How to Optimize Business Processes for Growth

Optimizing business processes fuels growth by streamlining operations and maximizing resources. Enhanced predictability through automated systems ensures consistent outcomes, improving cash flow and reducing errors. Businesses achieve scalability by managing higher workloads without increasing labor costs, while well-documented processes minimize overhead. This methodology not only lowers operating expenses but also boosts profitability, a critical metric for success. By refining processes, companies create a foundation for efficiency and adaptability, enabling them to stay competitive in dynamic markets.
Key Takeaways
Improving business processes helps companies grow by working smarter and saving money.
Using automation makes results steady, improves money flow, and cuts mistakes.
Finding and understanding current processes is key to fixing problems and planning better ways.
Tools like flowcharts can show how work is done and where to improve.
Setting clear and easy-to-measure goals keeps changes focused on business needs.
Checking processes often helps businesses stay updated and work well.
Involving workers and asking for ideas builds teamwork and makes changes easier.
Using tools like automation and data tools helps make better choices and work faster.
Understanding Business Processes
What Are Business Processes?
Business processes are the backbone of any organization. They consist of structured activities designed to achieve specific goals. These processes ensure that tasks are completed efficiently and consistently, contributing to the overall success of the business. Industry experts have defined business processes in various ways, as shown below:
Source | Definition |
|---|---|
Davenport (1993) | A structured, measured set of activities designed to produce a specific output for a particular customer or market. |
Hammer & Champy (1993) | A collection of activities that takes one or more kinds of input and creates an output that is of value to the customer. |
Rummler & Brache (1995) | A series of steps designed to produce a product or service, often cross-functional and essential for effective management. |
von Rosing et al. | Business processes can be operational, management, or supporting, each serving different roles in an organization. |
TechTarget | An activity or set of activities that accomplish a specific organizational goal, producing consistent outcomes. |
These definitions highlight the importance of business processes in delivering value to customers and achieving organizational objectives.
Types of Business Processes
Business processes can be categorized into three main types. Each type plays a unique role in ensuring the smooth functioning of an organization.
Operational Processes
Operational processes are the core activities that directly contribute to delivering products or services. These processes include manufacturing, sales, and customer service. For example, a retail company’s operational processes might involve inventory management, order fulfillment, and point-of-sale transactions. According to recent statistics, 84% of organizations use platforms to manage operational processes, emphasizing their critical role in daily operations.
Support Processes
Support processes provide the necessary infrastructure and resources for operational processes to function effectively. These include finance, accounting, human resources, and IT services. For instance, automating employee onboarding—a common support process—has been adopted by 58% of companies to improve efficiency. While these processes do not directly generate revenue, they are essential for maintaining organizational stability.
Management and Innovation Processes
Management and innovation processes focus on planning, monitoring, and improving business operations. These processes include strategic planning, performance evaluation, and research and development. Companies that prioritize innovation often gain a competitive edge by introducing new products or improving existing ones. Statistics show that organizations using process mining for performance analysis save significant costs, with some achieving savings of over $51,000 annually.
Understanding these types of business processes helps organizations identify areas for improvement and allocate resources effectively. By optimizing these processes, businesses can enhance efficiency and drive growth.
Why Business Process Optimization Matters
Driving Efficiency and Reducing Costs
Optimizing business processes significantly enhances efficiency while reducing operational costs. Automation plays a pivotal role in this transformation. For instance, a local boutique automated its inventory management system, aligning purchases with demand trends identified through data analytics. This approach not only reduced costs but also improved stock turnover rates.
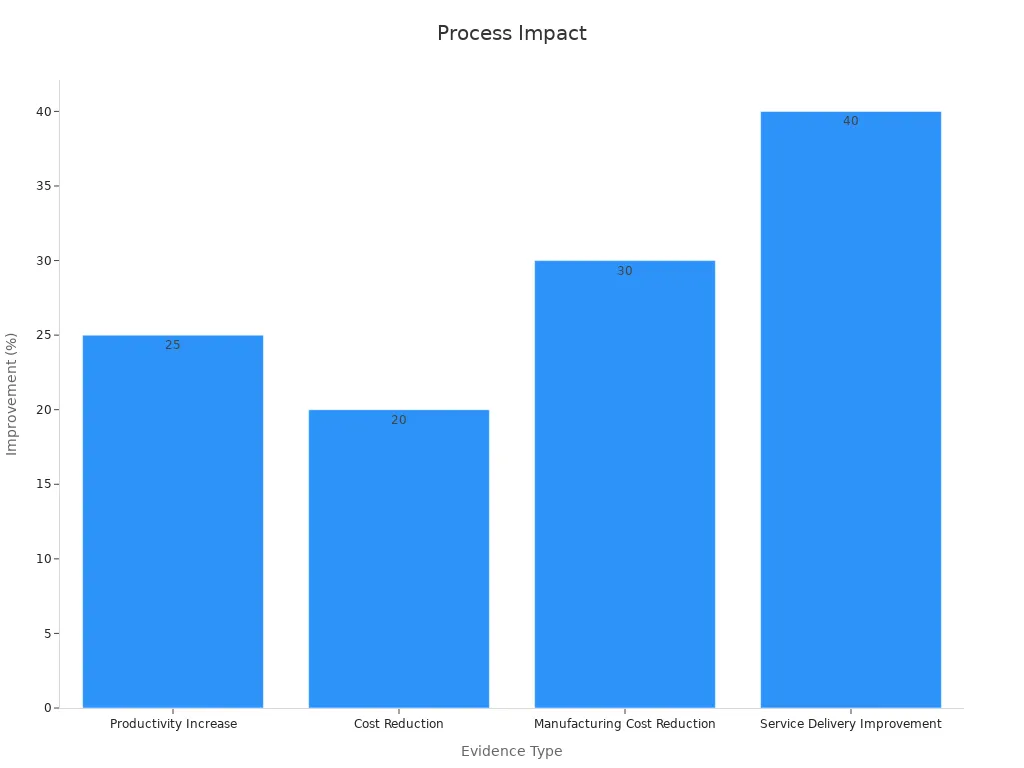
Businesses that excel in operational improvements achieve 25% higher productivity and 20% lower operating costs compared to competitors. Manufacturing firms report up to a 30% reduction in production costs, while service-based businesses experience 40% faster delivery times. These improvements demonstrate how process optimization directly impacts profitability and operational efficiency.
Tip: Identifying cost drivers and leveraging technology can help businesses lower expenses without compromising quality.
Enabling Scalability and Adaptability
Optimized business processes enable organizations to scale operations seamlessly. By streamlining workflows and adopting flexible systems, businesses can handle increased workloads without proportional increases in resources. For example, HCLTech's case study on an American cloud storage company highlights how implementing micro-services design improved scalability and reduced time to market.
Uber provides another example of scalability through process optimization. The company uses precise data analysis to enhance operational efficiency, allowing it to adapt quickly to market demands. This adaptability ensures businesses remain competitive in dynamic environments.
Note: Scalability improvements often result from enhanced decision-making and the adoption of innovative technologies.
Enhancing Customer Satisfaction and Competitiveness
Process optimization directly impacts customer satisfaction and competitiveness. Automation reduces errors and defects by 50%, leading to faster and more reliable service delivery. For instance, banks have redesigned their loan approval processes, cutting processing times from weeks to days and reducing errors by half.
Improved processes also elevate customer satisfaction by 30% and decrease complaints by 45%. These changes foster loyalty and engagement, giving businesses a competitive edge. Organizations that prioritize task optimization often exceed consumer expectations, strengthening their market position.
Metric | Improvement |
|---|---|
Reduction in errors and defects | 50% |
Increase in customer satisfaction | 30% |
Decrease in customer complaints | 45% |
By focusing on efficiency, scalability, and customer satisfaction, businesses can achieve sustainable growth and maintain a competitive advantage.
Steps to Optimize Business Processes

Identify and Map Current Processes
Conducting a Process Audit
A process audit serves as the foundation for identifying inefficiencies within business operations. This step involves reviewing existing workflows to determine their effectiveness and alignment with organizational goals. Teams should focus on gathering data from various departments to ensure a comprehensive understanding of current practices. For example, analyzing inventory management systems can reveal discrepancies in stock levels or delays in order fulfillment. A structured approach, such as the one outlined below, ensures thorough preparation and analysis:
Step | Description |
|---|---|
1 | Preparation: Equip teams to identify key processes and set actionable goals. |
2 | Diagnostic Phase: Use data to identify inefficiencies through qualitative and quantitative methods. |
3 | Optimization: Provide a strategic blueprint for re-engineering processes and updating policies. |
4 | Implementation: Integrate improvements into daily operations and ensure continuous monitoring. |
5 | Management: Embed a culture of continuous improvement and adaptation. |
By conducting a detailed audit, organizations can uncover hidden bottlenecks and establish a roadmap for improvement.
Using Process Mapping Tools
Process mapping tools play a critical role in visualizing workflows and identifying areas for optimization. Techniques such as flowcharts, SIPOC diagrams, and value stream mapping provide clarity on task sequences and responsibilities. For instance:
Flowcharts: Offer a simple visual representation of processes, making it easier to spot inefficiencies.
SIPOC Diagrams: Highlight key elements like suppliers, inputs, processes, outputs, and customers.
Value Stream Mapping: Focuses on eliminating waste by analyzing the flow of materials and information.
Methodology | Description | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
Flowcharts | Visual representation of processes. | Easy to understand and create. |
SIPOC Diagrams | High-level overview of processes, showing Suppliers, Inputs, Processes, Outputs, and Customers. | Helps in identifying key elements of a process. |
Value Stream Mapping | Focuses on the flow of materials and information to identify waste. | Enhances efficiency by eliminating waste. |
These tools not only improve communication among stakeholders but also provide actionable insights for streamlining business processes.
Analyze Inefficiencies and Bottlenecks
Identifying Pain Points
Identifying pain points requires a detailed examination of workflows to pinpoint areas causing delays or errors. Analytical techniques such as bottleneck analysis and data evaluation are particularly effective. For example, bottleneck analysis helps identify constraints within a system, while data analysis leverages key performance indicators (KPIs) to assess process performance. Metrics like cycle time and error rates often reveal inefficiencies that hinder productivity.
Technique | Description |
|---|---|
Bottleneck Analysis | A management tool to identify constraints and inefficiencies in a system or process. |
Data Analysis | Involves analyzing key performance indicators (KPIs) to gain insights into process performance. |
Process Mapping | Visual representation of workflows to identify inefficiencies and areas for improvement. |
By addressing these pain points, businesses can enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs.
Gathering Stakeholder Feedback
Stakeholder feedback is essential for understanding the practical challenges faced during daily operations. Engaging employees, managers, and customers provides valuable insights into inefficiencies and potential improvements. For instance, employees may highlight redundant tasks, while customers can identify service delays. Regular feedback sessions and surveys ensure that all perspectives are considered, fostering a collaborative approach to process optimization.
Set Clear Goals for Improvement
Defining Measurable Objectives
Setting measurable objectives ensures that process improvements align with organizational goals. Metrics such as customer satisfaction, compliance rates, and cost reductions provide a clear benchmark for success. For example:
Metric Type | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
Measure the ability of a process to achieve its intended results. | Customer satisfaction, Error rate | |
Control Metrics | Monitor compliance and conformance within a business process. | Compliance rate, Risk incidents |
Improvement Metrics | Assess the impact of changes made to multiple business processes. | Cost, Improvement in cycle time |
These metrics enable organizations to track progress and make data-driven decisions.
Aligning Goals with Business Strategy
Aligning goals with the broader business strategy ensures that process improvements contribute to long-term growth. For instance, a company aiming to enhance customer satisfaction might focus on reducing service delivery times. Strategic alignment also helps prioritize high-impact changes, ensuring optimal resource allocation. By integrating process optimization into the overall business strategy, organizations can achieve sustainable growth and maintain a competitive edge.
Leverage Automation and Technology
Selecting the Right Tools
Selecting the right tools is essential for leveraging automation and technology effectively. Businesses must evaluate their needs and choose solutions that align with their goals. Tools like Business Process Management (BPM) software centralize workflow modeling and automate repetitive tasks. This ensures consistency and continuous improvement. Cloud computing offers scalability and flexibility, enabling remote access and collaboration. Big data and analytics provide actionable insights, helping organizations identify bottlenecks and make data-driven decisions. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) enhance process optimization through intelligent automation and predictive maintenance.
Technology | Benefits |
|---|---|
BPM Software | Centralizes workflow modeling, automates processes, and ensures continuous improvement. |
Cloud Computing | Offers scalability and flexibility, enabling remote access and collaboration for process optimization. |
Big Data & Analytics | Provides insights into processes, identifies bottlenecks, and supports data-driven decision-making. |
AI & ML | Enables intelligent automation, predictive maintenance, and continuous process improvement. |
By adopting these technologies, businesses can streamline operations and improve efficiency. For example, a logistics company using AI to optimize delivery routes reduced fuel costs by 15% while improving delivery times. Selecting the right tools empowers organizations to achieve similar results.
Automating Repetitive Tasks
Automating repetitive tasks eliminates inefficiencies and frees up resources for higher-value activities. Tasks such as data entry, invoice processing, and customer support can be automated using tools like robotic process automation (RPA). This reduces human error and accelerates task completion. For instance, a financial services firm implemented RPA to handle invoice processing, cutting processing time by 60% and reducing errors by 40%.
Automation also enhances employee satisfaction by allowing them to focus on strategic initiatives. Employees spend less time on mundane tasks, leading to increased productivity and engagement. Organizations that embrace automation not only improve operational efficiency but also foster a more innovative and motivated workforce.
Monitor and Continuously Improve
Establishing KPIs
Key performance indicators (KPIs) provide measurable benchmarks for evaluating process performance. Businesses should define KPIs that align with their objectives, such as customer satisfaction, production efficiency, or cost reduction. For example, a global tech firm focused on customer engagement and satisfaction KPIs. This approach led to a 20% increase in customer retention, demonstrating the value of customer-centric metrics.
Industry | Case Study Description | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
Technology | A global tech firm implemented KPIs focused on customer engagement and satisfaction. | Resulted in a 20% increase in customer retention, highlighting the impact of customer-centric KPIs. |
Manufacturing | A manufacturing company introduced KPIs related to production efficiency and waste reduction. | Enhanced operational efficiency and employee engagement through collaborative KPI integration. |
Healthcare | A healthcare provider adopted KPIs centered on patient care outcomes and staff response times. | Improved patient satisfaction rates, fostering a more accountable and outcome-focused culture. |
KPIs enable organizations to track progress and identify areas for improvement. Regularly monitoring these metrics ensures that processes remain aligned with business goals.
Regular Process Reviews
Regular process reviews are crucial for maintaining efficiency and adapting to changing needs. These reviews involve analyzing performance data, gathering feedback, and identifying opportunities for improvement. For example, a manufacturing company that introduced KPIs for waste reduction conducted quarterly reviews. This practice enhanced operational efficiency and encouraged collaboration among employees.
Organizations should establish a schedule for process reviews and involve key stakeholders. This ensures that improvements are implemented effectively and that processes remain relevant. Continuous monitoring and improvement create a culture of accountability and innovation, driving long-term success.
Tools and Techniques for Business Processes Optimization
Optimizing business processes requires the right tools and techniques to streamline workflows, reduce inefficiencies, and enhance productivity. Organizations can leverage various solutions, including process mapping tools, workflow automation software, and data analytics, to achieve these goals. Each of these tools plays a unique role in improving operations and driving growth.
Process Mapping Tools
Process mapping tools help visualize workflows, making it easier to identify inefficiencies and areas for improvement. These tools provide a clear representation of task sequences, responsibilities, and dependencies. Industry surveys highlight the most effective process mapping tools, which include:
Creately
Lucidchart
MindMeister
Pipefy
ClickUp
EdrawMax
Microsoft Visio
GitMind
Canva
Cacoo
Visme
Notion
Smartsheet
Miro
Monday.com
These tools simplify complex processes, enhance collaboration, and support decision-making. For example, Lucidchart and Miro are widely used for their intuitive interfaces and real-time collaboration features. By adopting these tools, businesses can gain valuable insights into their workflows and implement targeted improvements.
Workflow Automation Software
Workflow automation software eliminates repetitive tasks, reduces errors, and accelerates task completion. Organizations using automation report significant improvements in several key areas:
Task Completion Times: Automation reduces the time required to execute processes, improving overall efficiency.
Error Rates: Automated workflows minimize human errors, ensuring consistent outcomes.
Response Times: Faster response times enhance user experience and operational agility.
Cost Savings: Reduced manual labor and increased efficiency lead to substantial financial benefits.
For instance, a company automating its customer support processes can handle inquiries faster, improving customer satisfaction. Workflow automation software not only optimizes operations but also empowers employees to focus on strategic initiatives.
Data Analytics for Process Improvement
Data analytics plays a critical role in identifying inefficiencies and driving process improvements. By analyzing metrics such as cycle time, throughput, error rates, and customer satisfaction scores, organizations can uncover valuable insights. Reducing cycle time and errors enhances productivity and customer satisfaction. Strategies like DataOps Observability and automation tools help teams minimize errors and complete tasks more efficiently.
To effectively use data analytics for process improvement, organizations can follow these steps:
Define Objectives and Goals: Establish clear objectives and KPIs to measure success.
Identify Data Sources: Determine relevant data sources for the targeted process.
Clean and Prepare Data: Ensure data accuracy and consistency.
Analyze Data: Use various analysis techniques to uncover insights.
Identify Improvement Opportunities: Pinpoint areas for optimization based on data findings.
Develop Actionable Insights: Create recommendations based on analysis.
Collaborate with Stakeholders: Engage stakeholders for support and alignment.
Pilot Test Solutions: Test proposed solutions on a small scale.
Implement and Monitor: Roll out improvements and track their impact.
Iterate and Refine: Continuously improve based on feedback and performance metrics.
By leveraging data analytics, businesses can make informed decisions, optimize their processes, and achieve better outcomes for customers.
Overcoming Challenges in Business Processes Optimization
Optimizing business processes often encounters obstacles that can hinder progress. Addressing these challenges effectively ensures smoother transitions and maximizes the benefits of optimization efforts.
Resistance to Change
Resistance to change is one of the most common barriers to process optimization. Employees may feel uncertain about new systems or fear that automation could replace their roles. Overcoming this resistance requires strategic efforts to build trust and demonstrate the value of change.
Building Employee Buy-In
Gaining employee buy-in is essential for successful process optimization. Organizations should involve employees early in the decision-making process. This approach fosters a sense of ownership and reduces resistance. Starting with a pilot project focused on a single, high-impact process can demonstrate quick wins. Employees witnessing tangible improvements are more likely to support broader changes. Additionally, providing tailored training ensures that employees feel confident using new tools and systems.
Communicating Benefits Effectively
Clear communication about the benefits of process optimization can alleviate concerns. Employees need to understand how changes will improve their work environment and contribute to organizational success. For example, emphasizing how automation reduces repetitive tasks allows employees to focus on more meaningful work. Research shows that perceived usefulness and ease of use significantly reduce resistance to change. When employees see the value and simplicity of new processes, they are more likely to embrace them.
Evidence Description | Effect on Resistance to Change |
|---|---|
Perceived usefulness has a negative effect on resistance to change. | Higher perceived usefulness reduces resistance. |
Perceived ease of use has a negative effect on resistance to change. | Higher perceived ease of use reduces resistance. |
Resistance to change is influenced by status quo bias, leading to higher resistance. | Individuals prefer to maintain the status quo. |
Resistance to change positively affects user resistance behavior. | Higher resistance leads to more resistance behavior. |
High perceived value of EHR reduces resistance to change. | Lower resistance when change is seen as valuable. |
Lack of Clear Communication
Poor communication can create confusion and slow down the optimization process. Ensuring transparency and providing adequate support are critical to overcoming this challenge.
Ensuring Transparency
Transparency builds trust and reduces uncertainty. Organizations should share detailed plans, timelines, and expected outcomes with all stakeholders. Regular updates on progress keep everyone informed and engaged. For example, using dashboards to display real-time performance metrics allows teams to track improvements and understand the impact of changes.
Providing Training and Support
Comprehensive training tailored to different user groups ensures strong adoption of new processes. Ongoing support, such as help desks or dedicated teams, addresses issues promptly. This approach minimizes disruptions and boosts confidence among employees. Establishing a culture of continuous improvement further reinforces the importance of learning and adaptation.
Balancing Costs and ROI
Process optimization often requires significant investment. Balancing costs with the expected return on investment (ROI) ensures that resources are allocated effectively.
Prioritizing High-Impact Changes
Focusing on high-impact changes delivers the greatest value with minimal resources. Organizations should identify processes that directly affect key performance indicators, such as customer satisfaction or operational efficiency. Starting small with a pilot project allows businesses to calculate ROI before scaling improvements across the organization.
Measuring ROI Effectively
Measuring ROI involves tracking both tangible and intangible benefits. Metrics such as cost savings, productivity gains, and customer satisfaction provide a clear picture of success. Advanced analytics tools help organizations monitor these metrics and identify areas for further improvement. Regular reviews of ROI ensure that optimization efforts remain aligned with business goals.
Tip: Establishing a culture of continuous improvement by leveraging performance data and analytics ensures long-term success.
By addressing resistance, improving communication, and balancing costs with ROI, organizations can overcome challenges and achieve sustainable process optimization.
Optimizing business processes is essential for driving growth and ensuring long-term success. It addresses challenges related to complexity and scale while improving efficiency and customer experiences. Key steps include mapping workflows, identifying inefficiencies, and leveraging tools like process mapping and automation software. Techniques such as Six Sigma and process mining further enhance effectiveness.
Companies that adopt the right strategies and technologies position themselves for sustainable growth. Taking proactive steps toward continuous improvement fosters adaptability and competitiveness in dynamic markets.
By prioritizing optimization, businesses can unlock their full potential and achieve lasting prosperity.
FAQ
What is business process optimization?
Business process optimization involves improving workflows to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and achieve organizational goals. It focuses on identifying inefficiencies, streamlining operations, and leveraging tools like automation and analytics to deliver better outcomes.
How does automation improve business processes?
Automation eliminates repetitive tasks, reduces human error, and accelerates workflows. Tools like robotic process automation (RPA) handle routine activities, allowing employees to focus on strategic initiatives. This improves productivity and operational efficiency.
What are the key benefits of process mapping?
Process mapping provides a visual representation of workflows, making it easier to identify inefficiencies and redundancies. It enhances communication among stakeholders, supports decision-making, and helps organizations implement targeted improvements.
How can businesses measure the success of optimization efforts?
Businesses can measure success using key performance indicators (KPIs) such as cost savings, cycle time reduction, customer satisfaction, and error rates. Regularly tracking these metrics ensures alignment with organizational goals and identifies areas for further improvement.
What challenges do companies face during process optimization?
Common challenges include resistance to change, lack of clear communication, and balancing costs with ROI. Addressing these issues requires employee engagement, transparent communication, and prioritizing high-impact changes.
How often should businesses review their processes?
Organizations should conduct regular process reviews, ideally quarterly or biannually. Frequent reviews ensure workflows remain efficient, adapt to changing needs, and align with business objectives.
What tools are essential for optimizing business processes?
Essential tools include process mapping software, workflow automation platforms, and data analytics solutions. These tools streamline operations, provide actionable insights, and support continuous improvement.
Why is stakeholder feedback important in process optimization?
Stakeholder feedback highlights practical challenges and improvement opportunities. Employees identify inefficiencies, while customers provide insights into service quality. Engaging stakeholders fosters collaboration and ensures optimization efforts address real-world needs.



