Boost Your Small Business with These Proven Systems

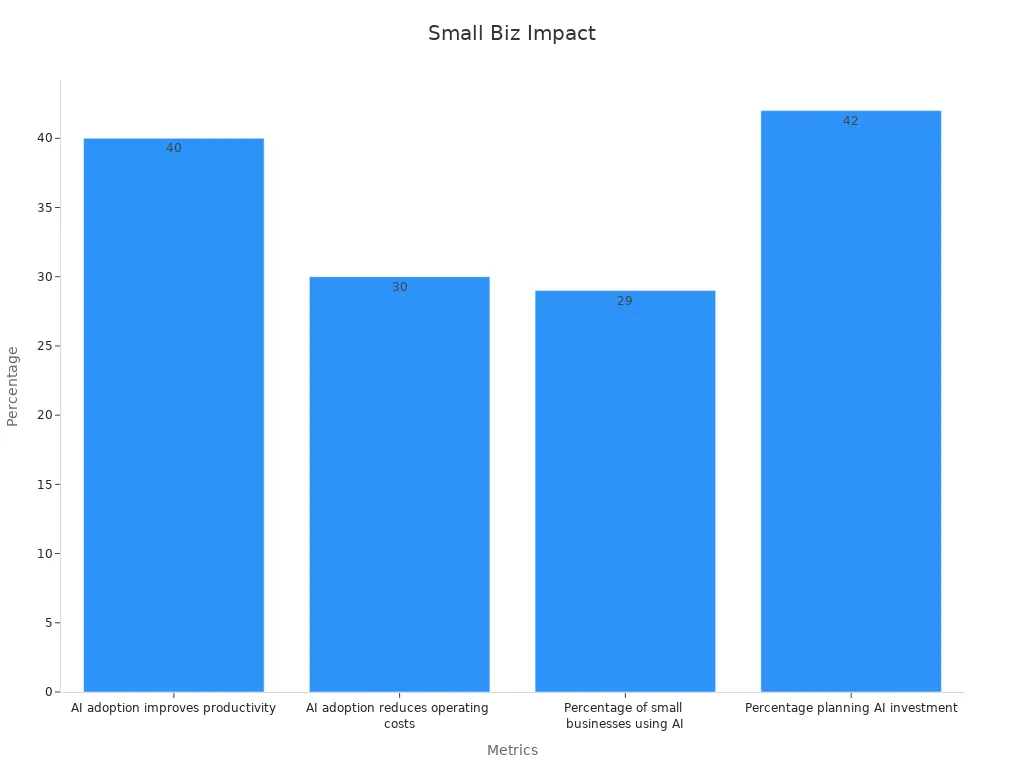
Small business systems transform the way a small business operates, driving efficiency and measurable growth. By adopting digital tools and simple process improvements, any small business can streamline operations and reduce manual effort. The right methodology and resources make systems accessible and scalable, even for teams with limited experience. Many small businesses have seen up to a 40% increase in productivity and a 30% reduction in costs through automation and process optimization.
Metric / Statistic | Impact / Value |
|---|---|
AI adoption improves productivity | 40% increase |
AI adoption reduces operating costs | Up to 30% reduction |
Small businesses using multiple digital tools | Higher revenue growth and faster expansion |
Percentage of small businesses using AI | 29% currently use AI tools |
Percentage planning AI investment | 42% plan to invest within a year |
Streamlined processes allow owners to step back, giving teams more independence and improving overall business performance.
Key Takeaways
Small business systems boost efficiency by automating repetitive tasks and reducing errors.
Using digital tools helps businesses scale smoothly without costly disruptions.
Good systems improve customer service with faster responses and consistent communication.
Clear roles and documented procedures (SOPs) ensure consistency and easier team training.
Choosing simple, affordable tools that fit your business needs leads to better results.
Regular training and smooth rollout plans help employees adopt new systems confidently.
Ongoing reviews and feedback keep systems effective and support continuous improvement.
Starting with urgent pain points and small changes can lead to big gains in growth and satisfaction.
Why Small Business Systems Matter
Small business systems play a vital role in supporting business growth, sustainability, and smooth operations. These systems help owners and teams manage daily tasks, track progress, and reach business goals. By using technology, automation, and simple processes, companies can scale their business without adding unnecessary complexity.
Key Benefits
Efficiency
Business systems help companies increase productivity by reducing duplicate work and streamlining tasks. When teams follow clear steps, they save time and avoid confusion. Management systems allow employees to focus on value-adding activities instead of repetitive chores. For example, cloud-based tools like MySQL and PostgreSQL offer secure storage and automation features that support both small and large businesses. These solutions help companies track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as throughput and labor efficiency, making it easier to measure improvements and adjust strategies.
Scalability
A strong business system allows a company to scale your business without major disruptions. Cloud-based data warehouses like Snowflake, Amazon Redshift, and Google BigQuery provide flexible, pay-as-you-go pricing. These platforms offer entry-level packages and user-friendly interfaces, making them accessible to companies with different technical skills. ERP systems such as NetSuite and Cetec ERP also support growth by integrating multiple business functions and offering affordable pricing. These tools eliminate the need for costly IT infrastructure and allow businesses to expand smoothly.
Customer Service
Business systems improve customer service by ensuring consistent communication and faster response times. Automated workflows help teams manage customer inquiries, process orders, and resolve issues quickly. When employees have access to organized information, they can deliver better service and build stronger relationships with clients. This leads to higher satisfaction and repeat business.
Common Myths
Some people believe that small business systems are too complex or only suitable for large companies. However, many modern solutions are designed for accessibility and scalability. For instance, both MySQL and PostgreSQL provide cost-effective options that grow with the company. Data shows that small businesses face real challenges in today’s economy. Between 2005 and 2015, the number of small retailers dropped by more than 20%, and small manufacturers declined by 13%. These trends highlight the need for effective business systems to stay competitive. Despite these challenges, most Americans trust small businesses and see them as positive forces in their communities. This trust shows the importance of building strong, reliable systems that support long-term success.
Identifying Business Systems Needs
Every small business faces unique challenges, but most share common areas where business systems can deliver the greatest impact. Identifying these areas helps owners focus their efforts and resources for maximum results.
Repetitive Tasks
Repetitive tasks often consume valuable time and lead to errors. Payroll, invoicing, and inventory management are examples where automation can make a difference. When a company automates these tasks, it saves time and reduces mistakes. For instance, HR departments have reported saving up to 20 hours each month by automating payroll. Dental organizations have cut simulation time by half through similar systems. By targeting these routine activities, business systems free up staff to focus on more important work.
High-Impact Areas
Some processes directly affect customer satisfaction and revenue. Prioritizing these high-impact areas ensures immediate benefits and builds momentum for further improvements. The table below highlights key areas where business systems can transform performance:
High-Impact Area | Description | Measurable Impact / Example |
|---|---|---|
Automation of repetitive tasks | Payroll, invoicing, inventory management automation saves time | HR saves 20 hours/month; dental org cut simulation time by 50% |
Customer satisfaction and revenue | Focus on workflows that impact customers and revenue | Highest ROI, faster results |
Cost reduction and efficiency | Streamlined processes reduce costs and errors | Tech company cut admin costs by 30%, increased retention by 15% |
Scalability | Modular systems and automation support growth | Cloud tools handle peak demand, easy upgrades |
Monitoring and optimization | KPIs and feedback loops drive improvement | Regular audits, better productivity, higher satisfaction |
Use of affordable tools | Cost-effective software consolidates functions | Reduces expenses, improves accountability |
Tip: Focusing on customer-facing and revenue-generating processes first often leads to the fastest improvements.
Workflow Assessment
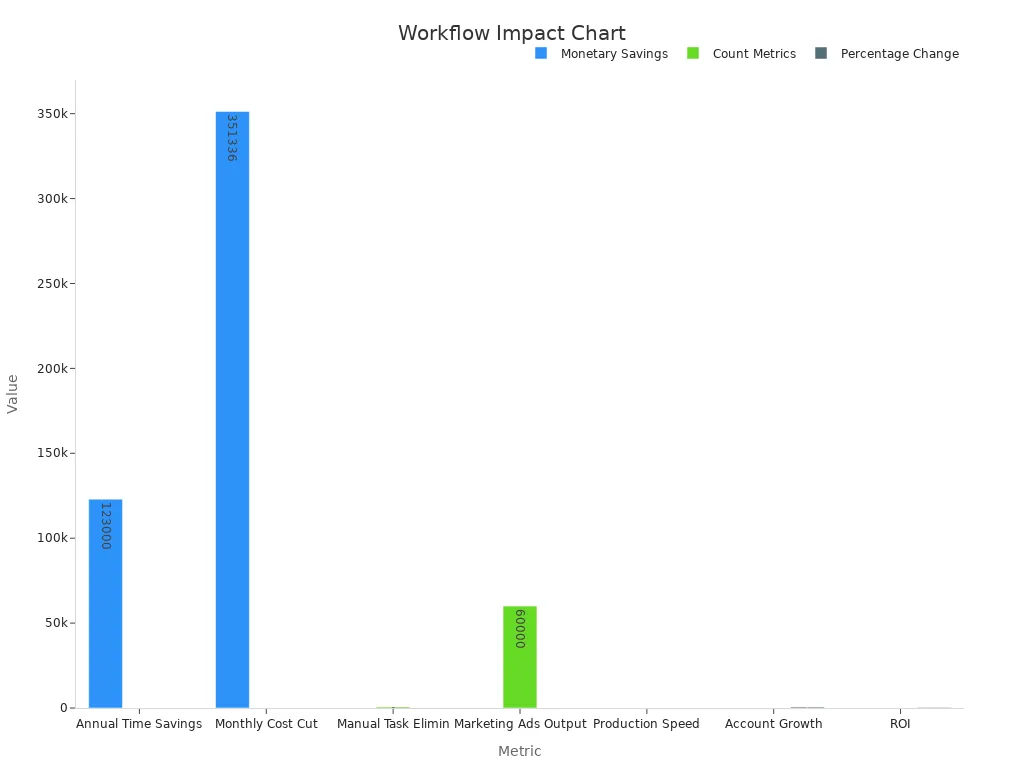
A workflow assessment helps businesses understand where to implement new systems. By mapping out each step in a process, teams can spot bottlenecks and unnecessary manual actions. This analysis reveals which tasks slow down operations or create errors. Companies that conduct workflow assessments often see dramatic results:
Metric | Measurable Impact |
|---|---|
Annual Administrative Time Savings | |
Monthly Cost Reduction | £351,336 saved monthly |
Manual Actions Eliminated | 657 manual tasks eliminated per month |
Marketing Creative Output | Tripled output (e.g., 60,000 ads) |
Production Speed | 40% faster completion |
Year-over-Year Account Growth | 517% increase |
Return on Investment (ROI) | Up to 346% ROI over three years |
A thorough workflow assessment, followed by the right business systems, leads to significant cost savings, higher productivity, and faster growth. Regular reviews and feedback ensure that each process remains efficient and continues to support business goals.
Core Business Systems

Modern business systems form the backbone of small business success. They organize daily activities, automate routine work, and provide valuable data for decision-making. Most small businesses use between 25 and 50 SaaS tools, but many do not fully use their features. By focusing on core systems in marketing, communication, and operations, companies can unlock greater efficiency and growth.
Marketing
Marketing systems help businesses attract, nurture, and convert leads. They track campaign performance, automate outreach, and keep marketing efforts on target.
Lead Management
Lead management systems organize potential customers and guide them through the sales funnel. Companies that integrate data across marketing and sales functions see up to a 15% increase in revenue growth. CRM platforms automate lead tracking, scoring, and follow-up, which prevents leads from slipping through the cracks. Salesforce data shows that 79% of marketing leads fail to convert without proper nurturing. Automated workflows and analytics in content marketing systems and email marketing systems help teams focus on high-quality leads and improve conversion rates.
Tip: Track key metrics such as website traffic, lead conversions, and customer acquisition cost to measure lead management success.
Social Media
Social media tools schedule posts, monitor engagement, and analyze campaign results. These systems help businesses reach wider audiences and build brand awareness. By tracking click-through rates and engagement, teams can adjust strategies for better results. Consistent use of social media platforms supports lead generation and strengthens customer relationships.
Communication
Effective communication systems keep teams connected and customers informed. They reduce misunderstandings and improve response times.
Team Collaboration
Team collaboration tools, such as Google Workspace and Office 365, support file sharing, project management, and real-time messaging. Communication audits and structured workshops improve clarity and reduce errors. Performance management systems track progress and encourage accountability. Companies that use these systems report fewer mistakes and better teamwork.
Customer Support
Client communication systems manage customer inquiries, support tickets, and feedback. Automated responses and organized records ensure timely and accurate service. Clear communication reduces errors and builds trust with clients. Case studies show that structured communication systems lower error rates and improve customer satisfaction.
Operations
Operations systems streamline inventory and order processing, which boosts efficiency and profitability.
Inventory
Inventory management systems track stock levels, prevent stock-outs, and reduce shrinkage. Real-time updates and automated alerts help avoid overstocking and lost sales. Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) like SphereWMS improve inventory accuracy, optimize storage, and lower carrying costs. These systems also provide data for better demand planning and cost control.
Order Processing
Order processing systems automate order entry, fulfillment, and shipping. They reduce cycle times and errors, leading to higher perfect order rates. Real-time tracking and automated updates keep customers informed and satisfied. Companies that use these systems see improved order accuracy and faster delivery.
Note: Regularly review key performance indicators such as order cycle time, inventory turnover, and customer satisfaction to drive ongoing improvements.
Finance
Finance systems form a critical part of business systems for small businesses. These systems help owners manage money, track spending, and keep financial records accurate. By using digital tools, companies can save time and avoid costly mistakes. Two main areas stand out: invoicing and expense tracking.
Invoicing
Invoicing systems automate the process of billing customers. They create, send, and track invoices with minimal manual effort. This automation reduces the time needed to process each invoice. Many companies see fewer errors and avoid late payment fees. Early payment discounts become easier to manage, which improves cash flow. Real-time tracking gives business owners a clear view of outstanding payments.
Automated invoicing helps small businesses get paid faster and reduces the risk of missed payments.
Modern invoicing software often integrates with other business systems, such as ERP and accounting platforms. This integration boosts operational efficiency and ensures that all financial data stays up to date. For example, when a business uses software instead of manual processes, the average cost to process a report drops from $58 per report to about $5 per active user each month. The percentage of reports with errors also falls sharply, saving money on corrections.
Metric | Manual Process Cost/Time | Software Process Cost/Time |
|---|---|---|
Average time to complete report | 20 minutes | N/A |
Average cost to process report | $58 per report | ~$5 per active user/month |
Percentage of reports with errors | 20% | Significantly reduced |
Cost to correct errors | $52 per correction | Significantly reduced |
Total cost for 100 reports | $6,840 (processing + corrections) | Much lower due to automation |
Expense Tracking
Expense tracking systems help businesses monitor spending and control costs. These tools record every purchase and categorize expenses automatically. Owners can see where money goes and spot trends quickly. Real-time tracking improves financial visibility and helps with budgeting.
Business systems that include expense tracking reduce the risk of missing receipts or misclassifying expenses. They also make it easier to prepare for tax season. Integration with accounting software means that all records stay organized and easy to access. Companies that use these systems often find that they save money by catching errors early and avoiding duplicate payments.
Tip: Regularly reviewing expense reports helps businesses find savings and improve their bottom line.
Finance systems, as part of a larger set of business systems, support better decision-making and long-term growth. By automating routine tasks, minimizing errors, and providing clear financial data, these systems give small businesses a strong foundation for success.
Building Small Business Systems
Creating effective small business systems requires a clear plan and a focus on simplicity. Every organization can benefit from a step-by-step approach that ensures consistency, efficiency, and growth. The following sections outline how to build strong systems that support daily operations and long-term success.
SOPs
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) form the foundation of any reliable system. SOPs document each process in detail, making it easy for employees to follow best practices. When an organization uses SOPs, it gains several advantages:
SOPs create valuable business assets. Investors see companies with documented procedures as more stable and predictable.
They allow rapid scaling. Teams can launch new products or services faster and increase profit margins.
SOPs ensure consistency. Customers receive the same high-quality experience every time, which strengthens the brand.
They reduce labor costs by streamlining repetitive tasks.
SOPs improve efficiency. Employees know exactly what to do, which increases productivity and reduces errors.
Documenting SOPs saves time and prevents mistakes. Employees do not lose track of steps or forget client requests. Even small teams benefit from having clear instructions, especially when onboarding new staff.
A well-known example is McDonald's. The company uses detailed SOPs for everything from food preparation to customer service. This systemization leads to fewer errors, less waste, and higher productivity. McDonald's can open new locations quickly because every process is standardized. The franchise model depends on these procedures, which support high profit margins and global brand consistency.
Assigning Roles
Assigning clear roles ensures that everyone in the organization knows their responsibilities. This step prevents confusion and helps teams work together smoothly. When building small business systems, leaders should:
Define each role and its main tasks.
Match employees' skills to the right responsibilities.
Set clear expectations for performance and accountability.
Companies with strong training programs see 24% higher profit margins than those without structured development plans. Active leadership involvement increases employee buy-in by 45%. When leaders communicate roles and expectations clearly, organizations report 23% higher success rates in operational improvement initiatives.
Tip: Use a simple table to outline roles and responsibilities for each process. This makes it easy to track progress and identify gaps.
Role | Main Responsibilities | Key Performance Indicators |
|---|---|---|
Process Owner | Oversees process, updates SOPs | Process efficiency, error rate |
Team Member | Follows SOPs, reports issues | Task completion, accuracy |
Supervisor | Monitors performance, trains | Productivity, training hours |
Organizations that systematically track progress are twice as likely to achieve their improvement goals. Continuous improvement efforts lead to 20-30% better performance across key metrics compared to competitors.
Choosing Tools
Selecting the right tools is essential for building scalable and affordable systems. Technology should support the process, not complicate it. When choosing tools, consider the following steps:
Select vendors with expertise in your industry. This ensures the tools fit your business needs.
Optimize internal processes before adopting new technology. Technology cannot fix broken workflows.
Plan data migration carefully. Make sure new tools work with your existing systems.
Integrate third-party services, such as G Suite or Salesforce, to centralize business tools and avoid data duplication.
Collect user feedback after deployment. This helps identify improvements and additional needs.
Provide ongoing support and maintenance. Regular updates keep systems running smoothly.
Align tool functionality with business goals and key performance indicators.
Start with a proof of concept if possible. Test the value of new tools before full-scale adoption.
Use AI technologies to automate routine tasks, forecast needs, and improve decision-making.
78% of business leaders see a positive impact on productivity from automation. Automation also leads to higher job satisfaction and faster decision-making.
Affordable, cloud-based solutions help small businesses scale without large upfront costs. For example, integrating automation tools allows 82% of sales teams to focus more on client relationships. Finance staff make faster decisions, and IT leaders report a 50% reduction in manual task time.
Choosing the right tools and documenting every process helps organizations achieve better resource utilization, lower costs, and improved customer satisfaction. Business Process Reengineering can reduce process costs by 75% and cycle times by 65%. Kaizen and Total Quality Management also deliver significant cost and quality improvements.
Keep systems simple and scalable. Start with basic tools and add features as the business grows.
Implementing Business Systems
Training
Effective training ensures that staff can use new business systems with confidence. Companies often choose a mix of instructor-led sessions, online modules, and blended learning. Many small businesses use learning management systems (LMS) to deliver training. Over 80% of companies rely on LMS platforms because they support both in-person and virtual learning. Research shows that when companies invest in technology-specific training, employees adopt new systems faster and productivity rises. Training should match the technology in use. For example, if a company adopts cloud-based automation tools, training should focus on computer literacy and technical skills.
Tip: Tailored training programs help employees understand both the technical and process changes. This approach prepares them for their roles and reduces stress.
Companies see better results when they provide hands-on practice and coaching before launching a new system. Employees gain confidence and can apply new skills right away. Ongoing support and refresher sessions help maintain high performance and prevent skill gaps.
Rollout
A smooth rollout sets the stage for successful system adoption. Leaders should plan each step, from initial testing to full deployment. Rigorous system testing before launch helps identify issues early. Data migration must preserve data integrity to avoid problems. Many companies use pilot programs to test new systems in a controlled environment. This approach allows teams to gather feedback and make improvements before a company-wide rollout.
Key steps for a successful rollout include:
Set clear expectations and communicate the rollout plan to all staff.
Monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) such as usage rates and error rates.
Gather user feedback to spot areas for improvement.
Adjust the system based on real-world usage and feedback.
Automation and cloud-managed IT solutions make rollouts easier. These tools allow for quick updates, remote access, and scalable deployment. Regular audits and reviews help maintain quality and adaptability.
Overcoming Resistance
Change can create uncertainty among staff. Leaders must address resistance to ensure smooth adoption. Involving employees from the start increases success rates. Creating cross-functional teams and feedback loops helps employees feel heard. Open forums and transparent communication build trust and alignment.
A phased approach to change works best. Incremental improvements allow employees to adjust gradually. Comprehensive training and ongoing support address skill gaps and reduce fear. Celebrating small wins boosts morale and builds momentum.
Note: Tracking KPIs like engagement and satisfaction scores helps leaders identify resistance early. Proactive support and targeted interventions keep adoption on track.
Companies that manage resistance well see higher consistency, better employee performance, and lower operational costs. Standardized processes and clear expectations lead to reliable results and easier scaling as the business grows.
Maintaining Systems
Consistency
Consistency forms the backbone of any successful business system. When teams follow the same steps every time, they reduce errors and deliver reliable results. Regular monitoring of maintenance metrics helps keep systems running smoothly. The table below shows important metrics that support long-term benefits:
Metric Name | Definition / Formula | Significance for Long-term Benefits |
|---|---|---|
Total operational time ÷ Total number of breakdowns | Higher MTBF means longer equipment uptime, indicating reliability and fewer disruptions. | |
Mean Time to Repair (MTTR) | Average time to repair equipment after failure | Lower MTTR reduces downtime, improving system availability and operational continuity. |
Number of pending work orders ÷ Total number of work orders | High backlog signals maintenance delays; managing backlog improves responsiveness and reduces downtime. | |
(Number of PM tasks completed on schedule ÷ Total number of PM tasks) × 100 | Indicates adherence to preventive maintenance schedules, reducing failures and extending equipment life. | |
Equipment Downtime | (Total downtime ÷ Total available production time) × 100 | Measures non-operational time; reducing downtime increases productivity and lowers costs. |
Availability × Performance × Quality | Provides a comprehensive view of equipment productivity and maintenance effectiveness, guiding improvements. |
By tracking these metrics, businesses can streamline operations and ensure that every process remains effective over time.
Review
Regular review stands as a key driver for ongoing improvement. Small businesses that schedule periodic reviews, internal audits, and feedback sessions see better alignment between daily activities and strategic goals. These reviews help teams spot inefficiencies and adapt to changing needs. Many organizations use the PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle or ISO 9001 standards to guide their review process. This approach supports compliance, identifies new opportunities, and builds a culture of continuous quality improvement.
Periodic reviews also help businesses collect feedback, analyze performance, and make evidence-based changes. Companies that commit to regular reviews experience lower turnover, higher productivity, and greater customer satisfaction. By embedding these reviews into their improvement plans, teams can adapt quickly and maintain high standards.
Feedback
Structured feedback keeps business systems healthy and responsive. Leading companies like Google and Adobe use real-time feedback through meetings and peer reviews. This approach improves performance evaluations and builds transparency. Adobe’s continuous feedback system, called Check-in, increased employee engagement and made reviews more collaborative. Google’s Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) framework uses regular feedback to set clear goals and track progress.
The table below highlights measurable impacts from structured feedback:
Measurable Impact Category | Description |
|---|---|
Participation Metrics | Employee engagement rates with feedback systems, including submission frequency and adoption. |
Schedule Quality Indicators | Improvements in schedule stability and better adherence to schedules. |
Employee Satisfaction Scores | Survey results on satisfaction related to work-life balance and perceived fairness. |
Operational Efficiency Gains | Time saved in schedule creation and administrative tasks. |
Business Impact Assessment | Reduced turnover, absenteeism, and increased employee productivity. |
ROI Analysis | Savings in staffing, recruitment, and overhead compared to implementation costs. |
Simple, repeatable feedback processes help every organization improve. Regular feedback sessions, clear communication, and open channels for suggestions keep teams engaged and systems up to date. This ongoing cycle of feedback and review ensures that each process continues to deliver value and supports long-term business growth.
Avoiding Pitfalls
Complexity
Many small businesses fall into the trap of overcomplicating their systems. When a process becomes too complex, employees struggle to follow steps and make mistakes. Simple systems work best. They allow teams to understand each process and complete tasks with confidence. Leaders should focus on clear instructions and easy-to-use tools. Overly detailed workflows can slow down progress and create confusion. A simple checklist or flowchart often works better than a long manual.
Tip: Start with the basics. Add new steps only when they solve a real problem or improve the process.
Team Buy-In
Team buy-in plays a key role in the success of any business system. Employees who feel involved and valued show more commitment to new processes. Research shows that higher emotional and intellectual buy-in leads to better performance for both individuals and organizations. Studies highlight several important factors:
Clear communication and trust between leaders and staff build engagement.
Empowering employees through shared decision-making increases buy-in.
Aligning personal and company goals helps everyone work toward the same outcome.
Peer coaching and shared accountability reinforce a culture of safety and support.
Psychological models explain that people need to find meaning in their work, feel responsible, and understand the results of their actions. When leaders address these needs, teams adapt to new processes more easily. A supportive environment, where staff can share feedback and learn from each other, leads to better results.
Updates
Regular updates keep business systems effective and relevant. Continuous improvement methods, such as Kaizen and Lean, focus on making small, data-driven changes to each process. These approaches encourage employees to suggest improvements and help track progress using key performance indicators. Consistent updates ensure that systems stay aligned with business goals and adapt to changes in the market.
Data consistency supports accurate reporting and better decisions.
Techniques like data validation and real-time monitoring help maintain reliable information.
Automation tools can analyze current processes and suggest ways to optimize them.
Collaboration among team members allows best practices to spread across the organization.
Leadership commitment and a culture that embraces change are essential for ongoing success. Regular reviews and updates prevent systems from becoming outdated or inefficient. By keeping each process simple, involving the team, and updating systems often, small businesses can avoid common pitfalls and achieve lasting growth.
Success Stories

Marketing System
A local bakery, Sweet Rise, struggled to attract new customers and manage its growing list of online orders. The owner decided to implement a customer relationship management (CRM) system and automated email marketing. The team used the CRM to track customer preferences and send personalized offers. After three months, Sweet Rise saw a 25% increase in repeat orders and a 15% boost in overall sales. The bakery also improved its website optimization, making it easier for customers to place orders and find promotions. The new marketing system helped the team respond faster to customer inquiries and track which campaigns worked best.
Note: Automated marketing tools can help small businesses reach more customers without extra staff.
Operations System
A small electronics retailer, TechNest, faced frequent inventory shortages and order delays. The management introduced an inventory management system that tracked stock levels in real time. Employees scanned products as they arrived and left the store, which reduced manual errors. Within six months, TechNest cut stockouts by 40% and improved order fulfillment speed by 30%. The system also generated weekly reports, allowing the team to adjust purchasing decisions quickly. Customers noticed faster delivery times and fewer out-of-stock messages, leading to higher satisfaction scores.
Metric | Before System | After System |
|---|---|---|
Stockouts per month | 15 | 9 |
Order fulfillment time | 4 days | 2.8 days |
Customer satisfaction | 78% | 91% |
Lessons Learned
These examples show that small business systems can deliver real results. Owners who invest in automation and clear processes see measurable improvements in efficiency and customer service. The key lessons include:
Start with the most urgent pain points, such as slow order processing or low customer retention.
Choose simple, scalable tools that fit the business size and budget.
Train staff and gather feedback to improve adoption and performance.
Review results regularly and adjust systems as the business grows.
Tip: Even small changes, like automating emails or tracking inventory, can lead to big gains in sales and customer loyalty.
Small business systems help teams work efficiently, support growth, and reduce owner dependency. Simple, scalable systems powered by technology make it easier to reach business goals. Readers can choose one area to systematize this week. Taking action now leads to smoother operations and stronger results.
Start building or improving a business system today for a more successful future.
FAQ
What is a business system in a small business?
A business system is a set of organized steps or tools that help a company complete tasks. These systems make work easier, faster, and more reliable. They often use technology to automate routine jobs.
How can a small business start building systems?
A small business can start by listing daily tasks. The owner should pick one process to improve. They can write clear steps, assign roles, and choose simple tools. Regular reviews help keep the system effective.
Do business systems cost a lot to set up?
Many business systems use affordable or free tools. Cloud-based software often charges monthly fees. Owners can start small and add features as the business grows. Careful planning helps avoid unnecessary costs.
Can business systems work for very small teams?
Yes, business systems help even the smallest teams. Clear steps and automation save time and reduce mistakes. Small teams can use checklists, templates, and simple apps to stay organized.
How often should a business update its systems?
A business should review its systems every few months. Regular updates keep processes efficient and fix problems early. Feedback from the team helps spot areas for improvement.
What are the risks of not having business systems?
Without systems, businesses may face confusion, errors, and wasted time. Teams might repeat work or miss important steps. Customers could receive poor service. Systems help prevent these problems.
Which business system should a company set up first?
Most companies start with systems that handle money or customers. Invoicing, expense tracking, and customer support often bring the fastest results. Owners should choose the area that causes the most trouble.
Do business systems replace employees?
Business systems do not replace employees. They help staff work better by removing boring or repetitive tasks. Employees can focus on important work, which helps the business grow.



