The Role of Business Management Systems in Modern Enterprises

Business Management Systems play a vital role in driving efficiency and innovation across enterprises. These systems empower organizations to optimize processes, allocate resources effectively, and improve decision-making. For example, leveraging predictive analytics and real-time insights allows businesses to identify inefficiencies, reduce redundancies, and anticipate customer needs. Additionally, the integration of hiring systems and data-driven tools enhances operational workflows, enabling firms to achieve continuous improvement. By adopting these systems and following optimization steps, businesses can adapt to market changes, mitigate risks, and maintain a competitive edge in dynamic environments.
Key Takeaways
Business Management Systems help by making work easier and saving resources.
Setting clear goals and tracking progress keeps work focused on plans.
Using tools like ERP and CRM helps make better choices and improves customer care.
Real-time data helps businesses quickly adjust to changes and needs.
Teaching workers new systems keeps them involved and helps them use them well.
Cloud-based tools are flexible and grow with the business as it expands.
Using data to decide things makes predictions better and work smoother.
Checking and improving systems often keeps everything running well.
Understanding Business Management Systems
Definition and Purpose
Business Management Systems refer to structured frameworks or tools that organizations use to manage and optimize their operations. These systems encompass a variety of processes, technologies, and methodologies designed to streamline workflows, enhance productivity, and achieve strategic goals. By integrating data collection, analysis, and reporting, they enable businesses to make informed decisions and maintain operational excellence.
A quantitative approach to defining these systems involves three key steps: setting SMART goals, executing action plans with a Daily Management System (DMS), and measuring results through Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). For instance, a company might establish profitability targets, implement a DMS to monitor daily operations, and use KPIs to track progress. This structured approach ensures that businesses can align their operations with their strategic objectives.
Importance in Modern Enterprises
Modern enterprises operate in a fast-paced and competitive environment, making Business Management Systems indispensable. These systems provide a centralized platform for managing various aspects of a business, from financial operations to customer relationships. They also foster a culture of continuous improvement by identifying inefficiencies and enabling data-driven decision-making.
Case studies highlight the transformative impact of these systems. For example, a furniture SME in Italy documented its journey from basic data collection methods to sophisticated performance measurement and management systems (PMMS). This evolution not only improved operational efficiency but also influenced organizational culture and management styles. Such examples underscore the importance of adopting these systems to stay competitive and adaptable.
Types of Business Management Systems
Business Management Systems come in various forms, each tailored to specific organizational needs. Common types include:
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): Integrates core business processes like finance, supply chain, and human resources into a unified system.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Focuses on managing customer interactions and improving customer satisfaction.
Business Process Management (BPM): Streamlines and automates workflows to enhance efficiency.
Performance Management Systems: Tracks and evaluates employee performance against organizational goals.
Compliance Management Systems: Ensures adherence to regulatory standards and reduces compliance risks.
The adoption of these systems is on the rise. The Business Process Management market, for instance, is projected to grow from $15.4 billion to $65.8 billion by 2032. Currently, 74% of businesses express interest in BPM adoption, with 70% already using at least one application for process management. However, only 4% of companies track their processes in detail, highlighting a significant opportunity for improvement.
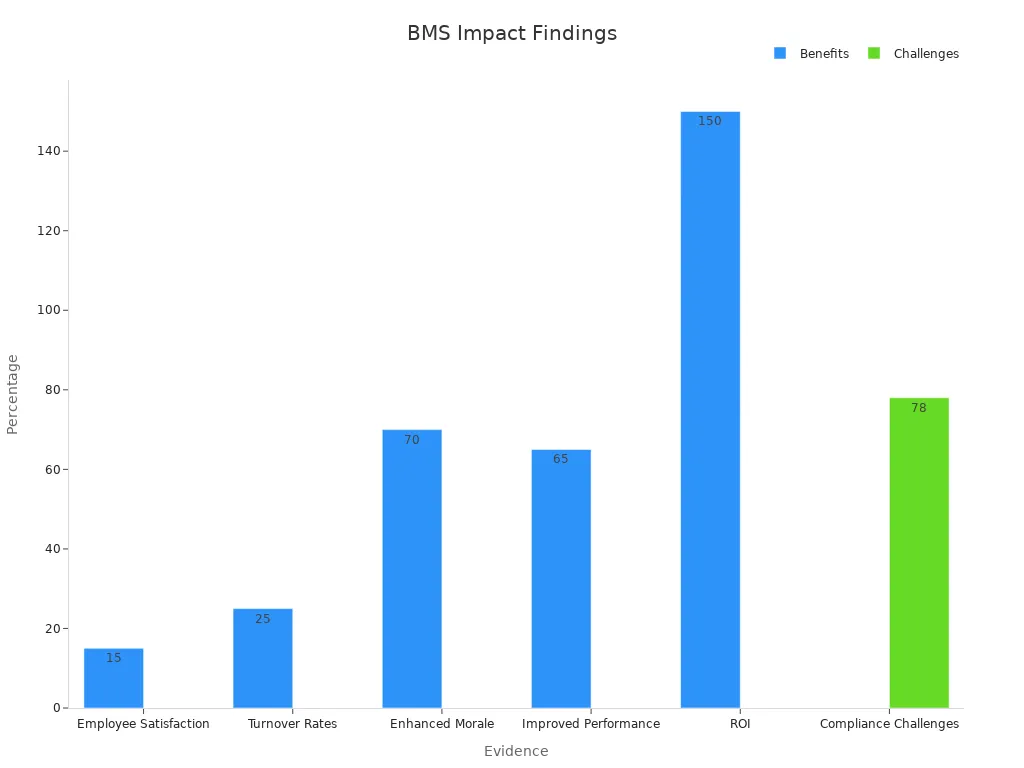
These statistics demonstrate the growing reliance on Business Management Systems to drive efficiency and innovation across industries.
Core Components of Business Management Systems
Financial Management
Financial management forms the backbone of Business Management Systems, enabling organizations to handle their financial operations with precision. Tools like Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software automate tasks such as recording, saving, and accessing financial data. This automation reduces the workload on human analysts and minimizes errors.
ERP systems help businesses save costs by reducing the need for additional financial analysts.
These tools streamline data management, allowing teams to focus on strategic planning.
Enhanced decision-making capabilities through financial management tools often lead to increased profitability.
By integrating financial management modules, enterprises can achieve better control over their budgets and improve overall financial health.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems play a pivotal role in fostering strong customer relationships. These systems provide teams with deeper insights into customer data, enabling them to personalize interactions and streamline sales processes. A well-structured CRM system helps businesses maintain meaningful connections with their customers, which drives repeat business and builds loyalty.
A recent poll revealed that 47% of CRM users believe these systems significantly improve customer retention rates.
By prioritizing CRM implementation, businesses can create predictable revenue streams and enhance customer satisfaction. This component of Business Management Systems ensures that enterprises remain customer-focused and competitive in their industries.
Inventory Management
Inventory management systems are essential for optimizing stock levels and ensuring smooth operations. These systems track inventory in real-time, helping businesses reduce holding costs and improve efficiency.
Metric | Result |
|---|---|
Reduction in Holding Costs | 24% |
Improvement in Data Availability | 97% |
Increase in Inventory Turn Rate | 5.4% |
Key performance metrics, such as turnover ratios and burn rates, allow businesses to monitor inventory depletion and make informed purchasing decisions. By leveraging these tools, companies can prevent stockouts, reduce waste, and maintain balanced inventory levels. Inventory management systems contribute significantly to operational efficiency and cost savings.
Human Resource Management (HRM)
Human Resource Management (HRM) systems are essential for optimizing workforce performance and fostering a productive organizational culture. These systems streamline processes such as recruitment, onboarding, performance evaluation, and employee engagement. By automating repetitive tasks, HRM tools allow HR teams to focus on strategic initiatives like talent development and succession planning.
HRM systems provide valuable insights into workforce metrics, enabling organizations to address challenges like turnover and performance gaps. For instance, tracking voluntary turnover rates helps identify dissatisfaction or compensation issues, while online ratings reflect employee perspectives on workplace culture. Performance ratings highlight individual and team achievements, guiding training and resource allocation.
Metric | Description |
|---|---|
Voluntary turnover rate | Indicates how many employees leave willingly, highlighting potential dissatisfaction or compensation issues. |
Online ratings | Reflects employee perspectives on workplace culture and management, influencing retention strategies. |
Performance ratings | Provides insights into individual and team achievements, indicating areas needing training or resources. |
By leveraging these metrics, HRM systems empower organizations to create a supportive work environment, reduce turnover, and enhance overall productivity. Businesses that integrate HRM systems into their Business Management Systems gain a competitive edge by aligning workforce strategies with organizational goals.
Process and Compliance Management
Process and Compliance Management systems ensure organizations operate efficiently while adhering to regulatory standards. These systems help businesses streamline workflows, reduce risks, and maintain stakeholder trust. By automating compliance tracking and process optimization, companies can allocate resources more effectively and avoid costly violations.
Organizations with robust compliance systems report significant benefits, including:
Lower compliance-related costs
Improved operational efficiency
Enhanced reputation
Compliance management also builds trust with customers and stakeholders, strengthening the organization's reputation. For example, businesses that prioritize compliance measures experience fewer regulatory violations and risks. This proactive approach fosters operational efficiency and ensures better resource allocation.
Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
Reduced Risks | Organizations with compliance systems experience fewer regulatory violations and risks. |
Improved Operational Efficiency | Compliance management leads to streamlined processes and better resource allocation. |
Enhanced Stakeholder Trust | Strong compliance measures build trust with customers and stakeholders, improving reputation. |
Integrating Process and Compliance Management systems into Business Management Systems enables enterprises to achieve operational excellence while safeguarding their reputation. These systems are vital for navigating complex regulatory landscapes and maintaining long-term sustainability.
Benefits of Business Management Systems
Enhanced Operational Efficiency
Business Management Systems significantly enhance operational efficiency by streamlining processes and optimizing resource utilization. These systems automate repetitive tasks, reducing manual errors and freeing up employees to focus on strategic initiatives. For instance, financial management modules in these systems improve cash flow tracking and expense management, while inventory management tools ensure optimal stock levels and reduce waste.
Efficiency metrics further illustrate the impact of these systems. The table below highlights key performance indicators that measure operational efficiency:
Metric | Description |
|---|---|
Gross Margin | Indicates operational efficiency by showing the difference between revenue and cost of goods sold. |
Net Profit Margin | Reflects overall profitability and effective management of expenses. |
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) | Measures the efficiency of marketing and sales operations in acquiring new customers. |
Customer Retention Rate | Indicates operational efficiency through customer loyalty and satisfaction. |
Cash Flow | Shows the net cash movement, indicating financial health and operational efficiency. |
Inventory Turnover | Reflects sales strength and inventory management efficiency. |
Cycle Time | Measures process efficiency by tracking the total time from start to finish. |
Capacity Utilization Rate | Indicates how much of potential output is being realized, highlighting resource utilization. |
Employee Productivity | Gauges efficiency in utilizing human resources, often measured as revenue per employee. |
Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT) | Indicates how well operations meet market demands, reflecting operational effectiveness. |
Quality Metrics | Assesses efficiency gains without compromising quality, including defect and error rates. |
By leveraging these metrics, organizations can identify inefficiencies, implement corrective measures, and achieve continuous improvement. Business Management Systems empower teams to operate at peak performance, ensuring long-term success.
Data-Driven Decision-Making
Data-driven decision-making (DDDM) is a cornerstone of modern Business Management Systems. These systems enable organizations to harness real-time insights and analytics, leading to more informed and strategic choices. By relying on empirical data, businesses can enhance forecasting accuracy and improve overall performance.
Key benefits of DDDM include:
Real-time data processing allows instant access to information, facilitating quicker responses to market changes and operational challenges.
Empirical data ensures decisions are grounded in reality, reducing the risk of errors and misjudgments.
Enhanced forecasting accuracy helps organizations anticipate trends and allocate resources effectively.
A survey by PwC revealed that highly data-driven organizations are three times more likely to report significant improvements in decision-making. This underscores the importance of integrating robust analytics tools into Business Management Systems. By doing so, enterprises can stay ahead of the competition and adapt to evolving market demands.
Scalability and Growth Enablement
Scalability is a critical feature of Business Management Systems, enabling enterprises to grow without compromising efficiency. These systems provide flexible solutions that adapt to changing business needs, whether it's expanding operations, entering new markets, or managing increased workloads.
Statistical trends highlight the role of scalability in driving growth:
Statistic | Description |
|---|---|
85% of enterprises | Predicted to rely on a multi-cloud strategy by 2025, indicating a shift towards scalable solutions. |
$947.3 billion | Expected global spending on cloud computing by 2026, highlighting the investment in scalable infrastructures. |
Cloud-based Business Management Systems exemplify scalability by offering remote accessibility and seamless integration with existing processes. These systems allow businesses to scale their operations efficiently, ensuring they can meet growing customer demands and capitalize on new opportunities. By investing in scalable infrastructures, organizations position themselves for sustained growth and success.
Improved Collaboration and Communication
Effective collaboration and communication are essential for any organization to thrive. Business Management Systems play a pivotal role in fostering these aspects by providing centralized platforms and tools that streamline interactions among teams. These systems eliminate silos, enabling employees to share information, coordinate tasks, and work towards common goals more efficiently.
One of the key ways these systems improve collaboration is through real-time communication tools. Features like instant messaging, video conferencing, and shared dashboards allow teams to stay connected, regardless of their physical location. For example, a project manager can use a shared dashboard to monitor progress, assign tasks, and provide feedback instantly. This level of connectivity ensures that everyone remains aligned and informed.
Additionally, Business Management Systems enhance knowledge sharing within organizations. They provide repositories where employees can store, access, and update critical documents. This reduces duplication of effort and ensures that teams have access to the latest information. For instance, a sales team can use a centralized CRM system to access customer data, track interactions, and collaborate on strategies to improve client relationships.
The impact of these systems on collaboration and communication can be measured through various metrics. The table below highlights some of the key indicators:
Metric Type | Description |
|---|---|
Tracks the number of messages exchanged, meeting frequency, response times, and participation levels. | |
Knowledge-sharing Metrics | Measures contributions to shared repositories, document sharing, and participation in forums. |
Employee Engagement Levels | Reflects collaboration through engagement and retention rates. |
Surveys and Questionnaires | Captures employees’ perceptions of teamwork and communication effectiveness. |
Peer Evaluations | Provides structured feedback on collaborative behaviors and contributions. |
Project Outcomes and Performance | Assesses collaboration success through project completion rates and customer satisfaction. |
Network Analysis | Maps relationships and communication channels within the organization. |
Technology-Based Collaboration | Analyzes user engagement and interaction patterns from collaboration tools. |
Observations and Behavioral Assessments | Evaluates team dynamics and contributions through direct observation. |
Occupancy Sensors | Tracks human interaction in collaborative spaces to gauge engagement levels. |
These metrics demonstrate how Business Management Systems create a more connected and collaborative work environment. For example, organizations that track communication metrics often notice improved response times and higher participation rates in meetings. Similarly, knowledge-sharing metrics reveal increased contributions to shared repositories, indicating a culture of collaboration.
By integrating these systems, businesses can break down barriers to communication and foster a more cohesive workforce. Employees can collaborate seamlessly, share ideas, and resolve issues faster. This not only boosts productivity but also enhances job satisfaction, as employees feel more connected and valued within their teams.
Steps to Implement Business Management Systems
Define Objectives and Assess Needs
Defining objectives is the first step in implementing Business Management Systems. Organizations must identify their goals and align them with measurable criteria to ensure success. For example, a company aiming to improve training efficiency might set a target of completing 100% of new employee training within 30 days of hire. This objective can be tracked through training records verification, ensuring alignment with quality policies.
Objective Description | Measurement Criteria | Example |
|---|---|---|
100% of training for new employees completed within 30 days of hire | Training records verification | Aligns with quality policy on personnel training |
85% of nonconformance reports closed within 45 days | Closure rate of reports | Realistic goal considering supplier dependencies |
Achieve zero major nonconformances during ISO 13485 recertification audit | Audit results | Clear metric for quality management success |
Assessing needs involves evaluating current processes and identifying gaps that Business Management Systems can address. Organizations should conduct a thorough analysis of workflows, employee performance, and customer satisfaction metrics. A clear vision of system requirements, combined with leadership support and effective communication with stakeholders, lays the foundation for successful implementation.
Research and Evaluate Solutions
Researching and evaluating solutions requires a systematic approach to selecting the right Business Management System. Organizations should benchmark their performance against industry standards to identify areas for improvement. Metrics such as cost per unit, production time, and customer satisfaction provide valuable insights into operational efficiency.
Benchmarking helps businesses compare their performance against competitors.
Regular performance data reviews inspire continuous improvement.
Sharing success stories motivates employees to enhance their performance.
Selecting the right system involves defining clear metrics that align with organizational values. Multi-source feedback ensures comprehensive evaluations, while fostering a culture of continuous improvement enhances the effectiveness of performance assessments. By comparing solutions based on functionality, scalability, and cost, organizations can choose systems that best meet their needs.
Plan Integration and Customization
Planning integration and customization is crucial for ensuring a smooth transition to a new Business Management System. Organizations must configure the system to align with existing workflows and set up user access before the official launch. Security considerations, such as data protection and access control, should be prioritized during this phase.
KPI Type | Description |
|---|---|
Business Performance | |
Employee Satisfaction | Assesses how employees feel about their work. |
Customer Experience | Evaluates improvements in customer interactions. |
Revenue Growth | Tracks increase in sales and income. |
Project Margin | Analyzes profitability of specific projects. |
Business Productivity | Measures efficiency in operations. |
A phased approach to integration often yields better results, with over 50% of organizations reporting success using this strategy. Companies hiring software consultants achieve an 85% success rate, while those with institutional leadership support see a 77% success rate. These strategies ensure the system is technically sound and ready for broader adoption.
Configure the system for compatibility with existing workflows.
Plan for security considerations and continuous optimization.
Ensure a smooth installation and integration process.
By carefully planning integration and customization, organizations can maximize the benefits of Business Management Systems and achieve long-term success.
Train Teams and Ensure Adoption
Training employees is a critical step in the successful implementation of Business Management Systems. Well-trained teams can maximize the system's potential, ensuring smooth adoption and long-term success. Organizations must prioritize structured training programs to familiarize employees with the system's features and functionalities. This approach not only boosts confidence but also minimizes resistance to change.
A well-planned training program positively impacts employee engagement and retention. The table below highlights key statistics that emphasize the importance of training during system deployment:
Statistic | Source | Year |
|---|---|---|
92% of employees believe well-planned training positively impacts engagement | Axonify | 2018 |
94% of employees would remain with a company that invests in their development | 2019 | |
Organizations using effective training see up to a 30% productivity increase | McKinsey Quarterly | N/A |
These figures demonstrate the value of investing in employee development. Training programs should include hands-on workshops, interactive tutorials, and role-specific modules to address diverse learning needs. Additionally, organizations should provide ongoing support through help desks or dedicated system experts to resolve queries promptly.
Encouraging employee feedback during training sessions fosters a sense of involvement and ownership. This feedback can guide adjustments to the training process, ensuring it remains relevant and effective. By equipping teams with the necessary skills and knowledge, businesses can achieve higher adoption rates and unlock the full potential of their Business Management Systems.
Monitor and Optimize System Performance
Monitoring and optimizing system performance is essential for maintaining efficiency and achieving continuous improvement. After implementation, organizations must regularly evaluate the system's effectiveness to identify areas for enhancement. This proactive approach prevents stagnation and ensures the system evolves with the business's needs.
Key strategies for optimization include performance analysis, feedback loops, and the use of modern technology. Regularly analyzing metrics such as task completion times and customer satisfaction scores helps pinpoint inefficiencies. Feedback from employees and stakeholders provides valuable insights for refining workflows and addressing challenges. Automation tools and CRM platforms further simplify adjustments, enhancing overall system performance.
Continuous improvement post-implementation is crucial for long-term success.
Regular performance analysis and feedback loops boost efficiency and competitiveness.
Modern technology simplifies adjustments and enhances workflows.
Employee engagement fosters active participation in improvement efforts.
Monitoring KPIs ensures ongoing progress and identifies growth areas.
Organizations should establish a robust framework for tracking Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). Metrics like cycle time, error rates, and customer feedback offer a clear picture of the system's impact. By addressing identified gaps, businesses can make incremental refinements that drive productivity and competitiveness.
Open communication with employees plays a vital role in optimization efforts. Encouraging team members to share their experiences and suggestions creates a collaborative environment. This approach not only improves system performance but also strengthens employee engagement and satisfaction. By continuously monitoring and optimizing their Business Management Systems, organizations can ensure sustained success and adaptability in a dynamic market.
Overcoming Challenges in Implementation
Addressing Resistance to Change
Resistance to change is one of the most common challenges during the implementation of Business Management Systems. Employees often feel uncertain about new processes, fearing that automation might replace their roles or disrupt their routines. To address this, organizations must foster a culture of transparency and inclusivity. Leaders should communicate the benefits of the system clearly, emphasizing how it will enhance efficiency and reduce repetitive tasks.
A case study highlights how entrenched organizational patterns can hinder the success of these systems. For example, rigid adherence to templates often fails to account for the unique needs of an organization. Adaptive approaches that consider context-specific factors tend to yield better results. The table below outlines key challenges encountered during implementation:
Key Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
Organizational Culture | Entrenched patterns can impede the success of Business Management Systems. |
Conflict Management | Managing conflicts effectively is crucial during the implementation process. |
Power Dynamics | Internal power struggles can significantly affect outcomes. |
Rigid Adherence to Templates | Strictly following templates may not work; flexibility is essential. |
Context-Specific Adaptation | Tailoring the system to the organization’s unique context ensures better results. |
Learning Mechanisms | Both constructive and prescriptive learning mechanisms drive successful implementation. |
Cultural Clashes | A culture of innovation may conflict with the structured approach of some systems, as seen in the case of 3M. |
Transformational Learning | Addressing deeply rooted organizational patterns often requires transformational learning. |
By addressing these challenges proactively, organizations can create an environment where employees feel supported and motivated to embrace change.
Managing Integration Complexities
Integrating a new Business Management System with existing processes can be a daunting task. Poor integration strategies often lead to inefficiencies and missed opportunities. Studies reveal that nearly 70% of mergers fail to achieve their intended benefits due to inadequate integration planning. This highlights the importance of a well-thought-out approach.
Key challenges during integration include aligning the new system with legacy software, ensuring data compatibility, and maintaining operational continuity. Companies that neglect these aspects risk losing up to $300,000 annually due to HR pitfalls, which can affect employee morale and productivity. To overcome these complexities, organizations should:
Conduct a thorough assessment of existing processes and identify potential bottlenecks.
Develop a phased integration plan to minimize disruptions.
Invest in training and support to help employees adapt to the new system.
A collaborative approach involving cross-functional teams can also streamline the integration process. By addressing these complexities strategically, businesses can ensure a smoother transition and maximize the benefits of their new systems.
Ensuring Employee Adoption
Employee adoption is critical to the success of any Business Management System. Even the most advanced systems can fail if employees do not use them effectively. Organizations must prioritize training and engagement to ensure widespread adoption. Structured training programs that cater to different learning styles can help employees understand the system’s features and benefits.
Surveys show that 92% of employees believe well-planned training positively impacts engagement. Additionally, 94% would stay with a company that invests in their development. These statistics underscore the importance of equipping employees with the necessary skills and knowledge. Hands-on workshops, interactive tutorials, and role-specific modules can make training more effective.
Encouraging feedback during the adoption phase fosters a sense of ownership among employees. Leaders should also recognize and reward early adopters to motivate others. By creating a supportive environment, organizations can ensure that employees embrace the new system and contribute to its long-term success.
Leveraging Expert Support
Implementing Business Management Systems often involves complex processes that require specialized knowledge. Expert support plays a crucial role in ensuring a smooth transition and maximizing the system's potential. Organizations that collaborate with experienced professionals can overcome challenges more effectively and achieve better outcomes.
Why Expert Support Matters
Experts bring valuable insights and technical expertise to the table. They understand the intricacies of system integration, customization, and optimization. Their experience allows them to identify potential pitfalls and recommend solutions tailored to the organization’s needs. For example, a consultant specializing in Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems can guide a company through data migration, ensuring minimal disruption to operations.
Tip: Partnering with experts early in the implementation process can save time and reduce costs in the long run.
Key Benefits of Expert Support
Customized Solutions
Experts analyze the unique requirements of an organization and design solutions that align with its goals. This ensures that the system addresses specific challenges and delivers maximum value.Efficient Problem-Solving
Professionals can quickly identify and resolve technical issues, minimizing downtime. Their expertise helps maintain operational continuity during the transition phase.Knowledge Transfer
Experts often provide training and resources to internal teams. This empowers employees to use the system effectively and fosters long-term self-sufficiency.Compliance Assurance
Regulatory requirements vary across industries. Consultants ensure that the system adheres to relevant standards, reducing the risk of non-compliance.
Choosing the Right Expert
Selecting the right expert is critical for success. Organizations should evaluate candidates based on their experience, industry knowledge, and track record. The table below outlines key criteria to consider:
Criteria | Description |
|---|---|
Experience | Years of experience in implementing similar systems. |
Industry Expertise | Familiarity with the specific challenges and regulations of the industry. |
Communication Skills | Ability to explain technical concepts in simple terms. |
Client References | Positive feedback from previous clients. |
Maximizing the Value of Expert Support
To get the most out of expert support, organizations should maintain open communication and set clear expectations. Regular progress reviews help ensure alignment with project goals. Additionally, involving internal teams in the process fosters collaboration and knowledge sharing.
Note: Experts act as partners, not replacements. Their role is to complement the organization’s efforts, not to take over entirely.
By leveraging expert support, businesses can navigate the complexities of Business Management Systems with confidence. This collaborative approach enhances the likelihood of a successful implementation and positions the organization for long-term success.
Future Trends in Business Management Systems

AI and Automation Integration
Artificial intelligence (AI) and automation are reshaping how organizations operate. These technologies streamline repetitive tasks, allowing employees to focus on strategic activities. For instance, AI-powered tools analyze data patterns to automate decision-making processes, improving efficiency and accuracy. Generative AI, now accessible to knowledge workers, enhances productivity by solving everyday challenges.
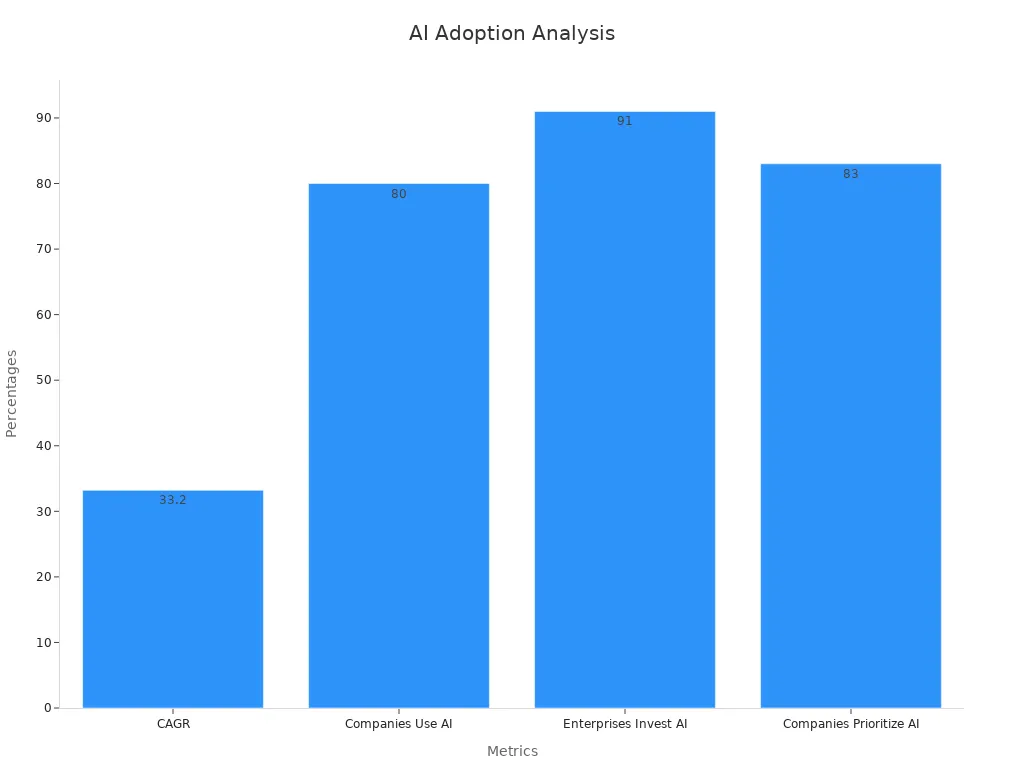
The adoption of AI is accelerating rapidly. By 2027, the global AI market is projected to reach $266.92 billion, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 33.2%. Currently, 80% of companies have incorporated AI into their operations, while 91% of leading enterprises are actively investing in it. Businesses that delay AI integration risk falling behind competitors.
Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
Projected Global AI Market Size by 2027 | $266.92 billion |
CAGR (2020-2027) | 33.2% |
Companies Incorporating AI | 80% |
Leading Enterprises Investing in AI | 91% |
AI also plays a pivotal role in enhancing IoT capabilities. It processes data in real-time, enabling faster decision-making and improved resource allocation. Integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) systems further optimize operations by combining data collection and transmission, opening new possibilities for environmental monitoring and smart agriculture.
Cloud-Based and Remote Accessibility
Cloud-based solutions are transforming Business Management Systems by offering flexibility and scalability. These systems enable remote access, allowing teams to collaborate seamlessly from any location. This capability has become essential in a world where hybrid and remote work models are increasingly common.
The rise of 5G connectivity further enhances cloud-based systems. Faster and more reliable networks support real-time applications, such as IoT device management and video conferencing. Edge computing complements this by processing data closer to its source, reducing latency and improving performance. Together, these technologies ensure that businesses can operate efficiently, even in decentralized environments.
Organizations adopting cloud-based systems benefit from cost savings and operational agility. Multi-cloud strategies, which involve using multiple cloud providers, are gaining traction. By 2025, 85% of enterprises are expected to rely on such strategies, highlighting the growing importance of cloud-based infrastructures.
Advanced Data Security and Privacy
As businesses increasingly rely on digital systems, data security and privacy have become top priorities. Advanced technologies like blockchain ensure data integrity and secure transactions. Blockchain's decentralized nature makes it ideal for protecting sensitive information in IoT environments.
Sustainability efforts also intersect with data security. Real-time data monitoring optimizes resource use while maintaining compliance with environmental regulations. For example, smart systems can track energy consumption and reduce waste, contributing to both security and sustainability goals.
The integration of AI further strengthens security measures. AI algorithms detect anomalies in real-time, preventing potential breaches. Companies that prioritize advanced security measures not only protect their assets but also build trust with customers and stakeholders.
Trend | Description |
|---|---|
Edge Computing | Processes data at the edge of the network for real-time insights and faster decision-making. |
5G Connectivity | Enables faster and more reliable IoT device adoption, supporting real-time applications. |
AI Integration | Enhances IoT capabilities by analyzing data for patterns and automating decisions. |
Blockchain for Security | Ensures data integrity and secure transactions in IoT environments. |
Sustainability Efforts | Optimizes resource use through real-time data, contributing to sustainability initiatives. |
By adopting these advanced technologies, businesses can safeguard their operations while staying ahead in a competitive market.
Real-Time Analytics and Insights
Real-time analytics has become a cornerstone of modern Business Management Systems. It empowers organizations to process and analyze data as it is generated, enabling faster and more accurate decision-making. This capability allows businesses to respond to market changes, customer demands, and operational challenges without delay.
Key Benefits of Real-Time Analytics
Faster Decision-Making
Real-time analytics eliminates the lag between data collection and analysis. Decision-makers gain immediate access to actionable insights, which helps them address issues promptly. For example, a retail company can monitor sales trends in real time and adjust inventory levels to meet demand.Improved Customer Experience
Businesses can use real-time data to personalize customer interactions. For instance, e-commerce platforms analyze browsing behavior to recommend products instantly. This approach enhances customer satisfaction and increases conversion rates.Operational Efficiency
Real-time insights optimize resource allocation and streamline processes. Manufacturing companies, for example, use real-time analytics to monitor equipment performance and predict maintenance needs. This reduces downtime and improves productivity.Risk Mitigation
Organizations can identify and address potential risks before they escalate. Financial institutions, for instance, use real-time fraud detection systems to prevent unauthorized transactions.
Applications in Business Management Systems
Real-time analytics integrates seamlessly into various components of Business Management Systems. Below are some examples:
Component | Application Example |
|---|---|
Financial Management | Tracks cash flow and detects anomalies in transactions. |
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) | Monitors customer interactions to provide instant support and personalized offers. |
Inventory Management | Tracks stock levels and predicts shortages or overstock situations. |
Human Resource Management (HRM) | Analyzes employee performance metrics to identify training needs. |
Tools and Technologies
Modern tools like dashboards, predictive analytics software, and AI-powered platforms enable real-time data processing. Cloud-based systems enhance accessibility, allowing teams to view insights from any location. For example, a logistics company might use IoT sensors and real-time dashboards to track shipments and optimize delivery routes.
Tip: Businesses should prioritize tools that offer user-friendly interfaces and customizable features. This ensures that teams can easily interpret and act on real-time insights.
Real-time analytics transforms how businesses operate. It provides a competitive edge by enabling agility, precision, and proactive decision-making. Organizations that embrace this technology position themselves for long-term success in an ever-changing market.
Business Management Systems empower enterprises to streamline operations, enhance decision-making, and achieve sustainable growth. Strategic implementation ensures these systems align with organizational goals, driving efficiency and scalability. Operational metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) provide measurable insights into performance and outcomes, making them essential tools for growth. Additionally, advanced technologies like business intelligence platforms and machine learning algorithms enable data-driven strategies. By evaluating needs and adopting the right systems, businesses can unlock their full potential and maintain a competitive edge in dynamic markets.
Metric Type | Description | Importance in Growth |
|---|---|---|
Operational Metrics | Measure the status of operations and strategies. | Essential for assessing business performance. |
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) | Track specific objectives and outcomes. | Critical for informed decision-making. |
FAQ
What are Business Management Systems?
Business Management Systems are tools or frameworks that help organizations manage operations, optimize workflows, and achieve strategic goals. They integrate processes like financial management, customer relationship management, and inventory tracking into a unified platform.
How do Business Management Systems improve decision-making?
These systems provide real-time data and analytics, enabling leaders to make informed decisions. By analyzing trends and patterns, businesses can forecast outcomes, allocate resources effectively, and respond to challenges with precision.
What industries benefit most from Business Management Systems?
Industries like manufacturing, retail, healthcare, and finance benefit significantly. These systems streamline operations, enhance customer experiences, and ensure compliance with regulations, making them essential for sectors with complex workflows.
Are Business Management Systems scalable for growing businesses?
Yes, most systems are designed to scale with business growth. Cloud-based solutions, for example, allow organizations to expand operations, add users, and integrate new functionalities without compromising efficiency.
What challenges arise during implementation?
Common challenges include resistance to change, integration complexities, and employee adoption. Addressing these issues requires clear communication, structured training, and expert support to ensure a smooth transition.
How does AI enhance Business Management Systems?
AI automates repetitive tasks, analyzes data patterns, and provides predictive insights. It improves efficiency, accuracy, and decision-making, making systems more adaptive to dynamic business environments.
What is the role of compliance management in these systems?
Compliance management ensures organizations adhere to regulatory standards. It reduces risks, prevents violations, and builds trust with stakeholders by maintaining transparency and accountability.
Can small businesses afford Business Management Systems?
Many systems offer scalable pricing models tailored to small businesses. Cloud-based solutions and modular systems provide cost-effective options, allowing smaller enterprises to benefit without significant financial strain.



