian, explains that BPA technologies streamline execution by moving data seamlessly with minimal user intervention. People can then focus on decisions while automation handles routine workflow steps. BPA often forms part of broader BPM strategies and uses low-code platforms, workflow engines, and cloud platforms to enhance operational performance.
BPA also helps organizations automate recurring manual tasks. This leads to faster, more precise, and consistent execution of activities such as ticket creation, routing requests, or generating reports. According to Gartner, BPA automates complex business processes and functions beyond simple data manipulation. It replaces repeatable, time-consuming tasks like invoicing, data entry, and inventory management. BPA supports digital transformation by streamlining workflows and improving efficiency.
Key Concepts
Several key concepts form the foundation of business process automation. These concepts help organizations understand how to apply BPA for maximum benefit.
BPA Type | Description |
|---|---|
Task Automation | Automates repetitive tasks like sending emails or updating statuses. |
Workflow Automation | Automates sequences of tasks, sometimes partially automated with human intervention. |
Process Automation | Automates entire processes end-to-end, including tasks and workflows. |
Robotic Process Automation | Uses software bots for structured, repetitive tasks without decision-making. |
Intelligent Automation | Combines BPA, RPA, and AI technologies for automating complex, decision-based tasks. |
Organizations often start by identifying repetitive, time-consuming processes that are prone to human error. They then integrate automation tools and platforms to enable seamless workflows across multiple systems. Teams monitor automated processes, track performance, and optimize for efficiency.
Process Categories
Business process automation covers several categories. Each category targets different types of processes within an organization.
Operational
Operational processes include the core activities that deliver value to customers. Companies automate tasks such as order fulfillment, supply chain management, and production scheduling. Automation in this category improves speed, accuracy, and consistency.
Support
Support processes help the main business functions run smoothly. Examples include IT support, human resources, and payroll. Automating these processes reduces administrative workload and ensures timely completion of essential tasks.
Management
Management processes involve planning, monitoring, and controlling business activities. Automation assists with compliance workflows, internal audits, and performance reporting. This leads to better oversight and faster decision-making.
Strategic
Strategic processes focus on long-term goals and business growth. Automation supports activities like market analysis, strategic planning, and innovation management. By automating data collection and analysis, organizations gain insights that guide future direction.
Companies in telecom and banking often automate customer service request routing, onboarding, compliance workflows, and financial operations. These efforts result in faster, more reliable, and scalable operations.
Automate Business Processes: Best Practices
Identify Areas for Improvement
Organizations achieve the best results when they first identify which processes need improvement before starting automation. Teams should look for tasks that take a lot of manual time, especially those that happen often or involve many steps. Processes that use multiple data sources or rely on a few key people can create bottlenecks and risks. Stable and repetitive workflows are usually the best candidates for automation.
A clear approach helps organizations select the right processes to automate. The following steps guide teams through this evaluation:
Map current workflows to spot inefficiencies and bottlenecks.
Set clear goals for automation, such as reducing costs or improving speed.
Choose technology that fits the organization's needs and can grow with the business.
Involve stakeholders early to ensure the solution meets everyone's needs.
Pilot automation in a controlled setting to gather feedback and make improvements.
Teams should also consider processes that require audit trails or have high error costs, such as those related to compliance or customer service. By focusing on these areas, organizations can maximize the benefits of automation and reduce the risk of mistakes.
Tip: Use process mining and mapping tools to visualize workflows and highlight areas for improvement. These tools help teams see where delays and errors occur most often.
Prioritize Automation
After identifying potential areas for improvement, organizations must decide which processes to automate first. Teams should focus on core, repetitive tasks that take up a lot of time, such as document approvals or data entry. Processes with clear, rule-based steps and digital inputs are easier to automate and deliver faster results.
A structured approach to prioritization includes:
Scoring each process based on manual effort, frequency, and ease of automation.
Considering business impact, such as time savings, error reduction, and customer satisfaction.
Checking technical feasibility, including system integration and data quality.
Aligning automation projects with business goals and available resources.
Starting with small, high-impact processes to build momentum and demonstrate value.
The table below summarizes key factors for prioritizing automation projects:
Factor Category | Key Considerations | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
Process Characteristics | Standardization, rule-based, digital input | Easier to automate and maintain |
Business Impact | Time savings, error reduction, customer impact | Delivers measurable benefits |
Technical Feasibility | Integration, data quality, security | Ensures smooth implementation |
Implementation Factors | Stakeholder support, resources, timeline | Supports successful rollout |
Prioritization Approach | Data-driven tools, start small | Builds confidence and enables scaling |
Teams should avoid automating processes that are not yet effective. Automating a poor process only makes problems worse. Keeping automation solutions simple and consistent helps with maintenance and user adoption.
Document Workflows
Thorough documentation is essential before automating any business process. Clear workflow documentation shows how work gets done, who is responsible for each step, and when tasks should happen. This clarity leads to better accountability, faster turnaround times, and fewer mistakes.
Best practices for documenting workflows include:
Mapping each step, including triggers, decision points, and possible failures.
Planning for delays and bottlenecks by adding contingency steps.
Prioritizing workflow steps based on their impact and importance.
Ensuring everyone involved has the resources and knowledge to complete their tasks.
Using tools to automate notifications and reminders for steps that do not need human approval.
Good documentation also supports compliance by recording every stage of a process. It helps teams track progress during automation, making sure no steps are missed. Involving employees in the documentation process improves accuracy and reduces errors.
Note: Well-documented workflows enable consistent service quality, easier communication, and higher customer satisfaction. They also make it easier to scale and adapt automation as the business grows.
By following these best practices, organizations can automate business processes more effectively, leading to greater efficiency, reliability, and long-term success.
Establish Roles
Clear role definition forms the backbone of successful business process automation. Every organization needs to assign ownership and accountability for maintaining, updating, and troubleshooting automated workflows. When teams know their responsibilities, they can respond quickly to issues and keep operations running smoothly.
A structured approach to role assignment includes several key elements:
Assign ownership for each automated process. Owners monitor performance, resolve problems, and update workflows as needed.
Establish an automation center of excellence (CoE) or a dedicated team. This group oversees best practices, provides training, and shapes the overall automation strategy.
Create an automation steering committee. This committee keeps automation efforts aligned with business goals and helps prioritize new initiatives.
Monitor automated processes regularly. Teams must watch for bottlenecks or negative impacts on customer and employee experiences.
Plan for scalability. Teams should consider how to integrate new technologies and expand automation as the business grows.
Tip: Role-based access controls (RBAC) help protect sensitive data. By restricting user permissions according to job functions, organizations improve security and compliance.
Involving employees as automation advocates increases engagement and helps scale automation across the company. Detailed logging of user actions and tasks supports internal security and regulatory compliance. These steps ensure governance, accountability, and continuous improvement as organizations automate business processes.
Train Users
Training prepares employees to work confidently with new automated systems. Effective training covers both the technology and the changes in business procedures. All employees, even those not directly using the new tools, need to understand how their roles may change.
Key training practices include:
Provide training after processes are fully defined but before old methods are replaced. This timing helps employees learn without confusion or disruption.
Adjust deployment schedules to allow enough time for thorough training. Rushed rollouts can lead to mistakes and operational problems.
Develop clear Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs). SOPs outline each step in the process, making it easier for employees to follow and repeat tasks correctly.
Involve IT early and ensure support resources are available. Quick access to help reduces frustration and downtime during the transition.
Note: Training should position automation as a tool that enhances employees’ work, not as a replacement. Encouraging participation and feedback builds trust and increases buy-in.
When organizations automate business processes, well-trained users help maximize the benefits. They adapt more quickly, make fewer errors, and support a smoother transition to new ways of working.
Implementation Steps

Analysis
Successful automation begins with a thorough analysis of existing business processes. Teams must understand how work gets done before making changes. They start by defining the scope of the analysis, focusing on specific processes that need improvement. Stakeholders play a key role, as their insights reveal pain points and opportunities. Visual mapping tools, such as flowcharts or diagrams, help teams see each step clearly.
Teams gather data on time spent, resource use, and error rates. This information highlights bottlenecks and redundancies. Engaging stakeholders provides feedback that uncovers hidden issues. Benchmarking against industry best practices shows where the organization stands. Collaborative brainstorming leads to potential solutions, which teams then prioritize based on impact and feasibility.
Designing the future state process incorporates these improvements. A detailed implementation plan guides the transition. Testing the new process on a small scale allows for adjustments. Teams monitor the process, collect feedback, and measure key performance indicators. Continuous optimization ensures lasting benefits.
Tip: Analyzing processes before automation prevents costly mistakes and break-fix cycles. Improving processes first maximizes the value of automation.
Tool Selection
Choosing the right automation tools is critical for success. Teams look for solutions that match their business goals and requirements. They focus on automating repetitive, high-volume tasks to save time and reduce errors. Rule-based and predictable processes offer the best results, as they require less manual oversight.
Stakeholders from different departments share their needs and pain points. This ensures the selected tool meets diverse requirements. Integration with existing platforms, such as Google Drive or Microsoft SharePoint, is essential for smooth data flow. User-friendly tools with minimal coding encourage adoption and reduce training time.
Customization options allow teams to tailor automation rules and compliance workflows. Scalability supports business growth without disruption. Security and compliance features protect sensitive data and meet legal standards. Teams also consider cost, balancing initial investment against long-term benefits and return on investment.
Criteria | Considerations |
|---|---|
Business Alignment | Supports goals like cost reduction or service |
Integration | Works with CRM, ERP, and other systems |
Scalability | Handles increased workloads and users |
User-Friendliness | Easy to adopt and use |
Security & Compliance | Meets regulations and protects data |
Customization | Adapts to unique business needs |
Cost & ROI | Offers value for investment |
Involving end users in the selection process encourages buy-in and ensures the tool fits real-world needs.
Integration
Integrating automation tools with existing systems presents several challenges. Legacy systems often lack APIs or have limited connectivity, making integration difficult. Teams use Robotic Process Automation (RPA) tools, such as UiPath, or middleware platforms like Zapier and Make to bridge gaps between old and new systems.
Managing large volumes of data requires scalable cloud storage solutions, such as AWS S3 or Google BigQuery. Robust data pipelines ensure efficient storage and retrieval. Standardizing processes before automation helps avoid errors caused by inconsistent data sources and workflows. Mapping tools, like Whimsical or Miro, assist in creating clear, standardized workflows.
Collaboration between technical and business stakeholders is vital. Workshops, shared documentation, and communication platforms, such as Notion, Miro, or Slack, foster alignment and clarify requirements. Selecting partners with both technical and business expertise prevents failed integrations. Teams watch for red flags, such as unrealistic timelines or generic solutions, to avoid costly mistakes.
Note: Addressing integration challenges early ensures a smooth transition and maximizes the benefits of automation.
Maintenance
Automated business processes require ongoing maintenance to deliver consistent results and long-term value. Teams must treat maintenance as a continuous effort, not a one-time task. Regular attention helps organizations avoid disruptions and keeps systems running smoothly.
A successful maintenance strategy begins with clear objectives. Teams set specific goals for each automated process. These goals guide daily operations and help validate the investment in automation. When objectives remain unambiguous, teams can measure progress and adjust strategies as needed.
Monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) plays a vital role in maintenance. Teams track metrics such as error rates, processing speed, and cost savings. These indicators show whether automation meets expectations. When KPIs fall below targets, teams investigate and resolve issues quickly.
Compliance remains essential for every organization. Teams must understand regulatory requirements and follow company policies. Automated processes often handle sensitive data, so regular audits ensure that systems meet legal standards. Compliance checks protect the organization from fines and reputational damage.
Thorough documentation supports effective maintenance. Teams record every change to workflows and automation rules. Documentation includes rollout plans, updates, and troubleshooting steps. When teams maintain clear records, they can resolve problems faster and train new employees more efficiently.
Employee training strengthens maintenance efforts. Teams invest in ongoing education to keep skills up to date. Training covers new features, security practices, and troubleshooting techniques. Well-trained employees manage automated systems confidently and respond to challenges with skill.
Tip: Teams should schedule regular reviews of automated processes. These reviews identify outdated workflows and highlight opportunities for improvement.
A maintenance checklist helps teams stay organized:
Review objectives and update them as business needs change.
Monitor KPIs and address any performance gaps.
Conduct compliance audits and update processes to meet new regulations.
Update documentation after every workflow change.
Provide refresher training for employees managing automation.
Maintenance Practice | Purpose | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
Set clear objectives | Guide operations and measure success | Validates investment |
Monitor KPIs | Track performance and ROI | Identifies issues early |
Ensure compliance | Meet legal and organizational standards | Reduces risk |
Document workflows | Record changes and updates | Improves consistency |
Train employees | Build skills and confidence | Enhances system reliability |
Teams that prioritize maintenance keep automated business processes efficient, secure, and aligned with organizational goals. Regular attention ensures that automation continues to deliver value and supports business growth.
Examples
Invoice Processing
Automating invoice processing helps organizations save time and reduce errors. Many companies handle thousands of invoices each month. Manual processing often leads to delays, lost documents, and high labor costs. Automation tools capture invoice data, match it with purchase orders, and route approvals automatically.
The following table shows how well-known companies improved their invoice processing with automation:
Company | Challenge | Automation Solution | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
Siemens | Fragmented OCR, slow processing | Hyland Brainware with SAP integration | |
Canal Barge | High paper volume, slow approvals | Hyland OnBase for data capture and workflow | No more paper, faster approvals, better tracking |
WeWork | Over 1 million invoices/year, high costs | Order.co for P2P automation | Reduced monthly invoices from 1M to 3,000, big savings |
SoulCycle | Manual AP, slow growth | Order.co for centralized payments | 1,500 invoices into one bill, thousands saved monthly |
PRN | Slow payments across 140+ locations | Order.co for centralized buying/payments | Better spending visibility, less processing time |
Automated invoice processing scales across industries. Companies see fewer errors, faster approvals, and lower costs. Teams gain more time for important work.
Customer Support
Customer support automation transforms how companies help their clients. Automated systems handle routine questions, sort tickets, and provide instant answers. This leads to faster response times and higher customer satisfaction.
Telefónica Germany used AI to answer common questions. The company saw a 20% drop in costs and a 35% rise in customer retention.
Pockit automated email sorting and replies. The team reduced its email backlog by 95% in just two weeks.
Jackpots.ch launched a 24/7 multilingual support system. Customers received instant help, which improved satisfaction.
Delta Airlines uses automated ticketing with natural language processing. This system speeds up ticket management and builds customer trust.
Verkkokauppa automated ticket classification and FAQ responses. The company saved 400 agent hours each week and cut costs by €330,000 a year.
Automated support lets human agents focus on complex problems. Customers get quick, accurate answers at any time.
Onboarding
Automated onboarding streamlines the process for new employees and customers. Companies use digital forms, automated document collection, and self-service portals. These tools guide users through each step, reducing manual work for HR and support teams.
A typical automated onboarding workflow includes:
Sending welcome emails and instructions automatically.
Collecting required documents through secure online forms.
Assigning training modules and tracking completion.
Setting up user accounts and permissions without manual input.
Scheduling check-ins and reminders for follow-up tasks.
Automated onboarding ensures a smooth start for every new team member or client. It reduces paperwork, speeds up access to resources, and improves the overall experience.
Inventory
Automating inventory management helps businesses keep track of stock levels, reduce waste, and avoid costly shortages. Many companies use inventory automation to improve accuracy and save time. Automated systems update stock counts in real time. They alert teams when supplies run low or when items need restocking. This reduces the risk of running out of popular products or over-ordering slow-moving items.
Retailers often use barcode scanners and RFID tags to track inventory. These tools connect to inventory management software, such as NetSuite, Zoho Inventory, or TradeGecko. The software records every sale, return, and shipment. It updates inventory numbers automatically. Warehouse teams use mobile devices to scan items as they move in and out. This process keeps records accurate and up to date.
Automated inventory systems help companies avoid manual data entry errors. They also speed up audits and make it easier to find products in large warehouses.
Manufacturers benefit from inventory automation by linking their systems to production schedules. When raw materials run low, the system can place orders with suppliers automatically. This keeps production lines running smoothly. Restaurants and grocery stores use similar systems to track perishable goods. They receive alerts before items expire, which helps reduce food waste.
The table below shows common inventory automation tools and their main features:
Tool | Key Features | Typical Users |
|---|---|---|
NetSuite | Real-time tracking, reporting | Retailers, wholesalers |
Zoho Inventory | Barcode scanning, order management | Small businesses |
TradeGecko | Multi-channel syncing, analytics | E-commerce stores |
Fishbowl | Manufacturing integration, alerts | Manufacturers |
Automated inventory management also supports better customer service. When teams know exactly what is in stock, they can fulfill orders faster. Customers receive accurate information about product availability. This builds trust and encourages repeat business.
Tip: Companies should review inventory reports regularly. Automated alerts help teams spot trends and adjust orders before problems arise.
Inventory automation gives businesses more control over their supply chains. It reduces costs, improves accuracy, and frees up staff for other important tasks.
Challenges
Resistance
Many organizations face resistance when introducing business process automation. Employees often worry about job security or feel uneasy about new technology. This resistance can slow down or even block automation projects. Leaders must address these concerns early to ensure a smooth transition.
Several factors contribute to resistance:
Unfamiliarity with new technology
Lack of clear communication about automation goals
Concerns about the impact on work quality
Organizations can overcome resistance by following proven strategies:
Communicate openly about why automation is necessary and how it benefits everyone.
Involve employees early in planning and pilot projects to create a sense of ownership.
Offer training and upskilling so employees feel confident in new roles.
Highlight quick wins by automating small processes and sharing results.
Foster a culture that views automation as a tool for innovation.
Encourage teamwork across departments to support smooth implementation.
Collect feedback regularly and use it to improve processes.
Use data to show the real value of automation.
Transparent communication and early involvement help reduce fear and build trust. When employees see the benefits, they become more willing to support automation.
Integration Issues
Integrating automation tools with existing systems presents another major challenge. Many organizations use legacy software that does not connect easily with modern automation platforms. This complexity can lead to delays, increased costs, and frustration among teams.
Common integration challenges include:
Difficulty connecting automation tools to old or custom systems
Multiple stakeholders with different needs and priorities
Complex business rules that require careful mapping
Poor data quality or inconsistent data sources
Misalignment between technical and business teams
A table below summarizes these challenges:
Challenge | Impact |
|---|---|
Legacy system compatibility | Slows down automation projects |
Multiple stakeholders | Causes confusion and delays |
Complex business rules | Increases setup time |
Poor data quality | Leads to errors and unreliable results |
Team misalignment | Results in inefficient solutions |
Organizations can address these issues by standardizing processes, improving data quality, and encouraging collaboration between technical and business teams. Early planning and clear communication help prevent many integration problems.
Security
Security remains a top concern when automating business processes. Automated systems often handle sensitive data, such as customer information or financial records. Any weakness in security can lead to data breaches, regulatory fines, or loss of trust.
Key security challenges include:
Protecting sensitive data during automation
Ensuring compliance with industry regulations
Managing user access and permissions
Monitoring automated processes for unusual activity
Organizations must set strict access controls and regularly audit automated workflows. They should update security protocols as threats evolve. Training employees on security best practices also reduces risks.
Regular reviews and strong security measures help organizations protect their data and maintain compliance. Security should remain a priority throughout the automation journey.
Measuring ROI
Measuring return on investment (ROI) in business process automation presents a challenge for many organizations. Teams often struggle to track the true impact of automation projects. They must consider both direct and indirect benefits. Direct benefits include reduced labor costs and fewer errors. Indirect benefits involve improved customer satisfaction and faster response times.
Many organizations use a simple formula to calculate ROI:
ROI = (Net Gain from Automation / Total Automation Cost) x 100%
Net gain includes savings from reduced manual work, lower error rates, and increased productivity. Total automation cost covers software, training, and maintenance expenses.
Teams face several obstacles when measuring ROI:
Difficulty linking automation to specific business outcomes
Delays in realizing benefits, especially for complex projects
Hidden costs, such as ongoing support or system upgrades
Challenges in collecting accurate data before and after automation
A table below summarizes common factors that affect ROI measurement:
Factor | Description | Impact on ROI Calculation |
|---|---|---|
Labor Cost Savings | Reduced need for manual work | Direct, easy to measure |
Error Reduction | Fewer mistakes and rework | Direct, sometimes hard to quantify |
Productivity Gains | More output with same resources | Direct, measurable over time |
Customer Experience | Higher satisfaction and retention | Indirect, harder to measure |
Training Costs | Expenses for employee education | Direct, must include in costs |
Maintenance Expenses | Ongoing support and updates | Direct, affects long-term ROI |
Tip: Teams should set clear goals and key performance indicators (KPIs) before starting automation. Tracking these metrics helps measure ROI more accurately.
Organizations often use dashboards to monitor performance. These dashboards display metrics such as processing speed, error rates, and customer feedback. Regular reviews help teams spot trends and adjust strategies. Some companies compare results to industry benchmarks for a clearer picture.
Teams should remember that ROI may not appear immediately. Some automation projects take months to show full benefits. Patience and consistent tracking lead to better decisions. When teams measure ROI carefully, they can justify investments and plan future automation projects with confidence.
Optimization Tips
Start Small
Many organizations achieve better results when they begin automation projects with small, manageable tasks. Teams often select a single process that is repetitive and easy to measure. This approach helps them learn quickly and adjust before scaling up. Starting small reduces risk and builds confidence within the team.
Choose a process with clear steps and measurable outcomes.
Set specific goals, such as reducing processing time or error rates.
Track progress and document lessons learned.
Tip: Teams that start with a pilot project can identify challenges early. They use these insights to improve future automation efforts.
Small wins create momentum. They show value to leadership and encourage wider adoption. Teams can expand automation to more complex processes after mastering the basics.
Stakeholder Involvement
Successful automation depends on strong stakeholder involvement. Stakeholders include employees, managers, IT staff, and sometimes customers. Each group brings unique insights and needs. Early engagement ensures that automation aligns with business goals and user expectations.
A table below highlights key stakeholder roles:
Stakeholder | Role in Automation | Benefit to Project |
|---|---|---|
Employees | Share workflow knowledge | Identify real pain points |
Managers | Set priorities and goals | Align with business strategy |
IT Staff | Provide technical expertise | Ensure smooth integration |
Customers | Offer feedback on service changes | Improve user experience |
Teams that involve stakeholders from the start avoid misunderstandings. They gather feedback, address concerns, and build trust. Regular meetings and open communication keep everyone informed and engaged.
Note: Stakeholder input helps teams design automation that fits real-world needs. This leads to higher adoption rates and better results.
Review Regularly
Continuous improvement is key to long-term automation success. Teams should review automated processes on a regular schedule. These reviews help identify outdated steps, new risks, or opportunities for further optimization.
Monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) such as speed, accuracy, and cost savings.
Collect feedback from users and stakeholders.
Update documentation to reflect any changes.
Regular reviews ensure that automation stays aligned with business goals. They also help teams respond quickly to changes in technology or regulations.
Teams that review regularly can adapt to new challenges. They keep processes efficient and maintain high standards. This proactive approach supports ongoing business growth and innovation.
Automating business processes transforms organizations by increasing efficiency, reducing errors, and improving customer satisfaction. Teams that follow best practices—such as identifying key areas, documenting workflows, and training users—see the greatest results. Companies can start small and build on early wins.
Ready to unlock these benefits? Reach out to systems and teams to learn more about automating your business processes and drive your organization forward.
FAQ
What types of business processes can companies automate?
Companies can automate repetitive, rule-based tasks. Examples include data entry, invoice processing, customer support ticketing, and inventory tracking. Automation works best for processes with clear steps and digital data.
How long does it take to implement business process automation?
Implementation time depends on process complexity and tool selection. Simple automations may take a few weeks. Larger projects with multiple systems may require several months. Planning and testing help ensure a smooth rollout.
Do employees need technical skills to use automation tools?
Most modern automation tools offer user-friendly interfaces. Employees do not need advanced technical skills. Training and clear instructions help users adapt quickly. IT teams usually handle setup and maintenance.
Is business process automation expensive?
Costs vary by tool and project size. Many solutions offer scalable pricing. Companies often see a strong return on investment through reduced labor costs and fewer errors. Careful planning helps control expenses.
Can automation improve data security?
Automation can improve data security by reducing manual handling and enforcing access controls. Automated systems track changes and provide audit trails. Regular reviews and updates keep systems secure.
What are common mistakes to avoid when automating processes?
Teams sometimes automate poorly designed processes. This can cause more problems. They should first review and improve workflows. Skipping documentation or training also leads to confusion and errors.
How do companies measure the success of automation projects?
Companies track key performance indicators such as processing speed, error rates, and cost savings. They also collect feedback from users and customers. Regular reviews help teams adjust and improve results.
Can automation scale as a business grows?
Yes, most automation platforms support scaling. Companies can add new processes or users as needed. Choosing flexible tools ensures automation continues to meet business needs over time.



