The Role of Business Automation in Modern Enterprises

Modern enterprises rely on business automation to thrive in a competitive landscape. This approach addresses operational inefficiencies by streamlining repetitive tasks and reducing errors, ultimately benefiting both clients and customers. For example, organizations save an average of $20 in labor costs for every document processed automatically. This optimization enables teams to complete financial processes 85 times faster while cutting task time by 30-40%. By improving workflows, businesses not only enhance productivity by 30% but also meet customer demands for faster, more reliable services. These optimization steps transform operations, making businesses more agile and focused on their clients' needs.
Key Takeaways
Business automation handles boring tasks, saving companies about $20 per document.
It boosts work speed by 30%, letting teams focus on big ideas.
Robots in automation cut mistakes and costs by doing tasks like data entry.
Smart AI tools give quick updates, helping businesses make better choices fast.
Automation makes customers happier with quicker service and personal attention.
Teaching workers and encouraging new ideas helps people accept automation.
Checking and improving automated systems keeps them working well for years.
Easy-to-use tools let anyone help with automation, speeding up digital changes.
Understanding Business Automation
Definition and Core Concepts
Business automation refers to the use of technology to streamline and optimize processes within an organization. It eliminates repetitive tasks, reduces errors, and enhances efficiency by leveraging tools such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and software applications. Automation enables businesses to focus on strategic goals by freeing employees from mundane activities. Centralized systems also improve data management, ensuring accuracy and consistency across operations.
Tip: Organizations that automate routine tasks often experience faster workflows and fewer bottlenecks, leading to higher productivity.
Types of Business Automation
Workflow Automation
Workflow automation simplifies complex processes by creating a sequence of automated steps. It ensures tasks are completed efficiently and consistently. For example, automating document approvals reduces delays and minimizes human intervention. Businesses report measurable increases in workflow speed due to the elimination of redundant tasks, allowing employees to focus on higher-value activities.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Robotic Process Automation uses software robots to perform repetitive tasks such as data entry, invoice processing, and customer support. RPA reduces labor costs and minimizes errors by handling high-volume operations with precision. Integrated workflows lead to fewer interruptions and faster project completions, improving profitability.
AI-Driven Automation
AI-driven automation incorporates advanced technologies like machine learning and predictive analytics to make intelligent decisions. It adapts to changing conditions and provides real-time insights for better strategies. By leveraging AI, businesses can improve inventory turnover, optimize resource utilization, and enhance customer experiences.
Metric Type | Description |
|---|---|
Inventory Turnover | Measures improvements in inventory management, such as faster turnover rates and better forecasting. |
Total Asset Turnover | Assesses sales profits relative to asset value, indicating efficiency of resource use. |
Accounting Operations | Includes metrics like error rates in data entry and efficiency in document management. |
Order Lead Times | Compares average lead times before and after automation implementation. |
Revenue Generated | Tracks revenue growth and cost savings post-automation. |
Cost of Investment vs. Revenue | Evaluates ROI by comparing net revenue increases to initial automation investments. |
The Growing Importance of Business Automation
Addressing Labor Shortages
Automation plays a critical role in addressing labor shortages by performing tasks that would otherwise require human intervention. Nearly 60% of surveyed businesses have implemented automation solutions to fill gaps in their workforce. This approach ensures continuity in operations and reduces dependency on manual labor.
Enhancing Operational Efficiency
Automated systems streamline processes, eliminate redundancies, and improve accuracy. For example, centralized data repositories cut down on duplicate work and allow for better data synchronization. Businesses report labor productivity increases of 30-50% with integrated processes, enabling employees to focus on strategic initiatives. Additionally, automation reduces defect rates by margins upward of 40%, positively impacting ROI and lowering rework costs.
Note: Studies show that 60% to 70% of work activities can be automated with current technology, highlighting significant potential for efficiency gains.
Benefits of Business Automation

Boosting Efficiency and Productivity
Automating repetitive tasks
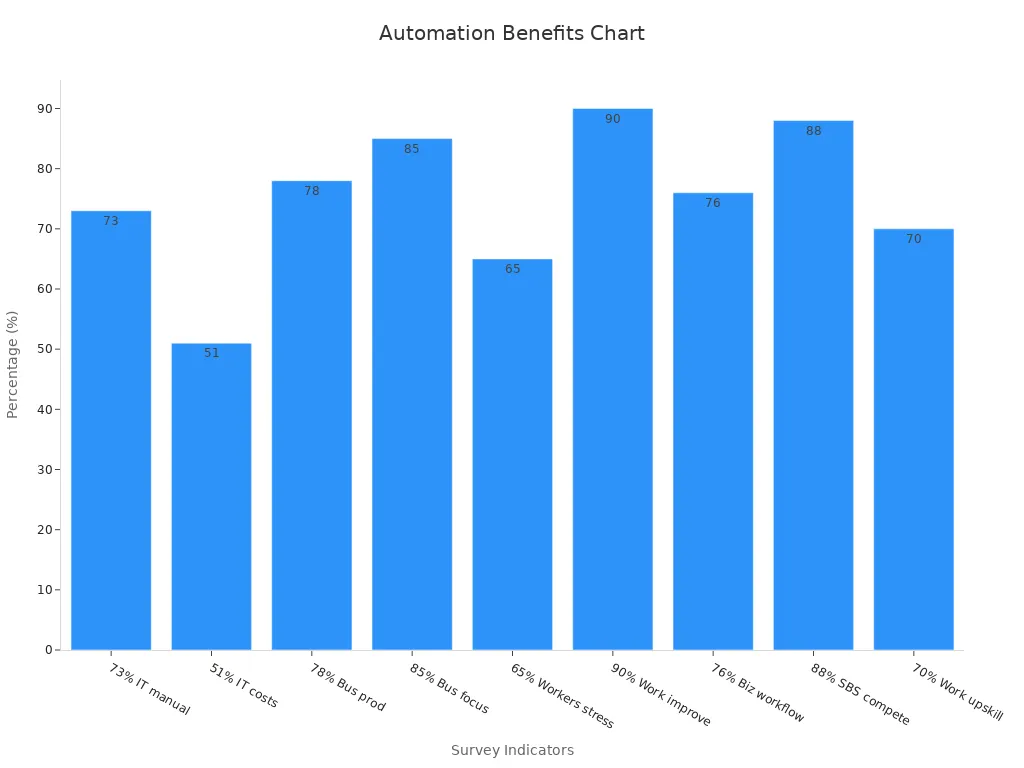
Business automation eliminates repetitive tasks, allowing employees to focus on strategic initiatives. Systems like Robotic Process Automation (RPA) handle high-volume operations such as data entry and invoice processing with precision. For example, 73% of IT leaders report that automation has reduced manual tasks by 50%. This shift not only accelerates workflows but also reduces employee stress, with 65% of knowledge workers feeling less burdened when automation handles routine activities.
Tip: Automating repetitive tasks improves worker productivity and enhances task completion rates, enabling teams to achieve more in less time.
Reducing human error
Automation minimizes human error by standardizing processes and ensuring consistency. Tools like AI-driven automation analyze data and make intelligent decisions, reducing the likelihood of mistakes. For instance, automated systems in finance have streamlined workflows and reduced errors, allowing professionals to focus on strategic tasks. Defect rates drop significantly, improving product reliability and customer satisfaction.
Cost Savings and Resource Optimization
Lowering operational costs
Business automation reduces labor costs by minimizing the need for human intervention in data processing tasks. Organizations can allocate resources to higher-value activities, enhancing overall efficiency. A McKinsey study highlights that automation can boost productivity by up to 30%, resulting in savings of approximately $200 billion in the manufacturing sector.
Key Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
Cost Savings | Automation reduces labor costs by minimizing the need for human resources in data processing tasks, allowing organizations to allocate resources to more valuable activities. |
Reduced Cost of Data Processing | Automating data pipelines decreases infrastructural costs associated with manual data processing, enabling businesses to scale operations without proportional cost increases. |
Maximizing resource utilization
Automation optimizes resource utilization by freeing employees from mundane tasks and enabling them to focus on strategic goals. For example, 85% of business leaders agree that automation allows employees to concentrate on high-impact initiatives. This approach enhances productivity and ensures better use of organizational resources.
Data-Driven Decision-Making
Leveraging analytics and AI
Automated systems leverage analytics and AI to provide actionable insights. These tools clean and normalize data, ensuring accuracy and reliability. For instance, Improvado streamlines data processing, reducing the need for manual intervention and enabling faster analysis. Organizations can identify trends and make smarter decisions, reducing errors and biases.
Evidence Description | Impact on Decision-Making |
|---|---|
Automation saves valuable time and minimizes the risk of human error. | Ensures that the data collected is reliable and up-to-date, enhancing the quality of decisions made. |
Improvado streamlines data processing by cleaning and normalizing data automatically. | Reduces the need for manual intervention, leading to faster and more accurate data analysis. |
Real-time insights for better strategies
Real-time insights empower businesses to react quickly to market changes and proactively address issues. Automated tools provide up-to-date information, enabling teams to refine strategies and improve outcomes. For example, 78% of business leaders report a positive impact on productivity due to automation, while 90% of knowledge workers agree that automation has significantly improved their work lives.
Note: Real-time insights enhance decision-making by providing accurate data, enabling businesses to stay ahead in competitive markets.
Enhancing Customer Experience
Faster service delivery
Business automation significantly accelerates service delivery by streamlining processes and reducing delays. Automated systems handle routine tasks like order processing, appointment scheduling, and customer inquiries with remarkable speed. For instance, chatbots powered by artificial intelligence (AI) respond to customer queries instantly, eliminating wait times. This efficiency ensures that customers receive timely assistance, enhancing their overall experience.
Companies that adopt automation in their operations often report noticeable improvements in customer satisfaction. A leading automation service provider in the industrials sector, for example, faced a 20% decline in customer satisfaction due to internal inefficiencies. By implementing automated workflows, the company improved its response times and regained market share. Faster service delivery not only boosts customer loyalty but also strengthens a business's competitive edge.
Tip: Automating repetitive tasks like data entry and ticket routing allows employees to focus on resolving complex customer issues, further improving service quality.
Personalized customer interactions
Automation enables businesses to deliver personalized experiences by leveraging customer data. AI-powered tools analyze purchase history, browsing behavior, and preferences to provide tailored recommendations. For example, automated tagging and AI-driven suggestions reduce human error, ensuring consistent and relevant interactions. Personalized product recommendations increase the likelihood of purchases and enhance customer satisfaction.
Customer relationship management (CRM) systems integrated with automation also play a vital role in personalization. These systems track customer interactions across multiple channels, creating a unified view of each customer. Companies that invest in automation for sales and CRM often see improved engagement levels. However, proper implementation is essential, as poorly executed automation can negatively impact service quality.
Note: Businesses that prioritize personalized interactions through automation often achieve higher customer retention rates and stronger brand loyalty.
Challenges in Business Automation
Financial Barriers
High initial investment
Implementing business automation often requires significant upfront costs. These expenses include purchasing software, upgrading infrastructure, and training employees. For many organizations, this financial burden can delay automation adoption. However, strategies like modular integration and leveraging cloud-based infrastructure can help mitigate these costs.
Strategy | Benefits |
|---|---|
Strategic Partnerships | - Shared infrastructure costs |
Modular Integration & Incremental Deployment | - Reduces upfront costs |
Leveraging Cloud and Scalable Infrastructure | - Reduced capital expenditure |
These approaches allow businesses to spread financial investments over time, making automation more accessible.
Balancing costs and ROI
Organizations often struggle to balance the costs of automation with the expected return on investment (ROI). While automation promises long-term savings, the initial implementation phase may not yield immediate results. Businesses must carefully evaluate potential benefits, such as increased efficiency and reduced labor costs, against the financial risks. Conducting pilot tests and setting measurable goals can help ensure a positive ROI.
Resistance to Change
Employee concerns and job security
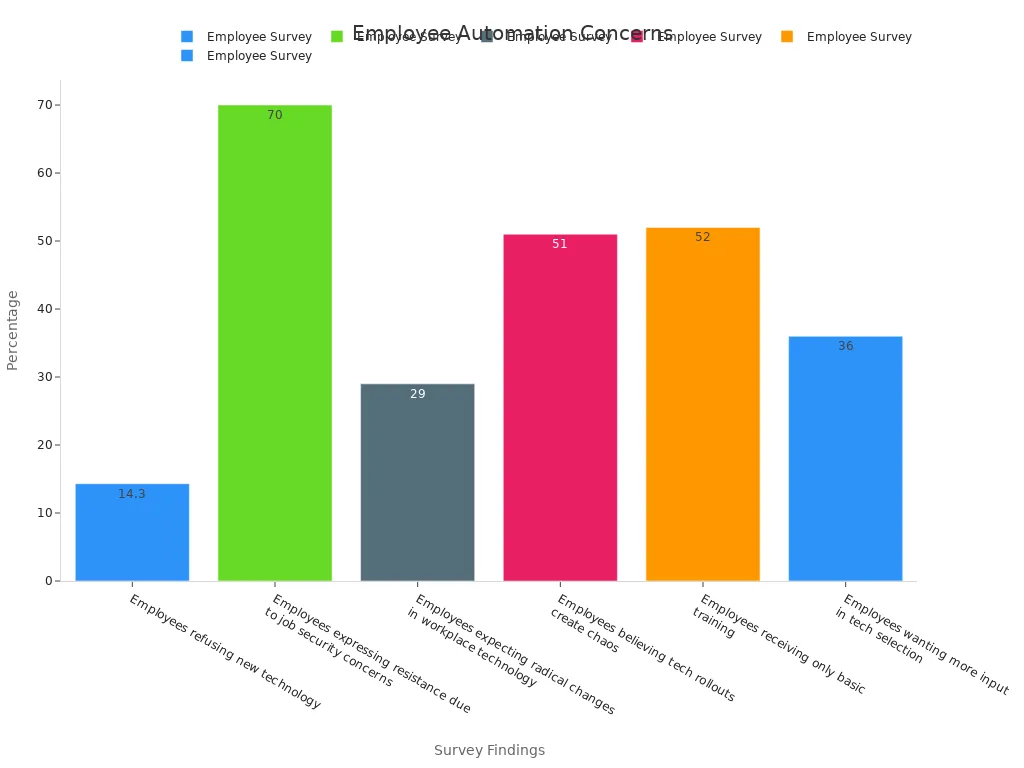
Automation can create anxiety among employees, particularly regarding job security. Surveys reveal that nearly 70% of employees express concerns about losing their jobs due to automation. Additionally, 1 in 7 employees refuses to adopt new technology, fearing workplace disruptions.
Finding | Statistic |
|---|---|
Employees refusing new technology | 1 in 7 |
Employees expressing resistance due to job security concerns | Nearly 70% |
Employees expecting radical changes in workplace technology | 29% |
Employees believing tech rollouts create chaos | 51% |
Employees receiving only basic training | 52% |
Employees wanting more input in tech selection | 36% |
Tip: Transparent communication and involving employees in the decision-making process can alleviate these concerns.
Overcoming organizational inertia
Resistance to change is not limited to employees. Organizations often face inertia when adopting new technologies. Leaders may hesitate to disrupt established workflows, fearing short-term losses. To overcome this, businesses should foster a culture of innovation and provide comprehensive training programs. Empowering employees with the skills to use automation tools effectively can ease the transition.
Integration and Compatibility Issues
Aligning with existing systems
Integrating new automation systems with legacy infrastructures presents significant challenges. Approximately 80% of organizations still rely on outdated systems, which complicates compatibility with modern tools. Legacy systems often lack the flexibility needed for seamless integration, leading to operational inefficiencies.
Legacy systems may not be compatible with modern RPA tools, leading to integration difficulties.
Data accessibility issues arise when RPA bots need to access data from various systems with strict controls.
A multinational corporation successfully integrated AI into its existing CRM system by creating a compatibility layer, ensuring smooth operations.
Ensuring data security and compliance
Automation introduces new risks related to data security and regulatory compliance. Automated systems often handle sensitive information, making them attractive targets for cyberattacks. Businesses must implement robust security measures, such as encryption and access controls, to protect data. Additionally, compliance with industry regulations, such as GDPR or HIPAA, is essential to avoid legal penalties. Upgrading network infrastructure and conducting regular audits can help address these challenges effectively.
Skill and Knowledge Gaps
Training employees for new tools
Adopting business automation requires employees to learn how to use new tools effectively. Many workers face challenges when transitioning to automated systems, especially if they lack prior experience with similar technologies. Training programs play a critical role in addressing this gap. These programs should focus on building familiarity with automation tools, such as Robotic Process Automation (RPA) software or AI-driven platforms.
Organizations that invest in comprehensive training see better results. Hands-on workshops, interactive tutorials, and role-specific training modules help employees gain confidence in using automation tools. For example, companies that provide scenario-based training enable workers to apply their knowledge in real-world contexts. This approach not only improves skill retention but also reduces the time needed to adapt to new systems.
Tip: Offering ongoing support, such as access to help desks or peer mentoring, ensures employees can troubleshoot issues as they arise.
Additionally, businesses should tailor training to different learning styles. Visual learners benefit from video tutorials, while kinesthetic learners thrive in practical, hands-on sessions. By addressing diverse needs, organizations can ensure that all employees, regardless of their background, feel equipped to handle automation technologies.
Bridging technical and non-technical expertise
Automation projects demand a blend of technical and non-technical skills. Workers must understand how to operate advanced tools while also excelling in areas like communication and teamwork. This combination ensures smooth collaboration between humans and machines.
The shift toward digital work environments highlights the need for multi-talented employees. Workers who can bridge technical and non-technical expertise are better equipped to manage automation projects. For instance:
Updated skills that combine technical knowledge with soft skills, such as emotional intelligence, are increasingly important.
Early career professionals often prioritize developing non-technical skills like teamwork and communication, which are essential for automation success.
Reskilling initiatives that focus on human capital development play a crucial role in preparing employees for automation.
Organizations should create integrated training programs that address these needs. For example, pairing technical workshops with sessions on leadership or problem-solving fosters well-rounded skill development. This approach helps employees adapt to the evolving demands of automated workplaces.
Note: Bridging skill gaps not only enhances individual performance but also strengthens team dynamics, ensuring automation projects achieve their full potential.
By prioritizing both technical and non-technical expertise, businesses can build a workforce capable of thriving in an automated future.
Strategies for Successful Business Automation
Identifying Automation Opportunities
Pinpointing repetitive tasks
Identifying repetitive tasks is the first step in implementing automation effectively. These tasks often consume valuable time and resources without adding significant value. For example, processes like data entry, invoice generation, and email responses are ideal candidates for automation. Proven methodologies such as Lean and Six Sigma help organizations streamline these workflows. A retail chain, for instance, used Lean principles to optimize inventory management, reducing excess stock and improving efficiency.
Organizations should conduct a thorough audit of their operations to uncover bottlenecks and redundancies. Tools like process mapping and time-tracking software can provide insights into areas where automation can make the most impact. By focusing on repetitive tasks, businesses can free up employees to concentrate on strategic initiatives, enhancing overall productivity.
Prioritizing high-impact areas
After identifying repetitive tasks, businesses should prioritize areas that offer the highest return on investment. High-impact areas often include customer service, supply chain management, and financial operations. For example, an e-commerce platform improved customer satisfaction by automating its chatbot system, leading to faster response times and higher engagement.
Using frameworks like Kaizen, organizations can continuously refine their processes to maximize impact. A technology startup, for instance, enhanced its employee onboarding process through automation, ensuring consistent training and faster integration of new hires. Prioritizing high-impact areas ensures that automation delivers measurable business improvements while aligning with strategic goals.
Choosing the Right Tools
Evaluating software and platforms
Selecting the right automation tools requires careful evaluation of available software and platforms. Businesses should assess tools based on their functionality, ease of use, and compatibility with existing systems. Metrics such as test stability, automation coverage, and return on investment (ROI) provide valuable insights during the evaluation process.
Metric | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
Test Stability | Measures the percentage of consistent outcomes in test executions. | High stability enhances confidence in automation tools. |
Automation Coverage | Tracks the percentage of tasks automated within a framework. | High coverage indicates effective resource utilization. |
Return on Investment (ROI) | Quantifies financial benefits relative to costs. | Justifies the investment in automation tools. |
Organizations should also consider scalability and flexibility when choosing tools. Scalable solutions allow businesses to expand their automation efforts as they grow, while flexible tools adapt to changing needs. Regular reviews and benchmarking ensure that selected tools remain effective over time.
Ensuring scalability and flexibility
Scalability and flexibility are critical for long-term success in automation. Scalable tools accommodate growth without requiring significant reconfiguration, while flexible solutions adapt to evolving business requirements. For instance, cloud-based platforms offer scalable infrastructure that supports seamless integration with other systems.
Businesses should involve stakeholders in the decision-making process to ensure alignment with organizational goals. Cross-referencing metrics with other testing artifacts provides a holistic view of tool performance, helping teams make informed decisions. By prioritizing scalability and flexibility, organizations can future-proof their automation strategies.
Employee Training and Engagement
Upskilling teams
Employee training is essential for the successful adoption of automation technologies. Upskilling programs equip teams with the knowledge and skills needed to operate new tools effectively. Research shows that 94% of employees are more likely to stay with companies that invest in their career development. Additionally, upskilling reduces turnover by as much as 50%, fostering a more stable workforce.
Outcome/Statistic | Description |
|---|---|
Lower Turnover | Upskilling reduces turnover by up to 50% when employees feel supported. |
Retention | 94% of employees stay longer at companies that invest in their development. |
Organizations should design training programs that cater to different learning styles. Hands-on workshops, video tutorials, and scenario-based exercises help employees gain confidence in using automation tools. Recognizing and rewarding training achievements further motivates teams to embrace new technologies.
Fostering a culture of innovation
A culture of innovation encourages employees to view automation as an opportunity rather than a threat. Transparent communication about the benefits of automation helps alleviate concerns about job security. Celebrating small wins, such as successful pilot projects, builds morale and reinforces the value of automation.
Engaging employees early in the process fosters cross-functional buy-in, ensuring smoother implementation. Assigning ownership of automation initiatives to specific teams or individuals enhances accountability and drives results. By fostering a culture of innovation, businesses can create an environment where employees actively contribute to the success of automation efforts.
Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
Setting measurable KPIs
Continuous monitoring ensures that business automation delivers consistent results. Setting measurable Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) allows organizations to track progress and identify areas for improvement. KPIs act as benchmarks, helping teams evaluate whether automation initiatives meet their goals. For example, tracking metrics like task completion time, error rates, and cost savings provides a clear picture of automation's impact.
Organizations should align KPIs with their strategic objectives. For instance, a company focused on customer satisfaction might monitor Net Promoter Scores (NPS) to gauge the effectiveness of automated customer service tools. Similarly, businesses aiming to improve operational efficiency could measure defect rates or cycle times. These metrics provide actionable insights, enabling teams to make data-driven decisions.
Methodology | Description | Performance Metrics |
|---|---|---|
Kaizen | Focuses on continuous, incremental improvement in processes. | Customer Satisfaction Scores (NPS) |
Six Sigma | Aims to reduce defects and improve quality through data-driven approaches. | Employee Engagement Metrics |
Lean | Seeks to maximize value by minimizing waste in processes. | Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) |
By adopting methodologies like Kaizen, Six Sigma, and Lean, businesses can refine their KPIs over time. These approaches emphasize small, consistent improvements, ensuring that automation efforts remain aligned with organizational goals.
Tip: Regularly reviewing KPIs helps businesses adapt to changing market conditions and maintain a competitive edge.
Refining processes over time
Automation is not a one-time solution. Businesses must refine their processes continuously to maximize the benefits of automation. Regular audits help identify inefficiencies and uncover opportunities for improvement. For example, analyzing workflow data can reveal bottlenecks that slow down operations. Addressing these issues ensures that automated systems operate at peak efficiency.
Feedback from employees and customers plays a crucial role in process refinement. Employees often provide valuable insights into how automation tools affect their daily tasks. Similarly, customer feedback highlights areas where service delivery can improve. Incorporating this input ensures that automation aligns with user needs and expectations.
Organizations should also leverage performance data to guide their refinement efforts. Metrics like employee engagement scores and defect rates highlight areas that require attention. For instance, a company using Six Sigma principles might focus on reducing error rates in automated billing systems. This approach not only improves accuracy but also enhances customer trust.
Note: Continuous refinement ensures that automation evolves alongside business needs, delivering long-term value.
By combining regular monitoring with feedback and data analysis, businesses can create a cycle of improvement. This proactive approach ensures that automation remains a powerful tool for achieving strategic objectives.
Trends Shaping the Future of Business Automation

AI and Machine Learning Integration
Predictive analytics and decision-making
AI and machine learning are revolutionizing predictive analytics by enabling businesses to make data-driven decisions with greater accuracy. Machine learning models, trained on historical data, optimize performance and predict outcomes for new scenarios. This capability allows organizations to anticipate customer behavior and market trends in real time. For instance:
Machine learning enhances predictive analytics by providing actionable insights into customer preferences.
Businesses use these insights to design personalized marketing campaigns and improve supply chain efficiency.
Industries such as retail and logistics have seen significant transformations through these applications.
By integrating AI into decision-making processes, companies can respond proactively to challenges and opportunities, ensuring a competitive edge in dynamic markets.
Autonomous systems and workflows
Autonomous systems powered by AI are streamlining workflows across industries. These systems adapt to changing conditions without human intervention, ensuring consistent performance. For example, AI-driven tools in manufacturing monitor equipment health and predict maintenance needs, reducing downtime. Similarly, autonomous customer service platforms handle routine inquiries, freeing employees to focus on complex tasks. These advancements demonstrate how AI fosters efficiency and reliability in business operations.
Hyperautomation
Combining multiple automation tools
Hyperautomation involves the integration of multiple automation technologies to create seamless workflows. This approach combines tools like robotic process automation (RPA), AI, and machine learning to address complex business challenges. Case studies highlight its impact:
Area of Impact | Evidence |
|---|---|
HR | Automation Anywhere’s bots reduced contract processing time from days to hours, improving productivity. |
Back-Office Automation | Studies indicate a potential 30% or more reduction in operating costs through hyperautomation. |
Operations & Supply Chain | AI-enhanced forecasting can reduce forecast errors by 20–50%, leading to better inventory management. |
Predictive Maintenance | Companies using AI for predictive maintenance reported a 5–10X return on investment in maintenance savings. |
Hyperautomation enables businesses to achieve higher efficiency and cost savings by leveraging the strengths of diverse technologies.
Achieving end-to-end automation
End-to-end automation transforms entire processes, from initiation to completion, without manual intervention. This approach ensures consistency, reduces errors, and accelerates task completion. For example, AI-powered tools in supply chain management automate demand forecasting, inventory tracking, and order fulfillment. Businesses adopting end-to-end automation report improved operational efficiency and customer satisfaction, making it a cornerstone of modern enterprise strategies.
Personalization in Automation
Tailored marketing strategies
Personalization in automation allows businesses to deliver targeted marketing campaigns that resonate with individual customers. AI and machine learning analyze demographic, behavioral, and psychographic data to create meaningful customer segments. This segmentation enables tailored messaging that drives engagement and conversions. For instance:
Personalized emails generate six times higher transaction rates than generic ones.
AI-driven recommendation engines, projected to reach a market value of $12 billion by 2025, suggest products based on customer behavior.
Predictive analytics anticipates customer needs, ensuring timely and relevant content delivery.
These strategies enhance marketing efficiency and foster stronger customer relationships.
Adaptive customer service solutions
Automation also enhances customer service by providing adaptive solutions tailored to individual needs. AI-powered chatbots handle routine inquiries while maintaining a personal touch. Advanced tools like sentiment analysis detect customer emotions in real time, enabling businesses to respond empathetically. Key features include:
Feature | Description |
|---|---|
Customer Intelligence | A 360-degree view consolidates data from all touchpoints, resulting in significantly more personalized interactions. |
AI-Powered Sentiment Analysis | Real-time detection of customer emotions can increase loyalty by 61%, demonstrating the impact of personalized service. |
Intelligent Self-Service | AI software can handle a significant portion of routine inquiries while maintaining personalization. |
These innovations ensure consistent, high-quality service across all customer interactions, boosting satisfaction and loyalty.
Low-Code and No-Code Platforms
Empowering Non-Technical Users
Low-code and no-code platforms empower non-technical users by enabling them to create applications and automate processes without requiring advanced programming skills. These platforms use intuitive interfaces, such as drag-and-drop tools, to simplify development. This accessibility allows employees from various departments, often referred to as "citizen developers," to contribute to digital transformation efforts.
The growing demand for low-code solutions stems from the high costs associated with hiring technical professionals. Businesses can now leverage their existing workforce to develop functional tools, reducing dependency on specialized developers. For example, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in industries like retail, manufacturing, and professional services have embraced these platforms to streamline operations. This trend highlights the versatility and inclusivity of low-code technology.
Tip: Encouraging employees to explore low-code platforms fosters innovation and reduces bottlenecks in IT departments.
Source | Key Findings |
|---|---|
Forrester | 83% of large businesses appreciate low-code for its flexibility, 63% for speed, and 67% for process automation. |
Forrester | 80% of respondents agree that integrating low-code solutions frees developers' time for strategic projects. |
Gartner | Low-code platforms enable cost-effective digitization and reduce the need for expensive programmers. |
Quixy | Most low-code users are from small and medium-sized enterprises, with high adoption in retail, manufacturing, and professional services. |
Accelerating Implementation Timelines
Low-code and no-code platforms significantly reduce the time required to develop and deploy applications. Traditional software development often involves lengthy coding processes, extensive testing, and multiple iterations. In contrast, low-code platforms streamline these steps by providing pre-built templates and reusable components. This efficiency allows businesses to bring solutions to market faster, giving them a competitive edge.
Companies benefit from shorter implementation timelines in several ways. First, they can respond quickly to market changes or customer demands. Second, they reduce operational delays caused by IT backlogs. Finally, they save costs by minimizing the need for extensive development cycles. According to industry studies, 63% of businesses value low-code platforms for their speed, while 67% recognize their role in automating processes efficiently.
Key Advantages of Faster Implementation:
Rapid prototyping and deployment of applications.
Improved agility in adapting to business needs.
Enhanced collaboration between technical and non-technical teams.
The adoption of low-code platforms continues to grow, particularly among SMEs, due to their ability to accelerate digital transformation. By enabling faster implementation, these tools help businesses stay ahead in competitive markets.
Note: Organizations that prioritize low-code solutions often experience improved productivity and reduced time-to-market, making them a valuable asset in modern enterprises.
Business automation has become a cornerstone for driving efficiency, reducing costs, and fostering innovation in modern enterprises. Over 90% of workers report increased productivity due to automation, while 85% highlight improved team collaboration. These tools also enhance decision-making speed and accuracy, enabling businesses to adapt quickly to market demands. For instance, Vonage leveraged automation to unify customer data, cutting account provisioning time from four days to mere minutes. This transformation not only streamlined operations but also reduced errors.
To ensure long-term success, businesses must proactively address challenges such as employee resistance and integration complexities. Transparent communication and robust training programs can ease transitions and maximize the benefits of automation. By embracing these technologies, organizations position themselves for sustained growth and a competitive edge in an evolving marketplace.
FAQ
What is business automation?
Business automation uses technology to streamline processes, reduce manual tasks, and improve efficiency. It employs tools like AI, RPA, and workflow automation to optimize operations and enhance productivity.
How does automation benefit small businesses?
Automation helps small businesses save time and reduce costs. It simplifies repetitive tasks, improves accuracy, and allows employees to focus on strategic goals. Tools like low-code platforms make automation accessible for smaller teams.
Is automation expensive to implement?
Automation requires an initial investment, but modular solutions and cloud-based tools reduce costs. Businesses often see long-term savings through improved efficiency and reduced labor expenses.
Can automation replace human workers?
Automation complements human workers by handling repetitive tasks. It allows employees to focus on creative and strategic activities. While some roles may change, automation creates opportunities for upskilling and innovation.
What industries benefit most from automation?
Industries like manufacturing, retail, healthcare, and logistics gain significant advantages. Automation improves supply chain management, customer service, and operational efficiency across these sectors.
How can businesses overcome resistance to automation?
Transparent communication and employee involvement ease concerns. Training programs and showcasing benefits help employees adapt to new technologies. Fostering a culture of innovation encourages acceptance.
Are automated systems secure?
Automated systems require robust security measures like encryption and access controls. Regular audits and compliance with regulations ensure data protection and minimize risks.
What tools are best for automation beginners?
Low-code platforms and workflow automation tools are ideal for beginners. They offer user-friendly interfaces and require minimal technical expertise, making them accessible for non-technical users.



