Mastering Six Sigma Methodology for Effective Quality Control

Mastering Six Sigma gives organizations a powerful quality management strategy. Six Sigma relies on data-driven quality management to reduce defects and process variation. Teams use statistical tools like the Five Whys and design of experiments to improve Systems and prevent out-of-spec conditions. In manufacturing, Six Sigma methodology helps lower defect rates and increase output predictability. Hospitals apply the methodology to boost patient safety and efficiency. Six Sigma leads to higher customer satisfaction, more efficient Resources, and better results for both beginners and professionals.
Key Takeaways
Six Sigma is a data-driven approach that helps organizations reduce defects and improve quality.
The DMAIC framework—Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control—guides teams through structured process improvement.
Customer focus is essential; understanding customer needs leads to better products and services.
Data-driven decision-making enhances quality control and helps teams identify areas for improvement.
Teamwork is crucial; diverse teams foster collaboration and innovative solutions to quality challenges.
Continuous improvement is a core principle; organizations should regularly evaluate and enhance their processes.
Training and certification empower employees with the skills needed to implement Six Sigma effectively.
Successful Six Sigma implementation requires strong management support and clear communication throughout the organization.
Six Sigma Methodology Overview
What Is Six Sigma
Six sigma stands as a proven approach for improving quality in organizations. This methodology uses data and statistical analysis to identify and reduce defects. Teams apply six sigma to control process variation and achieve consistent results. The six sigma methodology focuses on measurable objectives and aligns improvement efforts with business goals. Companies in manufacturing, healthcare, finance, and retail use six sigma to deliver better products and services. By setting clear targets and using structured problem-solving, six sigma helps organizations meet customer expectations and industry standards.
Six sigma combines rigorous analysis with practical steps, making it accessible for teams at every skill level.
Key Principles
Six sigma relies on several key principles that guide quality improvement:
Customer focus: Teams prioritize understanding and meeting customer needs.
Data-driven decision making: Six sigma uses facts and figures to guide actions.
Process variation reduction: The methodology aims to minimize inconsistencies in outputs.
Accountability: Roles and responsibilities are clearly defined.
Continuous improvement: Six sigma encourages ongoing evaluation and enhancement of processes.
These principles align with industry standards such as ISO 9001. Many leading organizations integrate six sigma with ISO 9001 to boost efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction. Six sigma also emphasizes teamwork, empowering employees to contribute ideas and solutions.
Component | |
|---|---|
Clear Objective Setting | Establishes specific and measurable quality objectives aligned with business goals. |
Defining Processes and Accountability | Outlines key activities and assigns roles to ensure accountability in maintaining quality standards. |
Establishing Inspection Procedures | Details testing and inspection methods, and corrective actions for deviations. |
Continuous Monitoring and Improvement | Incorporates regular data review and improvement mechanisms, aligning with Lean Six Sigma principles. |
DMAIC and DMADV Methodologies | Emphasizes structured approaches for defining quality objectives and controlling processes. |
Data-Driven Decision Making | Leverages data collection and statistical analysis for informed quality improvement decisions. |
Standardization | Helps stabilize outputs through clear guidelines and processes. |
Reducing Variation | Minimizes variations through standardized practices, achieving higher consistency in outputs. |
Eliminating Waste | Identifies non-value-adding activities, leading to waste reduction and streamlined operations. |
Enhancing Quality | Ensures products/services meet or exceed customer expectations through adherence to quality standards. |
Benefits
Organizations that adopt six sigma experience measurable improvements. Six sigma increases resource utilization by identifying bottlenecks and removing redundancies. Companies report higher return on investment; for example, GE saved over $12 billion in five years after implementing six sigma. Customer satisfaction rises as teams deliver consistent, high-quality products. Six sigma also strengthens organizational culture, promoting continuous improvement and employee empowerment.
Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
Improved Resource Utilization | Efficient use of human, material, and time resources by identifying bottlenecks and redundancies. |
Higher Return on Investment (ROI) | Significant savings reported by companies, e.g., GE saved over $12 billion in five years. |
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction | Consistent high-quality output reduces complaints and increases customer loyalty. |
Data-Driven Decision Making | Utilization of statistical tools for analytics and evidence-based decisions. |
Strengthened Organizational Culture | Promotes continuous improvement and employee empowerment. |
Competitive Advantage | Enhances brand perception and market credibility through certifications. |
Better Compliance | Ensures adherence to industry standards and regulations. |
Scalability | Adaptable methodology for businesses of all sizes, including small and global enterprises. |
Six sigma improves customer satisfaction by focusing on customer needs and enhancing service quality. For example, a retail chain increased satisfaction scores by 20% after using six sigma to address complaints. Bank of America saw a 10.4% rise in customer satisfaction and a 24% drop in customer issues after implementing six sigma. American Express improved its renewal card process, leading to better customer experiences.
Core Concepts of Six Sigma
Customer Focus
Customer focus stands at the heart of six sigma. Teams begin every project by understanding what customers expect from products or services. They gather feedback, study complaints, and analyze satisfaction scores. This approach helps organizations set clear goals that match customer needs. Six sigma encourages every employee to participate in quality improvement, which builds a culture of continuous improvement. When teams listen to customers, they find ways to reduce defects and deliver better results.
Organizations that use customer focus see measurable improvements in quality and efficiency. Employees feel more involved, and customers receive products that meet or exceed expectations.
Explanation | |
|---|---|
Understanding Customer Needs | Teams identify and meet customer expectations. |
DMAIC Process | The systematic process defines problems and implements improvements. |
Continuous Improvement Culture | Employees help solve quality issues and improve efficiency. |
Quality Management | Six sigma reduces process variation and defects. |
Employee Involvement | Employees take ownership of quality improvement. |
Competitive Edge | High-quality products help organizations stand out. |
Data and Measurement
Six sigma relies on data and measurement to guide decisions. Teams collect both qualitative and quantitative data. Qualitative data includes observations and descriptions. Quantitative data covers numbers like defect rates and satisfaction scores. Teams use statistical techniques to analyze this data. They choose tools based on the type of data they collect.
Types of Data Used in Six Sigma:
Qualitative Data: Observations and descriptions.
Quantitative Data: Numbers and metrics.
Effective Measurement Tools:
Identify the type of data.
Use software tools for analysis.
Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
Statistical analysis for six sigma projects. | |
Microsoft Excel | Organizes data and performs basic statistics. |
JMP | Visualizes and analyzes data. |
R / Python | Advanced data analysis techniques. |
Teams use these tools to find patterns, measure progress, and make improvements. Data-driven decisions help organizations reduce errors and improve quality.
Process Variation
Process variation affects the consistency of products and services. Six sigma aims to reduce this variation. Teams study data to find where processes change and why defects occur. They use statistical methods to analyze variation and control it.
Statistical Method | Description |
|---|---|
Summarizes data with mean, median, mode, range, and standard deviation. | |
Hypothesis Testing | Determines if differences are statistically significant. |
Regression Analysis | Finds relationships between variables. |
Design of Experiments (DOE) | Tests changes to improve processes. |
Statistical Process Control (SPC) | Uses control charts to monitor and control variation. |
Six sigma methodology uses these methods to keep processes stable. When teams control variation, they produce consistent results and fewer defects. This leads to higher customer satisfaction and better performance.
Teamwork
Teamwork plays a vital role in the success of six sigma projects. Every six sigma initiative depends on the combined efforts of employees who share a common goal. Teams work together to solve problems, share ideas, and develop solutions that improve quality. When employees collaborate, they build trust and encourage open communication. This environment helps everyone feel valued and motivated to contribute.
Teams are an integral part of any successful Six Sigma implementation. Each milestone on the quality journey involves teams and dedicated employees who are focused on developing best practices. These champions of change determine the best tactics to improve work functions by encouraging collaboration and cooperation. It is the interaction among these employees in their quest for excellence that makes the difference.
Six sigma teams often include members from different departments. Each person brings unique skills and perspectives. This diversity helps teams find creative solutions and address challenges from multiple angles. Leaders in six sigma methodology encourage team members to take ownership of their tasks. They support each other and celebrate achievements together.
The Six Sigma initiative is no different than other people involvement initiatives; it’s the work of the team members who ultimately determine the success of the project. I believe the data demonstrates that teams are critical to successful implementation.
Many organizations face challenges with employee engagement. Studies show that about 54% of respondents feel unappreciated at work, and 41% of that group feel unmotivated. Six sigma teams can help address this issue by recognizing contributions and fostering a sense of belonging. When employees feel appreciated, they become more committed to the project and strive for better results.
Six sigma methodology uses teamwork to drive continuous improvement. Teams meet regularly to review progress, discuss obstacles, and adjust strategies. They use data to guide decisions and measure success. Team members learn from each other and share best practices across the organization.
Key ways teamwork supports six sigma:
Encourages collaboration and open communication
Brings together diverse skills and viewpoints
Builds trust and motivation among employees
Supports problem-solving and innovation
Helps recognize and reward contributions
Drives continuous improvement through shared learning
Six sigma teams create a culture where everyone works toward common goals. They help organizations achieve higher quality, reduce defects, and improve customer satisfaction. Teamwork remains a cornerstone of six sigma success.
DMAIC Framework
DMAIC stands as the central improvement methodology within six sigma. Organizations use DMAIC to guide process improvement projects from start to finish. Each phase—Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control—offers a structured approach for reducing defects and enhancing quality. Teams follow DMAIC to identify problems, collect data, analyze root causes, implement solutions, and sustain improvements.
Define Phase
The Define phase sets the foundation for a successful six sigma project. Teams begin by clarifying the problem and outlining the project’s scope. They work together to ensure a shared understanding of the issues. This step helps everyone agree on what needs improvement.
Teams develop a clear problem statement. This statement describes the issue and its impact on the organization.
They define the scope of the project. Scope limits what the team will address and prevents distractions.
A project charter is created. The charter outlines objectives, expected outcomes, and roles. It also engages stakeholders and secures their support.
A well-defined project charter helps teams stay focused and measure progress. Stakeholders know what to expect, and everyone works toward the same goals.
By starting with a strong Define phase, organizations set clear goals and avoid confusion later in the project. This phase ensures that everyone understands the purpose and direction of the six sigma methodology.
Measure Phase
The Measure phase focuses on collecting data to understand the current process. Teams use measurement techniques to establish a baseline and identify areas for improvement. Accurate data helps teams make informed decisions and track progress.
Technique | Description |
|---|---|
Teams monitor process stability over time by plotting data points and identifying variations. | |
Process Mapping | Teams visually represent a process to find bottlenecks and inefficiencies. |
Cause-and-Effect Diagrams | Analytical tools help teams identify potential causes for specific problems and break down complex issues. |
Teams also take these steps:
Establish performance indicators. These indicators show how well the process works.
Create a data collection plan. The plan explains what data to collect, how, and when.
Develop a baseline performance measure. This baseline shows the starting point before changes are made.
Teams that use effective measurement techniques can pinpoint problems and set realistic improvement targets.
The Measure phase gives organizations the facts they need to move forward. Reliable data supports the six sigma methodology and helps teams focus on the most important issues.
Analyze Phase
During the Analyze phase, teams use root cause analysis to find out why problems occur. They study the data collected in the Measure phase and look for patterns or trends. The goal is to identify the underlying causes of defects and process variation.
Tool Name | Description |
|---|---|
Teams graphically display potential reasons for a problem, showing causal links. | |
The 5 Whys Exercise | Teams use this root cause analysis technique to break down a problem to its origin. |
Graphical Analysis Tools | Visual representations help teams understand patterns and relationships in the data. |
Process Map Maturation | Teams create detailed maps of activities and decisions in a procedure. |
Pareto Charts / Pareto Principle | Teams prioritize and evaluate the importance of potential solutions to multiple issues. |
Failure Mode Effects Analysis (FMEA) | Teams identify failure points in a process and assess their severity. |
Statistical Process Control (SPC) | Teams monitor and control a process using statistical methods to improve it. |
Teams often use root cause analysis tools like the 5 Whys and cause-and-effect diagrams. These tools help break down complex problems and reveal the true source of defects. By focusing on data and analysis, teams avoid guessing and base decisions on evidence.
Root cause analysis leads to targeted solutions. Teams address the real issues instead of symptoms, which results in lasting improvements.
The Analyze phase empowers organizations to understand their processes deeply. By finding the root causes, teams can develop effective solutions and move closer to their improvement goals.
Improve Phase
The Improve phase marks a turning point in the dmaic process. Teams use this stage to put solutions into action and see real changes in their processes. They focus on ideas that address the root causes found in the Analyze phase. The goal is to reduce defects and make the process more efficient.
Teams often start by brainstorming possible solutions. They select the best ideas and test them through experiments or pilot projects. This careful approach helps them see what works before making big changes. For example, a team might change the order of steps in a manufacturing process to reduce errors. They measure the results to make sure the new method leads to fewer defects.
Testing solutions on a small scale helps teams avoid costly mistakes and learn quickly.
Organizations that use six sigma in the Improve phase often see strong results. They report financial benefits ranging from $174,000 to $1 million per project. These savings come from better performance and fewer mistakes. The Improve phase also encourages teams to share their findings with others, spreading good ideas across the company.
Key actions in the Improve phase include:
Generating and selecting solutions that target root causes
Running pilot tests to check if solutions work
Measuring the impact of changes on process performance
Adjusting solutions based on feedback and data
The Improve phase shows the power of six sigma and dmaic. By focusing on data and careful testing, teams can make lasting improvements that benefit the whole organization.
Control Phase
The Control phase helps organizations keep their gains after making improvements. Teams use this stage to make sure changes last and do not fade over time. They build systems to monitor the process and catch problems early.
A strong control plan is key to this phase. Teams work with project leaders and process owners to create a plan that fits the new process. They look for ways to automate measurements of important steps. If automation is not possible, they make sure data collection is simple and clear. Leaders add control checks to their regular routines, which keeps everyone accountable.
Steps to ensure sustainability in the Control phase:
Develop a control plan with the project team, including the project Champion and process owner.
Automate measurement systems of critical inputs where possible, or at least simplify and standardize the method to source data on critical inputs.
Incorporate control plan checks into leader standard work to drive accountability for actions and maintain improvements.
Teams use tools like control charts to watch for changes in the process. If they see a problem, they act quickly to fix it. Training and clear instructions help everyone follow the new process. Regular reviews keep the focus on quality and prevent old habits from returning.
The Control phase completes the dmaic cycle. It ensures that six sigma improvements stay in place and continue to deliver value. Organizations that follow this phase see long-term benefits and higher customer satisfaction.
Process Improvement in Action
Identifying Problems
Successful process improvement begins with identifying the right problems. Teams using six sigma look for signs that a process does not meet expectations. They rely on clear indicators to spot issues early. Common indicators include:
Cycle time: Measures how long it takes to complete a process from start to finish.
Defect rate: Shows the percentage of products or services that do not meet quality standards.
First pass yield: Tracks the percentage of items that pass through a process without needing rework.
Capacity utilization: Reveals how much of the available process capacity is being used.
Cost per unit: Calculates the average cost to produce one unit.
These indicators help teams focus their process improvement efforts where they matter most. By monitoring these metrics, organizations can quickly detect problems and set priorities for six sigma projects.
Reducing Defects
Reducing defects stands as a core goal of six sigma. Teams use process improvement tools to lower the number of errors and deliver better results. They measure defects per million opportunities (DPMO) to understand the current state and track progress. Statistical techniques, such as control charts and statistical process control (SPC), help teams maintain consistency and signal when changes are needed.
Evidence Description | Impact on Defects |
|---|---|
DPMO quantifies defects per million opportunities, establishing a baseline for process outcomes. | Lower DPMO indicates higher process sigma rating and improved reliability. |
Control charts track DPMO over time, signaling when interventions are needed. | Visual representation of process stability and improvement. |
General Electric's improvement from ~20,000 DPMO to under 10 DPMO. | Demonstrates significant defect reduction through systematic problem-solving. |
Lean six sigma uses real data to drive process improvement and reduce variation. The ultimate goal is to reach only 3.4 defects per million products, which reflects a very high standard of quality. Teams that use these methods see fewer mistakes and more reliable outcomes.
Enhancing Efficiency
Process improvement also aims to make operations faster and more efficient. Six sigma projects often lead to shorter cycle times, fewer errors, and better use of resources. Organizations have seen impressive results by applying these methods.
Metric | Improvement |
|---|---|
Reduction in Errors | 70% decrease in missing items on customer statements |
Improved Digital Channels | 88% reduction in defects in electronic platforms |
Faster Mortgage Processing | Cycle times reduced by 15 days |
Fraud Mitigation | 28% decrease in non-credit losses |
Financial Gains | Cumulative benefits exceeding $2 billion |
Customer Delight | 25% improvement in customer satisfaction metrics |
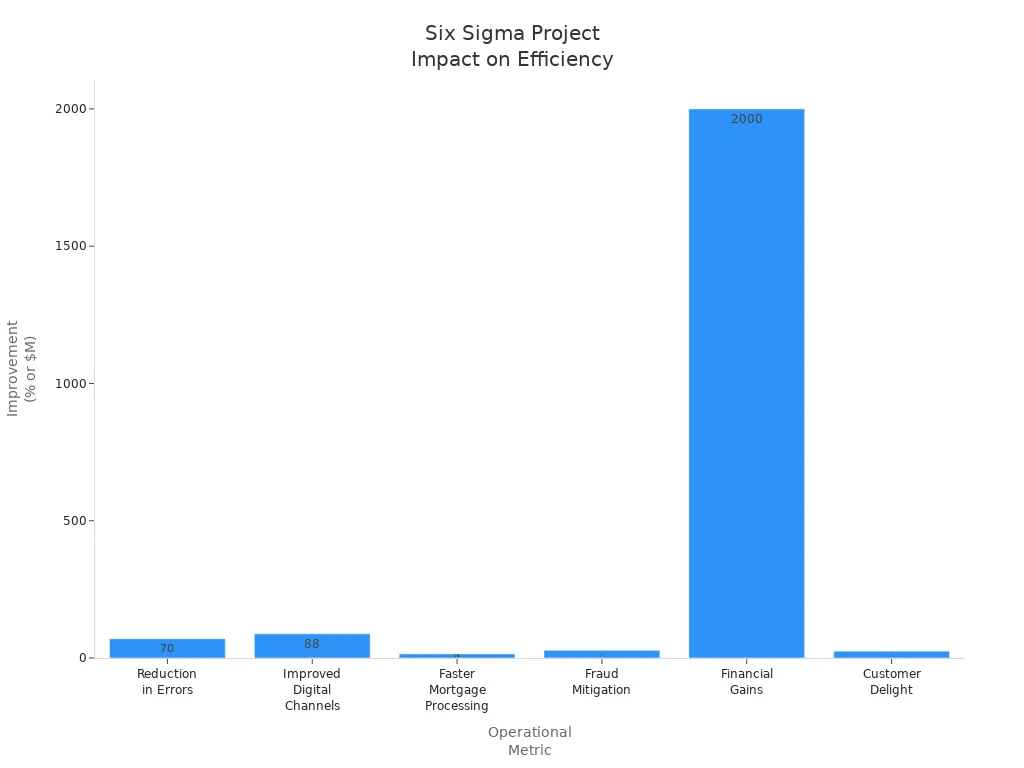
Teams that focus on process improvement with six sigma see gains in both speed and quality. They reduce waste, improve customer satisfaction, and achieve financial benefits. These results show how six sigma and process improvement work together to transform organizations.
Implementing Six Sigma
Getting Started
Organizations that want to implement six sigma need a clear plan from the beginning. The first step involves developing a Lean Six Sigma plan that matches the company’s goals and objectives. Leaders should include all stakeholders in this planning stage. This approach helps everyone understand the purpose and expected results.
Develop a Lean Six Sigma plan that aligns with business goals.
Involve all stakeholders early to ensure smooth adoption.
Set clear objectives and define success metrics.
Communicate the vision and benefits to the entire organization.
To succeed, Six Sigma must be a permanent part of the business strategy and practice. It must be at the core of management’s vision for the company. Adoption of Six Sigma requires the full support of upper management.
A strong start ensures that six sigma becomes part of the company’s culture. When leaders support the process, teams feel confident to move forward. This foundation helps organizations achieve effective quality control and lasting results.
Building a Team
A successful six sigma project depends on the right team structure. Organizations often form cross-functional teams. These teams bring together people from different departments, such as production, quality, and customer service. Each member offers unique skills and perspectives.
Cross-functional teams bring diverse expertise to solve complex problems.
Collaboration creates a shared sense of purpose and unity.
Team diversity encourages new ideas and innovative solutions.
Regular communication and feedback build trust among team members.
Team members develop leadership and teamwork skills that help both the project and their own growth.
A typical six sigma team includes roles like project champions, black belts, green belts, and team members. Project champions guide the team and remove obstacles. Black belts and green belts lead projects and analyze data. Team members support the work with their knowledge of daily operations.
Clients working within these systems and teams benefit from clear roles and responsibilities. This structure allows for better communication and faster problem-solving. When everyone understands their part, the team can focus on reducing defects and improving quality.
Training and Certification
Training and certification play a key role in six sigma success. Well-trained employees understand the tools and methods needed for quality improvement. Certification programs help team members gain the skills to lead projects and deliver results.
Certification Program | Cost | Description |
|---|---|---|
Green Belt | Online training included, no renewal required. | |
Black Belt | $499 | Advanced course for experienced professionals, includes project component. |
Master Black Belt | $699 | Highest level certification, includes project component and coaching preparation. |
ASQ Green Belt | $469 | Certification only, does not include training, renewals needed. |
ASQ Black Belt | $568 | Certification only, does not include training, renewals needed. |
Many organizations choose SSGI certification for its affordability and flexibility. Over 1,500 positive reviews on the Project Management Institute show its value. ASQ certifications are also respected in the industry. These programs help professionals lead six sigma projects and improve quality control.
Training ensures that team members know how to use six sigma tools, such as statistical analysis and process mapping. Certification proves their ability to apply these skills in real projects. With proper training, teams can achieve better results and maintain high standards.
Overcoming Challenges
Implementing six sigma in any organization brings many benefits, but teams often face several challenges along the way. Understanding these obstacles and knowing how to address them helps organizations achieve better results.
Challenges with People
Many employees may not have enough information about six sigma. This lack of knowledge can slow down progress. Teams can solve this by engaging people right after training sessions. When employees feel included and informed, they become more willing to participate in six sigma projects.Resistance to Change
Some workers worry that new processes will make their jobs harder or even unnecessary. Leaders should communicate clearly that six sigma aims to improve efficiency, not to eliminate jobs. Open discussions and regular updates help reduce fear and build trust.No Management Support
Without support from management, six sigma projects often fail. Teams need to explain the benefits of six sigma to leaders. When managers understand how six sigma can improve quality and save money, they are more likely to support the effort.Poor Execution
Sometimes, teams do not align six sigma projects with the main goals of the business. This misalignment can cause projects to lose focus. Assigning top talent and making sure every project matches business objectives keeps six sigma efforts on track.Incorrect Scope
Projects can grow too large if teams do not monitor progress closely. This problem, called scope creep, can waste time and resources. Teams should remind themselves of the original project scope and check progress often to stay focused.
Tip: Regular team meetings and clear communication help everyone stay on the same page during six sigma implementation.
Organizations that address these challenges early see better results from their six sigma projects. They build stronger teams, improve processes, and reach their quality goals faster.
Six Sigma Results

Quality Gains
Organizations that invest in six sigma certification see clear improvements in product and service quality. Teams use six sigma tools to identify defects and reduce process variation. By applying six sigma techniques, they create more reliable systems and deliver consistent results. Clients in manufacturing, healthcare, and finance report fewer errors and higher standards after completing six sigma certification programs.
Six sigma tools help teams measure quality at every step. For example, process mapping and control charts allow them to track changes and spot problems early. When teams use six sigma techniques, they find root causes and fix them quickly. This approach leads to fewer rejected products and better customer experiences.
Teams that complete six sigma certification often share best practices across departments. This collaboration helps everyone maintain high quality and encourages continuous improvement.
Cost Savings
Many organizations achieve significant cost savings by using six sigma certification and six sigma tools. Teams focus on removing waste and improving efficiency. Six sigma techniques help them analyze data and find ways to lower expenses. Companies like GE and Motorola have reported impressive results.
GE saved $12 billion over five years and added $1 to its earnings per share.
Honeywell (AlliedSignal) recorded more than $800 million in savings.
GE produces annual benefits of over $2.5 billion across the organization from six sigma.
Motorola reduced manufacturing costs by $1.4 billion from 1987-1994.
Six sigma reportedly saved Motorola $15 billion over the last 11 years.
Teams that earn six sigma certification learn how to use six sigma tools to cut costs. They apply six sigma techniques to streamline operations and reduce unnecessary steps. These changes help organizations use resources more effectively and boost profits.
Customer Satisfaction
Six sigma certification leads to higher customer satisfaction. Teams use six sigma tools to address complaints and improve service quality. Six sigma techniques help them reduce wait times and deliver better products. For example, the DMAIC methodology helped one team lower average wait times to four minutes. After making these changes, customer satisfaction scores increased by 20 percent.
Teams used six sigma certification to solve customer complaints about long wait times.
After targeted solutions, the average wait time dropped to four minutes, improving customer experience.
Customer satisfaction scores rose by 20 percent, showing better service quality.
A manufacturing company used six sigma tools to lower product rejection rates, which improved customer satisfaction.
Six sigma is a data-driven methodology that reduces defects and variability. When teams use six sigma certification and six sigma techniques, they deliver higher-quality products and services. Clients at systems and teams see measurable gains in customer satisfaction, which helps build loyalty and trust.
Mastering Six Sigma methodology for quality control involves several essential steps:
Teams use the DMAIC framework to guide structured process improvement.
Data-driven decision-making helps organizations optimize quality and efficiency.
Collaboration and training foster a culture of continuous improvement.
Continuous improvement supports long-term success and empowers employees to solve problems.
Organizations measure success by tracking process capability and customer value.
Those interested in starting a Six Sigma project or pursuing training can reach out for further information or support.
FAQ
What is the main goal of Six Sigma?
Six Sigma aims to reduce defects and process variation. Teams use data and analysis to improve quality. The goal is to deliver consistent products or services that meet customer expectations.
Who can benefit from Six Sigma training?
Employees at all levels can benefit. Managers, engineers, and frontline workers use Six Sigma tools to solve problems and improve processes. Organizations in manufacturing, healthcare, and services see strong results.
How long does it take to complete Six Sigma certification?
Most Green Belt programs take two to three months. Black Belt programs may require four to six months. The timeline depends on the course format and the learner’s pace.
What is the difference between Lean and Six Sigma?
Lean focuses on removing waste and speeding up processes. Six Sigma targets defect reduction and process control. Many organizations combine both methods for better results.
Does Six Sigma work for small businesses?
Yes. Small businesses use Six Sigma to improve quality and cut costs. The tools and methods scale to fit any organization size.
What are common Six Sigma tools?
Teams use control charts, process maps, cause-and-effect diagrams, and Pareto charts. These tools help find problems, analyze data, and track improvements.
Is Six Sigma only for manufacturing?
No. Six Sigma works in healthcare, finance, retail, and more. Any organization that wants better quality and efficiency can use Six Sigma.
How does Six Sigma improve customer satisfaction?
Six Sigma helps teams find and fix problems that affect customers. By reducing errors and delays, organizations deliver better products and services. This leads to higher satisfaction and loyalty.



