How to Improve Team Collaboration Through Lean Six Sigma Process Mapping

Lean Six Sigma Process Mapping empowers teams to work more effectively by providing a clear visualization of workflows. It simplifies complex processes, reduces inefficiencies, and ensures every team member understands their role. This structured approach fosters alignment and enhances communication, creating a collaborative environment where ideas flow freely. By integrating optimization steps into daily operations, teams can identify bottlenecks and improve productivity. Lean Six Sigma combines precision with practicality, making it a cornerstone of modern business management. Its emphasis on shared knowledge drives continuous improvement and strengthens team dynamics.
Key Takeaways
Lean Six Sigma Process Mapping simplifies complex workflows, making it easier for teams to visualize and understand their roles and responsibilities.
Involving team members in the mapping process fosters collaboration and open communication, leading to a stronger sense of ownership and accountability.
Regularly reviewing and updating process maps helps teams identify inefficiencies and ensures alignment with organizational goals.
Using visual tools like flowcharts and SIPOC diagrams enhances clarity, reduces misunderstandings, and bridges communication gaps in cross-functional teams.
Identifying and eliminating bottlenecks through process mapping can significantly improve productivity and streamline operations.
Aligning team goals with organizational objectives through process mapping motivates team members by showing how their contributions impact overall success.
Celebrating successes and learning from challenges during the mapping process strengthens team dynamics and promotes a culture of continuous improvement.
Understanding Lean Six Sigma Process Mapping
What Is Lean Six Sigma Process Mapping?
Lean Six Sigma Process Mapping is a structured technique that visually represents the steps, inputs, and outputs of a process. It provides a clear flowchart that outlines how tasks progress from start to finish. This method simplifies complex workflows by breaking them into smaller, manageable components. Teams use it to identify inefficiencies, redundancies, and areas for improvement.
The mapping process serves as a foundation for analyzing operations. It highlights every interaction and activity within a system, ensuring no detail gets overlooked. By visualizing the entire workflow, teams gain a comprehensive understanding of how processes function. This clarity enables them to pinpoint bottlenecks and streamline operations effectively.
Key Features of Lean Six Sigma Process Mapping
Lean Six Sigma Process Mapping incorporates several essential features that make it a powerful tool for process improvement:
Clarity and Simplicity: The maps use standardized symbols to represent tasks, decisions, and flows. This ensures that all team members can easily interpret the information.
Focus on Inputs and Outputs: Each step in the process connects to specific inputs and outputs, providing a complete picture of how resources transform into results.
Identification of Inefficiencies: The visual nature of the map makes it easier to spot redundancies, delays, or unnecessary steps.
Collaboration-Friendly Design: Teams can work together during the mapping process, fostering open discussions and shared insights.
Adaptability: The maps can be tailored to suit various industries and workflows, from manufacturing to service-based operations.
These features make Lean Six Sigma Process Mapping an indispensable tool for organizations aiming to enhance their operational efficiency.
Why It Is Essential for Team Collaboration
Lean Six Sigma Process Mapping plays a critical role in improving team collaboration. It creates a shared understanding of workflows, ensuring that every team member knows their responsibilities and how their tasks contribute to the overall process. This alignment reduces confusion and fosters better communication.
By involving team members in the mapping process, organizations encourage active participation and idea-sharing. This collaborative approach builds trust and strengthens relationships within the team. Additionally, the visual representation of workflows helps bridge communication gaps, especially in cross-functional teams where members may have different expertise or perspectives.
The process map also serves as a reference point during discussions or problem-solving sessions. Teams can use it to identify pain points, propose solutions, and track progress. This structured framework ensures that everyone stays on the same page, leading to more efficient and productive teamwork.
Benefits of Lean Six Sigma Process Mapping for Team Collaboration
Clarifying Roles and Responsibilities
Lean Six Sigma Process Mapping provides a clear framework for defining roles and responsibilities within a team. By visually outlining each step of a process, it becomes easier to assign specific tasks to the appropriate individuals. This clarity ensures that every team member understands their duties and how their contributions fit into the larger workflow.
For example, in manufacturing environments, Lean Six Sigma has been instrumental in optimizing production processes. Teams have used process maps to identify inefficiencies and assign tasks more effectively, leading to improved productivity and cost savings. When roles are clearly defined, team members can focus on their specific responsibilities without confusion or overlap, fostering a more organized and efficient work environment.
Reducing Misunderstandings and Communication Gaps
Misunderstandings often arise when team members lack a shared understanding of workflows. Lean Six Sigma Process Mapping addresses this issue by creating a visual representation of processes that everyone can interpret. These maps serve as a common language, bridging communication gaps between team members with different expertise or perspectives.
In cross-functional teams, where collaboration between departments is essential, process mapping has proven invaluable. For instance, in the manufacturing industry, Lean Six Sigma methodologies have revolutionized communication by reducing waste and improving overall productivity. Teams that use process maps can identify potential points of confusion and resolve them before they escalate into larger issues. This proactive approach strengthens communication and ensures smoother collaboration.
Fostering a Shared Understanding of Workflows
A shared understanding of workflows is critical for effective teamwork. Lean Six Sigma Process Mapping enables teams to visualize the entire process from start to finish, ensuring that everyone is aligned on how tasks progress. This alignment helps eliminate redundancies and ensures that all team members are working toward the same goals.
By fostering this shared understanding, teams can identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies more effectively. For example, in systems where Lean Six Sigma has been implemented, teams have unlocked higher levels of efficiency and quality. Process maps provide a foundation for discussions, allowing teams to collaboratively propose solutions and track improvements. This shared perspective not only enhances collaboration but also drives continuous improvement within the organization.
Identifying and Eliminating Bottlenecks
Bottlenecks disrupt workflows and hinder team productivity. Lean Six Sigma Process Mapping provides a structured approach to identify and eliminate these obstacles. By visually representing each step in a process, teams can pinpoint areas where delays or inefficiencies occur. These bottlenecks often result from redundant tasks, unclear responsibilities, or resource constraints.
For example, manufacturing teams have used this methodology to optimize production processes. They identified bottlenecks in assembly lines, such as excessive wait times between steps or unnecessary movements of materials. By addressing these issues, they achieved higher efficiency and reduced operational costs. Teams can replicate this success by analyzing their workflows and focusing on areas that slow progress.
The elimination of bottlenecks requires collaboration. Team members must share insights and propose solutions during mapping sessions. This collective effort ensures that all perspectives are considered, leading to practical and effective improvements. Once bottlenecks are resolved, teams experience smoother workflows, enhanced productivity, and improved morale.
Aligning Team Goals with Organizational Objectives
Alignment between team goals and organizational objectives is essential for long-term success. Lean Six Sigma Process Mapping helps bridge this gap by providing a clear visualization of how team activities contribute to broader business outcomes. Teams can use process maps to ensure their efforts align with the company’s strategic priorities.
In industries like manufacturing, this alignment has led to remarkable improvements. Teams have used process mapping to reduce waste and enhance product quality, directly supporting organizational goals of cost efficiency and customer satisfaction. By understanding how their tasks impact the larger picture, team members feel more motivated and engaged.
To achieve alignment, leaders should involve teams in the mapping process. This participation fosters a sense of ownership and accountability. Teams can identify areas where their workflows deviate from organizational objectives and make necessary adjustments. Regularly reviewing and updating process maps ensures that team goals remain aligned with evolving business needs.
Types of Process Maps in Lean Six Sigma

SIPOC Diagrams
SIPOC diagrams provide a high-level overview of a process by outlining its key components: Suppliers, Inputs, Processes, Outputs, and Customers. This type of map helps teams understand the broader context of their workflows. It identifies the relationships between each element, ensuring that all critical factors are considered during process analysis.
For example, manufacturing teams often use SIPOC diagrams to evaluate production workflows. By clearly defining suppliers and inputs, they can pinpoint inefficiencies in material sourcing or delivery. Similarly, identifying outputs and customers ensures that the final product meets quality standards and customer expectations. SIPOC diagrams serve as a foundation for process improvement, offering clarity and direction for teams aiming to optimize their operations.
Key Insight: SIPOC diagrams excel in simplifying complex processes, making them accessible to all team members. They encourage collaboration by providing a shared understanding of how inputs transform into outputs.
Value Stream Mapping
Value stream mapping focuses on analyzing the flow of materials and information required to deliver a product or service. This type of map highlights value-added and non-value-added activities, enabling teams to identify waste and streamline workflows. It is particularly effective in industries like manufacturing and logistics, where efficiency directly impacts profitability.
Teams using value stream mapping can uncover bottlenecks, delays, or redundancies in their processes. For instance, a manufacturing team might identify excessive lead times caused by unnecessary steps in the production line. By eliminating these inefficiencies, they can reduce costs and improve productivity. Value stream mapping not only enhances operational efficiency but also aligns team efforts with organizational goals.
Real-World Impact: Companies implementing value stream mapping have reported significant reductions in waste and lead times. These improvements contribute to higher customer satisfaction and increased profitability.
Swimlane Diagrams
Swimlane diagrams visually separate tasks and responsibilities across different team members or departments. Each "lane" represents a specific role or function, making it easy to see who is responsible for each step in a process. This clarity reduces confusion and ensures accountability within teams.
Cross-functional teams benefit greatly from swimlane diagrams. For example, in a finance department, these diagrams can clarify the handoff points between accounting, auditing, and compliance teams. By clearly defining responsibilities, swimlane diagrams minimize errors and improve collaboration. They also help teams identify inefficiencies in communication or task delegation, leading to smoother workflows.
Practical Application: Swimlane diagrams foster transparency and accountability. Teams can use them to streamline cross-departmental processes, ensuring that everyone understands their role in achieving shared objectives.
Flowcharts and Their Applications
Flowcharts serve as a versatile tool in Lean Six Sigma process mapping. They visually represent workflows, making it easier for teams to understand and analyze processes. By using standardized symbols, flowcharts provide a clear and concise depiction of tasks, decisions, and their sequence. This simplicity allows teams to identify inefficiencies and improve operations effectively.
Key Applications of Flowcharts in Team Collaboration
Simplifying Complex Processes
Flowcharts break down intricate workflows into manageable steps. Teams can use them to visualize each task and its relationship to the overall process. For example, manufacturing teams often rely on flowcharts to streamline production lines. By mapping out every step, they can pinpoint redundancies and eliminate unnecessary actions, leading to increased productivity.Enhancing Communication Across Teams
Flowcharts act as a universal language for team members with diverse expertise. They bridge communication gaps by providing a shared understanding of workflows. Cross-functional teams, such as those in finance and compliance, benefit significantly from this clarity. Flowcharts ensure that everyone stays aligned, reducing misunderstandings and fostering collaboration.Identifying Process Inefficiencies
Teams use flowcharts to uncover bottlenecks and areas of waste. For instance, in logistics, flowcharts help identify delays in supply chain processes. By addressing these inefficiencies, organizations achieve cost savings and improved operational efficiency. This proactive approach enhances both team performance and customer satisfaction.Supporting Decision-Making
Flowcharts include decision points that guide teams through various scenarios. These visual aids help teams evaluate options and choose the most efficient path forward. In industries like manufacturing, decision-based flowcharts assist in optimizing resource allocation, ensuring that processes run smoothly and effectively.Training and Onboarding New Team Members
Flowcharts simplify the onboarding process by providing a clear overview of workflows. New team members can quickly grasp their roles and responsibilities within the system. This structured approach reduces training time and ensures consistency in task execution.
Insight: Teams that integrate flowcharts into their operations report significant improvements in efficiency and communication. Flowcharts not only enhance collaboration but also contribute to better decision-making and streamlined workflows.
Practical Tips for Creating Effective Flowcharts
Use standardized symbols to ensure clarity and consistency.
Focus on the sequence of tasks and avoid overcomplicating the design.
Involve team members during the creation process to gather diverse perspectives.
Regularly review and update flowcharts to reflect changes in workflows.
Flowcharts remain an essential component of Lean Six Sigma process mapping. Their ability to simplify processes, enhance communication, and identify inefficiencies makes them invaluable for teams striving for continuous improvement. By leveraging flowcharts effectively, organizations can align team efforts with broader business objectives and achieve sustainable success.
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating a Lean Six Sigma Process Map
Step 1: Define the Process Scope and Objectives
Defining the scope and objectives sets the foundation for effective process mapping. Teams must identify the boundaries of the process they aim to analyze. This includes determining where the process begins and ends, as well as specifying the key deliverables. Clear objectives help teams focus on what they want to achieve, such as reducing inefficiencies or improving communication.
For example, a manufacturing team might define their scope as the assembly line process, with the objective of minimizing production delays. By narrowing the focus, teams avoid unnecessary complexity and ensure that the mapping effort remains targeted. Establishing these parameters early ensures alignment among all participants and provides a clear direction for the mapping exercise.
Step 2: Gather Input from Team Members
Input from team members is essential for creating an accurate and comprehensive process map. Each team member brings unique insights based on their role and experience. Gathering this input ensures that no critical steps or details are overlooked.
Teams can organize brainstorming sessions or workshops to collect information. During these sessions, participants should describe their tasks, responsibilities, and any challenges they face. For instance, in a cross-functional team, members from different departments can highlight handoff points or areas where communication breaks down. This collaborative approach fosters a sense of ownership and encourages active participation.
Tip: Use tools like SIPOC diagrams to structure the input-gathering process. These diagrams help teams outline suppliers, inputs, processes, outputs, and customers, providing a high-level overview that guides further mapping efforts.
Step 3: Map Out the Current Workflow
Mapping the current workflow involves visually representing each step of the process as it exists today. Teams should use standardized symbols to depict tasks, decisions, and flows. This ensures clarity and consistency, making the map easy to interpret.
Start by documenting the sequence of activities, including inputs and outputs for each step. Identify who performs each task and how it connects to the next. For example, a value stream map can be used to analyze the flow of materials and information in a manufacturing process. This type of map highlights both value-added and non-value-added activities, helping teams identify inefficiencies.
Key Insight: Avoid overcomplicating the map. Focus on capturing the essential details that impact the process. A simple and clear representation is more effective for analysis and collaboration.
Once the current workflow is mapped, teams can review it together to ensure accuracy. This step provides a shared understanding of the process and lays the groundwork for identifying pain points and opportunities for improvement.
Step 4: Identify Pain Points and Inefficiencies
Teams must analyze the current process map to uncover pain points and inefficiencies. These issues often manifest as delays, redundancies, or unnecessary steps that hinder productivity. By focusing on these areas, teams can prioritize improvements that yield the most significant impact.
To identify inefficiencies, teams should:
Examine Bottlenecks: Look for steps where tasks pile up or progress slows. For instance, excessive wait times between stages in a manufacturing process may indicate a bottleneck.
Spot Redundancies: Identify repetitive tasks that do not add value. These could include duplicate data entry or unnecessary approvals.
Evaluate Resource Utilization: Assess whether resources, such as personnel or materials, are being used effectively. Misallocated resources often lead to inefficiencies.
Analyze Communication Gaps: Review handoff points between team members or departments. Miscommunication at these points can cause delays or errors.
Pro Tip: Use tools like SIPOC diagrams to gain a high-level overview of the process. These diagrams help teams understand the relationships between suppliers, inputs, processes, outputs, and customers, making it easier to pinpoint inefficiencies.
Once the pain points are identified, teams should document them clearly. This documentation ensures that everyone understands the issues and agrees on the areas requiring improvement.
Step 5: Collaboratively Design the Future-State Process
After identifying inefficiencies, teams should work together to design an optimized future-state process. Collaboration is essential during this step to ensure that all perspectives are considered and the new process aligns with team goals.
To design the future-state process:
Define Objectives: Establish clear goals for the new process. These could include reducing lead times, eliminating redundancies, or improving communication.
Involve Key Stakeholders: Engage team members, department heads, and other stakeholders in brainstorming sessions. Their input ensures that the new process addresses real-world challenges.
Incorporate Lean Principles: Focus on value-added activities while eliminating waste. For example, use Value Stream Maps to identify and remove non-value-added steps.
Visualize the New Workflow: Create a draft of the future-state process map using tools like flowcharts or swimlane diagrams. Ensure that the map clearly outlines roles, responsibilities, and task sequences.
Key Insight: Swimlane diagrams are particularly useful for clarifying responsibilities in cross-functional teams. By visually separating tasks across different roles, these diagrams ensure accountability and reduce confusion.
The collaborative design process fosters team alignment and ownership. When team members contribute to the new process, they are more likely to support its implementation.
Step 6: Validate the Process Map with the Team
Validation ensures that the future-state process map is accurate, practical, and aligned with team objectives. Teams should review the map collectively to confirm that it addresses all identified pain points and inefficiencies.
Steps to validate the process map:
Conduct a Team Review: Organize a meeting where team members can examine the map. Encourage open discussions to identify any overlooked details or potential challenges.
Simulate the Workflow: Walk through the process step by step to test its feasibility. This simulation helps teams identify any gaps or inconsistencies in the workflow.
Gather Feedback: Collect input from all stakeholders, including those who will execute the process. Their feedback ensures that the map is realistic and actionable.
Refine the Map: Make necessary adjustments based on the feedback. Ensure that the final version of the map is clear, concise, and free of ambiguities.
Practical Tip: Use flowcharts to simplify the validation process. Their standardized symbols and clear structure make it easier for teams to spot errors or inefficiencies.
Validation builds confidence in the new process and ensures that all team members are on the same page. A well-validated process map serves as a reliable guide for implementation and continuous improvement.
Step 7: Implement and Monitor the New Workflow
Implementing the new workflow requires a structured approach to ensure its success. Teams must transition from planning to execution while maintaining focus on the objectives outlined during the process mapping phase. A clear implementation plan helps guide this transition and ensures that all team members understand their roles.
Steps for Effective Implementation:
Communicate the New Workflow
Share the updated process map with all team members. Use visual tools like SIPOC diagrams or flowcharts to explain the changes. These tools provide clarity by illustrating the sequence of tasks, inputs, and outputs. Ensure that every individual understands their responsibilities within the new framework.Provide Training and Resources
Equip team members with the necessary skills and tools to execute the new workflow. For example, if the process involves value stream mapping, offer training sessions to familiarize the team with its application. Providing resources ensures that everyone can perform their tasks efficiently.Assign Accountability
Clearly define who is responsible for each step in the process. Use swimlane diagrams to visually separate tasks across roles or departments. This approach reduces confusion and ensures accountability, especially in cross-functional teams.Pilot the Workflow
Test the new process on a smaller scale before full implementation. Piloting allows teams to identify potential issues and make adjustments. For instance, manufacturing teams might implement the updated workflow on one production line to evaluate its effectiveness.
Monitoring the Workflow:
Monitoring ensures that the new process achieves its intended goals. Teams must track performance metrics and gather feedback to assess the workflow's efficiency.
Track Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Identify measurable outcomes, such as reduced lead times or improved output quality. Regularly review these metrics to evaluate the workflow's success. For example, value stream maps can help track the flow of materials and information, highlighting areas for further improvement.Gather Team Feedback
Encourage team members to share their experiences with the new process. Their insights can reveal challenges or opportunities for refinement. Open communication fosters a culture of continuous improvement.Conduct Regular Reviews
Schedule periodic reviews to assess the workflow's performance. Use tools like SIPOC diagrams to revisit the process and ensure alignment with organizational objectives. Regular reviews help teams stay proactive in addressing inefficiencies.
Pro Tip: Use digital process mapping tools to monitor workflows in real-time. These tools provide valuable data and visualizations, making it easier to identify trends and make informed decisions.
Implementing and monitoring the new workflow transforms plans into actionable results. By following a structured approach, teams can ensure a smooth transition and achieve sustained improvements. For organizations seeking expert guidance on Lean Six Sigma process mapping, reaching out to experienced professionals can provide valuable support and insights.
Practical Applications of Lean Six Sigma Process Mapping in Team Collaboration
Facilitating Open Discussions During Mapping Sessions
Lean Six Sigma Process Mapping encourages open discussions by providing a visual framework for analyzing workflows. Teams gather around process maps to share insights, identify inefficiencies, and propose solutions. This collaborative environment fosters transparency and ensures that every team member's perspective is considered.
During mapping sessions, tools like flowcharts and value stream maps play a crucial role. Flowcharts simplify complex processes into clear, sequential steps, making it easier for teams to pinpoint areas of improvement. Value stream maps, on the other hand, offer a broader view by highlighting value-added and non-value-added activities. These tools guide discussions and help teams focus on eliminating waste and enhancing efficiency.
Example: In a manufacturing setting, teams use value stream maps to identify delays in production workflows. By discussing these bottlenecks during mapping sessions, they collaboratively design solutions that reduce lead times and improve output quality.
Facilitating open discussions not only strengthens team collaboration but also builds trust. When team members actively participate in mapping sessions, they feel more invested in the outcomes, leading to smoother implementation of process improvements.
Using Process Maps to Resolve Bottlenecks
Bottlenecks disrupt workflows and hinder productivity. Lean Six Sigma Process Mapping provides a structured approach to identify and resolve these issues. By visually representing each step in a process, teams can locate areas where delays or inefficiencies occur.
For instance, swimlane diagrams are particularly effective in cross-functional teams. These diagrams separate tasks by roles or departments, making it easier to identify handoff points where bottlenecks often arise. Teams can then analyze these points to determine the root cause of delays, such as miscommunication or resource constraints.
Insight: Process maps also help teams prioritize solutions. By focusing on high-impact bottlenecks, they can achieve significant improvements with minimal effort. For example, addressing a delay in material delivery might streamline the entire production process.
Resolving bottlenecks requires collaboration. Teams must share their observations and work together to implement changes. This collective effort ensures that solutions are practical and sustainable, leading to enhanced workflow efficiency and team performance.
Onboarding New Team Members with Process Maps
Onboarding new team members becomes more efficient with the use of process maps. These visual tools provide a clear overview of workflows, helping newcomers understand their roles and responsibilities within the system. By simplifying complex processes, process maps reduce the learning curve and ensure consistency in task execution.
Flowcharts are particularly useful during onboarding. They break down workflows into manageable steps, making it easier for new team members to grasp the sequence of tasks. SIPOC diagrams also play a vital role by outlining the key components of a process—Suppliers, Inputs, Processes, Outputs, and Customers. These diagrams help new hires understand how their tasks contribute to the overall objectives.
Practical Tip: Organizations can integrate process maps into training materials. For example, a finance team might use swimlane diagrams to explain the handoff points between accounting and compliance departments. This approach ensures that new team members quickly adapt to their roles.
Using process maps for onboarding not only accelerates the integration of new hires but also fosters a culture of clarity and collaboration. When team members start with a solid understanding of workflows, they can contribute more effectively to the team's success.
Aligning Process Maps with Team and Organizational Goals
Aligning process maps with team and organizational goals ensures that workflows contribute directly to broader business objectives. This alignment fosters a sense of purpose among team members and enhances overall efficiency. Lean Six Sigma process mapping provides the tools necessary to bridge the gap between daily tasks and strategic priorities.
Establishing Clear Connections Between Processes and Goals
Process maps serve as a visual representation of how tasks and workflows support organizational objectives. Tools like value stream maps excel in this area by offering a high-level view of operations. These maps highlight every step in a process, from supplier to customer, and evaluate each task based on the value it adds to the final product. By identifying non-value-added activities, teams can eliminate waste and focus on actions that align with company goals.
Example: A manufacturing team might use a value stream map to streamline production workflows. By reducing overproduction and unnecessary motion, they align their efforts with the organization's goal of minimizing costs and maximizing efficiency.
Enhancing Team Accountability Through Visual Clarity
Process maps clarify roles and responsibilities, ensuring that every team member understands their contribution to organizational success. Swimlane diagrams are particularly effective for this purpose. These diagrams separate tasks by roles or departments, making it easy to see who is responsible for each step. This clarity reduces confusion and fosters accountability.
Practical Application: In a finance department, swimlane diagrams can illustrate the handoff points between accounting, auditing, and compliance teams. By clearly defining responsibilities, these diagrams ensure that all team members work cohesively toward shared objectives.
Using Process Mapping Tools to Track Progress
Modern process mapping software tools provide valuable insights into workflow performance. Tools like Microsoft Visio, Lucidchart, and IBM Blueworks Live allow teams to monitor processes in real-time. These platforms enable organizations to measure key performance indicators (KPIs) such as lead times, error rates, and resource utilization. Tracking these metrics ensures that workflows remain aligned with organizational goals.
Key Insight: Teams that regularly review and update their process maps using software tools can adapt to changing business needs. This adaptability ensures sustained alignment between team efforts and company objectives.
Encouraging Collaboration to Align Goals
Collaboration plays a crucial role in aligning process maps with organizational goals. Teams should involve all stakeholders during the mapping process to gather diverse perspectives. This inclusive approach ensures that the final process map reflects both team capabilities and strategic priorities.
Tip: During mapping sessions, tools like flowcharts can simplify complex workflows into manageable steps. These visual aids help teams identify inefficiencies and propose solutions that align with organizational objectives.
Driving Continuous Improvement Through Alignment
Aligning process maps with goals is not a one-time effort. Organizations must regularly review and refine their workflows to maintain alignment. Lean Six Sigma emphasizes continuous improvement, encouraging teams to revisit their processes and make adjustments as needed.
Pro Tip: Use value stream maps to periodically assess workflows. These maps provide a comprehensive view of operations, helping teams identify new opportunities for improvement and ensuring that processes continue to support organizational goals.
By aligning process maps with team and organizational objectives, systems and teams can achieve greater efficiency and purpose. This alignment not only enhances productivity but also motivates team members by showing them how their efforts contribute to the company's success. For organizations seeking expert guidance on process mapping, reaching out to experienced professionals can provide the support needed to achieve these outcomes.
Overcoming Challenges in Lean Six Sigma Process Mapping
Addressing Resistance to Change
Resistance to change often emerges as a significant challenge during the implementation of Lean Six Sigma Process Mapping. Team members may feel apprehensive about altering familiar workflows or adopting new methodologies. This hesitation can stem from a lack of understanding, fear of increased workload, or concerns about job security.
To address this resistance, organizations must prioritize clear communication and active engagement. Leaders should explain the purpose and benefits of process mapping, emphasizing how it improves efficiency and collaboration. Hosting workshops or training sessions can help team members understand the methodology and its positive impact on their roles. Encouraging open dialogue allows individuals to voice concerns and fosters a sense of inclusion.
Tip: Involving team members in the mapping process from the beginning builds trust and ownership. When individuals contribute to designing the workflow, they are more likely to support its implementation.
Stakeholder management also plays a crucial role in overcoming resistance. Leaders must identify key stakeholders and ensure their alignment with the project’s objectives. By addressing their concerns and demonstrating the value of Lean Six Sigma Process Mapping, organizations can create a supportive environment for change.
Ensuring Clarity in Process Definitions
Unclear process definitions can hinder the effectiveness of Lean Six Sigma Process Mapping. Ambiguities in workflows lead to confusion, miscommunication, and inefficiencies. Teams must ensure that every step, input, and output is clearly defined and documented.
To achieve clarity, organizations should focus on problem definition and project scoping. Defining the scope of the process helps teams establish boundaries and avoid unnecessary complexity. For example, specifying where a process begins and ends ensures that all participants share a common understanding. Clear objectives guide the mapping effort and keep the team focused on desired outcomes.
Practical Tip: Use standardized symbols and terminology in process maps. This consistency makes the maps easier to interpret and reduces the risk of miscommunication.
Gathering input from team members is essential for accurate process definitions. Each individual brings unique insights based on their role, ensuring that no critical details are overlooked. Collaborative brainstorming sessions or interviews can help teams identify potential gaps and refine their workflows.
Avoiding Overcomplication in Mapping
Overcomplicating process maps can overwhelm teams and reduce their effectiveness. Complex maps with excessive details make it difficult to identify inefficiencies or communicate workflows clearly. Simplicity and focus are key to creating actionable and user-friendly process maps.
Teams should prioritize the most critical steps and avoid including unnecessary information. For instance, focusing on value-added activities helps streamline the map and highlights areas for improvement. Tools like SIPOC diagrams provide a high-level overview of processes, making them accessible to all team members.
Key Insight: A simple process map is more effective for analysis and collaboration. Teams can always add details later if needed, but starting with a clear and concise representation ensures better engagement.
Leaders must also guide teams in maintaining focus during the mapping process. Setting clear objectives and defining the scope prevents unnecessary complexity. Regular reviews of the map help identify and eliminate redundant or irrelevant elements.
By addressing these challenges, systems and teams can unlock the full potential of Lean Six Sigma Process Mapping. Organizations seeking expert guidance can reach out to professionals for tailored support and insights.
Maintaining Team Engagement Throughout the Process
Sustaining team engagement during Lean Six Sigma process mapping ensures the success of the initiative. Teams that remain motivated and involved contribute valuable insights and foster a collaborative environment. Leaders must adopt strategies that keep team members actively participating throughout the process.
1. Foster Open Communication
Clear and consistent communication builds trust and keeps team members informed. Leaders should encourage open dialogue by creating opportunities for team members to share their thoughts and concerns. Regular check-ins and feedback sessions help address challenges early and maintain alignment.
Key Insight: Open communication reduces misunderstandings and ensures that everyone feels heard. Teams that engage in transparent discussions are more likely to stay committed to the process.
2. Define Clear Objectives and Roles
Clarity in objectives and roles eliminates confusion and provides direction. Teams perform better when they understand the purpose of the process mapping exercise and their individual responsibilities. Leaders should outline specific goals and assign tasks based on each member’s expertise.
Actionable Tip: Use tools like SIPOC diagrams to provide a high-level overview of the process. These diagrams help team members see how their contributions fit into the larger workflow.
3. Recognize and Celebrate Contributions
Acknowledging team efforts boosts morale and reinforces engagement. Leaders should celebrate milestones, no matter how small, to show appreciation for the team’s hard work. Recognition motivates individuals to stay involved and continue contributing.
Example: A manufacturing team that successfully identifies and resolves a bottleneck can celebrate the achievement with a team lunch or public acknowledgment during a meeting.
4. Provide Training and Resources
Equipping team members with the necessary skills and tools ensures their confidence and competence. Training sessions on Lean Six Sigma principles, such as problem definition and project scoping, empower teams to participate effectively. Access to resources like process mapping software simplifies the task and enhances productivity.
Pro Tip: Offer hands-on workshops where team members can practice creating process maps. This practical approach builds familiarity and reduces resistance to change.
5. Encourage Collaboration and Inclusion
Involving all stakeholders fosters a sense of ownership and accountability. Leaders should create an inclusive environment where every team member feels valued. Collaborative brainstorming sessions allow diverse perspectives to shape the process map, leading to more comprehensive solutions.
Insight: Teams that collaborate effectively during mapping sessions often uncover innovative ideas and achieve better outcomes.
6. Monitor Engagement Levels
Regularly assessing team engagement helps identify potential issues early. Leaders should observe participation during meetings and solicit feedback to gauge morale. Addressing disengagement promptly prevents it from affecting the overall progress.
Actionable Tip: Use surveys or one-on-one discussions to gather honest feedback about the process. Adjust strategies based on the input to maintain high engagement levels.
Maintaining team engagement requires intentional effort and strategic planning. Systems and teams that prioritize communication, clarity, and collaboration experience smoother workflows and better results. For organizations seeking expert guidance on Lean Six Sigma process mapping, reaching out to experienced professionals can provide valuable support and insights.
Real-World Examples of Lean Six Sigma Process Mapping Enhancing Collaboration
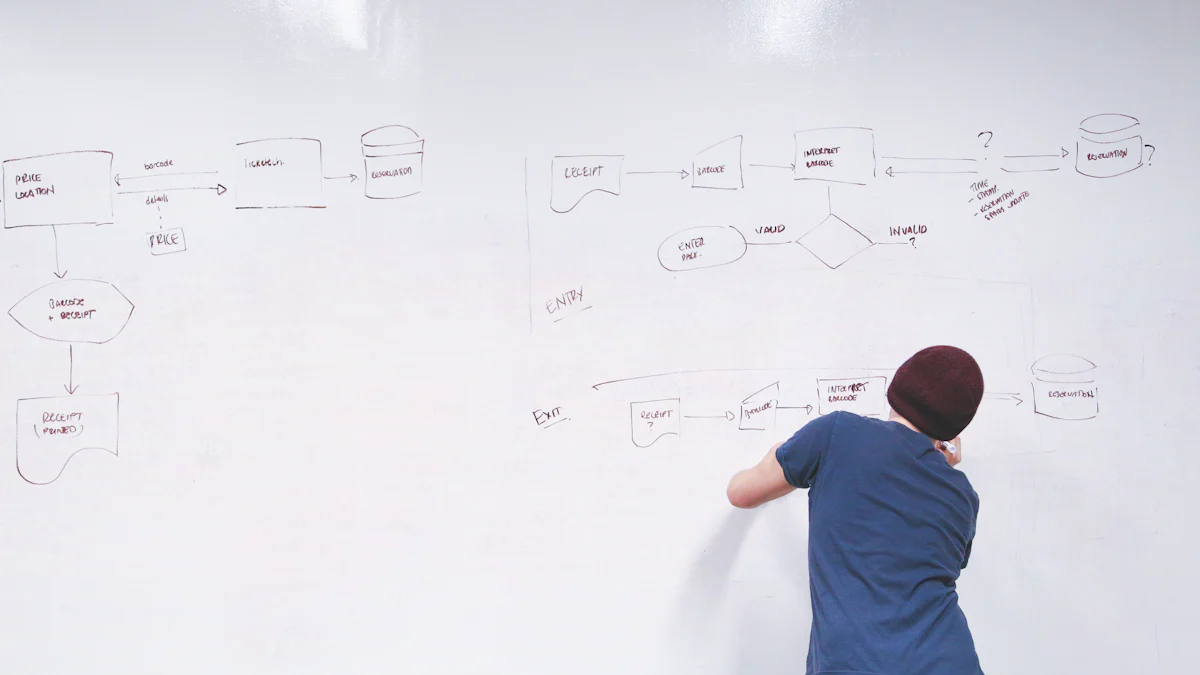
Case Study 1: Streamlining Communication in a Marketing Team
A marketing team at a mid-sized organization faced challenges in coordinating campaigns across multiple channels. Miscommunication between team members caused delays in project timelines and inconsistencies in messaging. To address these issues, the team adopted Lean Six Sigma process mapping.
Using tools like flowcharts and swimlane diagrams, the team visualized their workflows. They identified redundant approval steps and unclear handoff points between content creators and campaign managers. By simplifying the process and clarifying responsibilities, they eliminated unnecessary delays. The team also introduced automated notifications to ensure timely communication.
Outcome: The streamlined workflow improved collaboration and reduced campaign delivery times by 30%. Team members reported higher satisfaction due to the clarity in roles and responsibilities.
Case Study 2: Improving Workflow Efficiency in a Manufacturing Team
A manufacturing company struggled with inefficiencies in its production line. Despite a steady supply of raw materials, the output consistently fell short of expectations. The company suspected bottlenecks and waste within the process. A Lean Six Sigma Green Belt led the initiative to resolve these issues.
The team conducted a thorough process analysis using value stream mapping. They pinpointed delays in material delivery and redundancies in assembly tasks. To address these problems, they standardized document requirements, introduced automated quality checks, and implemented error-proofing measures. These changes reduced defects and minimized rework.
Outcome: The improvements resulted in a significant increase in productivity and a 20% reduction in operational costs. The team achieved smoother workflows and higher-quality outputs, aligning their efforts with organizational goals.
Case Study 3: Enhancing Cross-Department Collaboration in a Tech Company
A tech company faced challenges in coordinating projects between its development and customer support teams. Misaligned priorities and communication gaps led to delays in resolving customer issues. The company turned to Lean Six Sigma process mapping to bridge these gaps.
The teams used SIPOC diagrams to understand the relationship between inputs, processes, and outputs. They identified inefficiencies in the handoff process between departments. By redesigning the workflow, they established clear communication protocols and defined accountability for each step. Regular review sessions ensured alignment between the teams.
Outcome: The enhanced collaboration reduced response times for customer issues by 40%. Both teams reported improved morale and a stronger sense of shared purpose.
These real-world examples highlight the transformative impact of Lean Six Sigma process mapping. Systems and teams that adopt these methodologies can achieve better communication, streamlined workflows, and stronger alignment with organizational objectives. For organizations seeking to implement similar improvements, reaching out to experienced professionals can provide valuable guidance and support.
Tools and Software for Lean Six Sigma Process Mapping
Overview of Popular Process Mapping Tools
Lean Six Sigma practitioners rely on various tools to create effective process maps. These tools simplify workflows, enhance visualization, and improve collaboration among team members. Popular options include:
Microsoft Visio: A widely used tool for creating flowcharts, swimlane diagrams, and value stream maps. Its drag-and-drop interface makes it user-friendly for teams across industries.
Lucidchart: A cloud-based platform that supports real-time collaboration. Teams can work together to design and edit process maps, making it ideal for remote or distributed teams.
IBM Blueworks Live: This tool specializes in business process modeling. It offers features for documenting, analyzing, and optimizing workflows, making it a favorite among large organizations.
Minitab Workspace: Designed specifically for Lean Six Sigma projects, this software includes templates for SIPOC diagrams, value stream maps, and other process mapping tools.
Draw.io: A free, web-based tool that provides basic process mapping capabilities. It is suitable for teams seeking a cost-effective solution.
Survey results from financial institutions implementing Lean Six Sigma revealed that tools like Microsoft Visio and Lucidchart significantly reduced underwriting resubmits by improving workflow clarity.
These tools cater to different needs, from basic mapping to advanced analytics. Selecting the right one depends on the complexity of the process and the team's requirements.
Features to Look for in Process Mapping Software
Choosing the right process mapping software requires careful evaluation of its features. Effective tools should offer functionalities that align with Lean Six Sigma principles. Key features to consider include:
Ease of Use: Intuitive interfaces reduce the learning curve for team members. Drag-and-drop functionality and pre-built templates simplify the mapping process.
Collaboration Capabilities: Real-time editing and commenting features enable teams to work together seamlessly. This fosters better communication and ensures alignment during mapping sessions.
Customization Options: The ability to tailor maps to specific workflows enhances their relevance. Look for software that allows users to modify symbols, colors, and layouts.
Integration with Other Tools: Compatibility with project management or data analysis software streamlines workflows. For example, integration with Minitab or Excel can enhance data-driven decision-making.
Cloud Accessibility: Cloud-based platforms provide flexibility for remote teams. They allow users to access and edit process maps from any location.
Reporting and Analytics: Advanced tools offer insights into workflow performance. Features like bottleneck analysis and KPI tracking help teams identify inefficiencies and measure improvements.
Teams in finance have reported that software with robust collaboration features improved cross-departmental communication, leading to smoother project execution.
Selecting software with these features ensures that systems and teams can create accurate, actionable process maps that drive continuous improvement.
Tips for Choosing the Right Tool for Your Team
Selecting the best process mapping tool involves understanding the team's needs and evaluating available options. Follow these tips to make an informed decision:
Assess Team Requirements
Identify the complexity of the processes and the team's technical expertise. For simple workflows, tools like Draw.io may suffice. For advanced analysis, consider Minitab Workspace or IBM Blueworks Live.Prioritize Collaboration
Choose software that supports real-time collaboration if the team operates remotely or across departments. Lucidchart excels in this area, enabling multiple users to edit and comment simultaneously.Consider Budget Constraints
Evaluate the cost of the software against its features. Free tools like Draw.io are suitable for small teams, while larger organizations may benefit from investing in premium options like Microsoft Visio.Test Before Committing
Many tools offer free trials or demos. Encourage the team to test different options to determine which one aligns best with their workflow and preferences.Seek Scalability
Select software that can grow with the organization. Scalable tools accommodate increasing complexity and additional users as the team expands.Evaluate Integration Needs
Ensure the tool integrates with existing systems. For example, teams using data analysis software should look for tools compatible with platforms like Excel or Minitab.
Financial institutions implementing Lean Six Sigma have found that scalable tools with strong integration capabilities supported long-term process optimization efforts.
By following these tips, systems and teams can select a process mapping tool that enhances collaboration, streamlines workflows, and aligns with organizational goals. For expert guidance on choosing the right software, reach out to professionals experienced in Lean Six Sigma methodologies.
Sustaining Collaboration Through Continuous Process Improvement
Regularly Reviewing and Updating Process Maps
Regular reviews of process maps ensure workflows remain efficient and relevant. Teams should revisit their maps periodically to identify outdated steps or inefficiencies. This practice helps maintain alignment with organizational goals and adapts processes to evolving needs.
For example, manufacturing teams often use process maps to track production workflows. By reviewing these maps, they can pinpoint areas where delays or defects occur. Adjustments based on these insights lead to smoother operations and higher-quality outputs. Regular updates also prevent stagnation, ensuring processes continue to meet customer expectations.
Key Insight: A detailed and accurate process map promotes a clear understanding of workflows. This clarity fosters better ideas and solutions during improvement initiatives.
Teams should establish a schedule for reviewing process maps. Quarterly or biannual reviews work well for most organizations. During these sessions, team members can analyze performance metrics, such as lead times or error rates, to assess the effectiveness of current workflows. Incorporating feedback from these reviews ensures continuous improvement.
Encouraging Team Feedback and Participation
Team feedback plays a vital role in sustaining collaboration. Involving team members in process improvement fosters a sense of ownership and accountability. Their insights often reveal inefficiencies or challenges that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Systems and teams can organize workshops or brainstorming sessions to gather input. For instance, cross-functional teams benefit from open discussions where members share their perspectives on handoff points or communication gaps. These sessions encourage active participation and strengthen team dynamics.
Practical Tip: Use visual tools like flowcharts or SIPOC diagrams during feedback sessions. These tools provide a clear representation of workflows, making it easier for team members to identify pain points and propose solutions.
Encouraging participation also builds trust within the team. When individuals see their suggestions implemented, they feel valued and motivated to contribute further. This collaborative approach not only enhances workflows but also strengthens relationships among team members.
Integrating Process Mapping into Team Meetings
Integrating process mapping into regular team meetings ensures continuous focus on improvement. Teams can use these meetings to review workflows, discuss challenges, and propose adjustments. This practice keeps process optimization at the forefront of daily operations.
For example, teams resolving bottlenecks often rely on process maps to visualize issues and track progress. By incorporating these maps into meetings, they can monitor changes and ensure alignment with team objectives. This proactive approach prevents small inefficiencies from escalating into larger problems.
Real-World Impact: Experts use process mapping to obtain a visual representation of workflows. This clarity helps teams track progress and identify areas for improvement effectively.
To integrate process mapping seamlessly, teams should allocate dedicated time during meetings. Leaders can present updated maps, highlight key metrics, and facilitate discussions on potential improvements. Using digital tools, such as Lucidchart or Microsoft Visio, enhances collaboration by allowing real-time edits and annotations.
Pro Tip: Encourage team members to prepare for meetings by reviewing process maps in advance. This preparation ensures productive discussions and actionable outcomes.
By embedding process mapping into team routines, systems and teams create a culture of continuous improvement. This integration not only sustains collaboration but also drives long-term success. For organizations seeking expert guidance on process mapping, reaching out to experienced professionals can provide valuable support and insights.
Celebrating Successes and Learning from Challenges
Recognizing achievements and reflecting on challenges play a vital role in sustaining team collaboration and motivation. Systems and teams that celebrate milestones foster a positive work environment, while analyzing setbacks promotes continuous improvement. Lean Six Sigma process mapping provides a structured framework to support both practices effectively.
Acknowledging Team Achievements
Celebrating successes boosts morale and reinforces the value of teamwork. Teams that achieve process improvements, such as resolving bottlenecks or streamlining workflows, should take time to acknowledge their efforts. Recognition can take various forms:
Public Acknowledgment: Leaders can highlight accomplishments during team meetings or company-wide updates. For example, a team that reduced production delays through process mapping deserves recognition for their contribution to operational efficiency.
Incentives and Rewards: Offering tangible rewards, such as certificates or team lunches, shows appreciation for hard work. These gestures motivate team members to continue striving for excellence.
Visual Displays of Progress: Displaying updated process maps with marked improvements serves as a visual reminder of the team's success. This practice reinforces the impact of their efforts and encourages further collaboration.
"A detailed and accurate process map is critical to improvement as it promotes a clear understanding of the process, leading to more ideas and better solutions." Teams that celebrate their achievements often generate innovative ideas for future projects.
Reflecting on Challenges for Growth
Challenges provide valuable learning opportunities. Teams should analyze setbacks to identify root causes and develop strategies for improvement. Lean Six Sigma process mapping facilitates this reflection by offering a clear visualization of workflows. Key steps include:
Reviewing Process Maps
Teams can revisit their process maps to pinpoint where issues occurred. For instance, a bottleneck identified during onboarding might reveal inefficiencies in task delegation or communication.Encouraging Open Discussions
Creating a safe space for team members to share their perspectives fosters transparency. Teams can discuss what went wrong, why it happened, and how to prevent similar issues in the future.Documenting Lessons Learned
Recording insights from challenges ensures that teams retain valuable knowledge. These lessons can guide future process mapping efforts and improve overall performance.
Experts use process mapping to obtain a visual representation of the workflow and track the progress of processes. This approach helps teams identify areas for improvement and implement effective solutions.
Balancing Success and Challenges
Striking a balance between celebrating successes and addressing challenges strengthens team dynamics. Systems and teams that focus on both aspects create a culture of continuous improvement. Recognizing achievements builds confidence, while learning from setbacks fosters resilience.
Teams that wish to enhance their collaboration through Lean Six Sigma process mapping can benefit from expert guidance. For tailored support and insights, organizations are encouraged to reach out to experienced professionals.
Lean Six Sigma Process Mapping empowers teams to achieve better collaboration by providing clarity and transparency in workflows. It simplifies complex processes, enabling team members to work with a shared understanding and focus on common goals. By following the outlined steps, systems and teams can identify inefficiencies, resolve bottlenecks, and foster alignment with organizational objectives. Starting small and involving team members ensures smoother implementation and continuous improvement. Teams that embrace this approach unlock innovative ideas and sustainable efficiency. For tailored guidance, systems and teams can reach out to experienced professionals to maximize their results.
FAQ
What is Lean Six Sigma Process Mapping?
Lean Six Sigma Process Mapping is a visual tool that outlines the steps, inputs, and outputs of a process. It helps teams understand workflows by breaking them into smaller, manageable components. This method highlights inefficiencies, redundancies, and areas for improvement. Experts emphasize its value in providing a clear representation of workflows, which aids in tracking progress and identifying bottlenecks.
Expert Insight: "Experts also use process mapping to obtain a visual representation of the workflow and to track the progress of processes."
How does Lean Six Sigma Process Mapping improve team collaboration?
Lean Six Sigma Process Mapping enhances collaboration by creating a shared understanding of workflows. Teams gain clarity on roles, responsibilities, and task sequences. This alignment reduces confusion and fosters better communication. Visual tools like flowcharts and swimlane diagrams bridge gaps between team members, especially in cross-functional teams.
What types of process maps are used in Lean Six Sigma?
Lean Six Sigma employs several types of process maps, including:
SIPOC Diagrams: Provide a high-level overview of Suppliers, Inputs, Processes, Outputs, and Customers.
Value Stream Maps: Focus on identifying value-added and non-value-added activities.
Swimlane Diagrams: Separate tasks by roles or departments to clarify responsibilities.
Flowcharts: Represent workflows in a simple, sequential format.
Each type serves specific purposes, helping teams analyze and optimize workflows effectively.
How can process mapping help identify bottlenecks?
Process mapping visually represents each step in a workflow, making it easier to pinpoint delays or inefficiencies. Bottlenecks often appear as areas where tasks pile up or progress slows. Tools like value stream maps highlight these issues by distinguishing between value-added and non-value-added activities. Teams can then focus on resolving these obstacles to improve productivity.
What are the key benefits of using process mapping for onboarding new team members?
Process mapping simplifies onboarding by providing a clear overview of workflows. New team members can quickly understand their roles and how their tasks fit into the larger system. Tools like flowcharts and SIPOC diagrams make complex processes more accessible, reducing training time and ensuring consistency in task execution.
How do teams sustain collaboration through Lean Six Sigma Process Mapping?
Teams sustain collaboration by regularly reviewing and updating process maps. This practice ensures workflows remain efficient and aligned with organizational goals. Encouraging team feedback during these reviews fosters a sense of ownership. Integrating process mapping into team meetings keeps improvement efforts ongoing and relevant.
What challenges might teams face when implementing process mapping?
Teams may encounter challenges such as resistance to change, unclear process definitions, or overcomplicated maps. Addressing these issues requires clear communication, standardized symbols, and a focus on simplicity. Leaders should involve team members in the mapping process to build trust and ensure alignment.
How can systems and teams choose the right process mapping tool?
Selecting the right tool depends on team needs and workflow complexity. Key features to consider include ease of use, collaboration capabilities, and integration with existing systems. Popular tools like Microsoft Visio, Lucidchart, and IBM Blueworks Live offer various functionalities to support Lean Six Sigma initiatives.
Can process mapping align team goals with organizational objectives?
Yes, process mapping bridges the gap between team activities and organizational goals. Tools like value stream maps provide a high-level view of workflows, helping teams focus on value-added activities. This alignment ensures that daily tasks contribute directly to broader business outcomes.
How can systems and teams get started with Lean Six Sigma Process Mapping?
To begin, teams should define the process scope and objectives. Gathering input from team members ensures accuracy and inclusivity. Using tools like SIPOC diagrams or flowcharts, teams can map out current workflows, identify inefficiencies, and design optimized processes. For expert guidance, systems and teams can reach out to professionals experienced in Lean Six Sigma methodologies.



