3 Ways Six Sigma Methodology Improves Quality

The Six Sigma Methodology empowers organizations to achieve exceptional quality standards by reducing defects and improving process consistency. It employs a data-driven approach to identify and address variability, enabling businesses to deliver reliable products and services. For instance, Six Sigma aims to achieve fewer than four defects per million units, ensuring superior quality. By systematically applying tools like the DMAIC framework, businesses can pinpoint inefficiencies and implement targeted improvements. This methodology fosters continuous improvement, helping industries like manufacturing and healthcare save time and resources. As a result, companies enhance customer satisfaction and remain competitive in business management, leveraging their knowledge to boost sales and operational efficiency.
Key Takeaways
Six Sigma cuts mistakes by finding and fixing main problems.
Making processes the same reduces changes and keeps quality steady.
Checking quality often, like with audits, stops mistakes early.
Lean Six Sigma removes waste, making work faster and cheaper.
Using data to decide improves accuracy and solves problems quickly.
Teaching workers Six Sigma helps them improve and aim for quality.
Changing processes to fit customer needs makes them happier and loyal.
Six Sigma uses proven methods to ensure success and great results.
Reducing Defects with Six Sigma Methodology
Reducing defects is one of the core objectives of the six sigma methodology. By identifying root causes and implementing quality control measures, organizations can achieve significant improvements in product and process quality. This section explores how six sigma techniques, such as the DMAIC method, help businesses minimize defects and ensure consistent outcomes.
Identifying and Addressing Root Causes
Using the DMAIC framework to analyze and resolve issues
The DMAIC method—Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control—provides a structured approach to uncovering and addressing the root causes of defects. Teams begin by defining the problem and measuring current performance. They then analyze data to identify underlying issues, implement improvements, and establish controls to sustain the gains.
For example, six sigma teams often use tools like the 5 Whys and Fishbone Diagrams to pinpoint the root causes of quality issues. The 5 Whys technique involves repeatedly asking "Why?" to drill down to the core problem, while the Fishbone Diagram visually maps potential causes. These tools enable teams to focus on the most critical factors affecting quality.
Description | |
|---|---|
Missing Values | Instances where data entries are absent. |
Invalid Entries | Data that does not conform to expected formats or values. |
Duplicate Records | Repeated entries that can skew analysis and results. |
Outdated Information | Data that is no longer current or relevant. |
Inconsistent Formats | Variations in data formats or naming conventions across systems. |
In automotive manufacturing, for instance, applying DMAIC has led to remarkable defect reductions. A study revealed that the automotive industry improved its sigma level from 3.5σ (22,700 defects per million opportunities) to 5.1σ (233 defects per million opportunities), achieving a 99% reduction in defects.
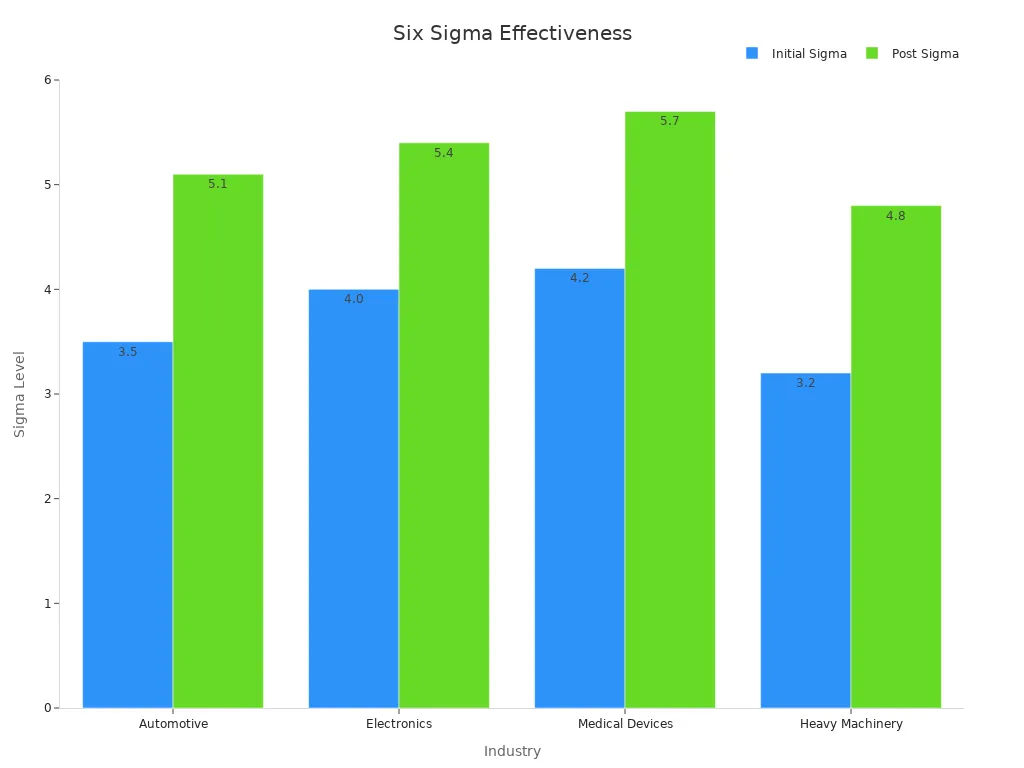
Example: Reducing defects in automotive manufacturing
Automotive manufacturers have successfully used six sigma techniques to enhance production quality. By employing the DMAIC framework, they identified inefficiencies in assembly lines and addressed them through process optimization. This approach not only reduced defects but also improved customer satisfaction by delivering reliable vehicles.
Implementing Quality Control Measures
Standardizing processes to ensure consistency
Standardization is a key aspect of six sigma. By creating uniform procedures, organizations can minimize variability and ensure consistent results. Statistical process control methods, for example, monitor production processes to detect deviations early. Regular inspections and audits further help maintain quality standards.
Lean six sigma emphasizes eliminating waste and streamlining workflows. Teams often adopt real-time monitoring systems to quickly identify and correct errors. Additionally, ongoing employee training ensures that staff understand and adhere to quality control measures.
Key practices for minimizing variability:
Standardizing work instructions to reduce errors.
Conducting regular audits to identify inconsistencies.
Encouraging a culture of continuous improvement.
Example: Error-proofing in healthcare to prevent medication errors
In healthcare, six sigma has been instrumental in reducing medication errors. Hospitals have implemented error-proofing techniques, such as barcoding systems for medication administration. These systems ensure that patients receive the correct dosage and medication, significantly improving safety and reducing variability in care delivery.
By combining the DMAIC method with robust quality control measures, organizations across industries can achieve world-class performance. Six sigma's focus on defect reduction not only enhances product quality but also builds trust with customers.
Enhancing Process Efficiency Through Six Sigma
Streamlining Operations
Eliminating waste and non-value-added activities
Six Sigma methodology focuses on eliminating waste and non-value-added activities to streamline operations. By identifying inefficiencies, organizations can optimize workflows and improve overall productivity. Lean Six Sigma principles play a crucial role in this process, emphasizing the removal of unnecessary steps and redundancies. Teams often use tools like Value Stream Mapping to visualize processes and pinpoint areas for improvement.
For example, retail companies have successfully applied Lean Six Sigma to enhance supply chain efficiency. By analyzing inventory management and transportation processes, they reduced lead times and minimized stockouts. This approach not only improved operational performance but also enhanced customer satisfaction by ensuring timely product availability.
Key Benefits of Streamlining Operations:
Faster delivery times.
Improved process stability.
Goal | Description |
|---|---|
Identify and remove non-value-added activities. | |
Reduction of Variability | Enhance consistency of process outputs. |
Customer-Centric Focus | Drive improvements impacting customer satisfaction. |
Optimizing Resource Allocation
Balancing workloads and reducing downtime
Six Sigma provides tools to optimize resource allocation by balancing workloads and reducing downtime. The DMAIC framework helps teams analyze resource utilization and identify bottlenecks. By redistributing tasks and improving scheduling, organizations can maximize efficiency and minimize idle time.
Industries like call centers have leveraged Six Sigma to increase productivity. For instance, by analyzing call patterns and employee performance, managers implemented better shift rotations and workload distribution. This resulted in shorter wait times for customers and higher employee satisfaction.
Industry/Company | Outcome |
|---|---|
Catalent Pharma Solutions | Reduced mistake rates and improved production through Six Sigma methodologies. |
Texas Department of Licensing | Streamlined record management and reduced storage costs using Six Sigma. |
Baxter Manufacturing | Enhanced environmental performance and reduced waste while increasing revenue. |
Aerospace Manufacturer | Achieved a 46% reduction in machining cycle time and improved profitability. |
Ford Motors | $2.19 billion in waste reduction and a five-point increase in customer satisfaction. |
Shimadzu Medical | 40% decrease in defects in contact lens manufacturing through Lean Six Sigma principles. |
By optimizing resource allocation, organizations can achieve better results with fewer resources. This approach not only reduces costs but also enhances process efficiency, making Six Sigma a valuable tool across industries.
Improving Customer Satisfaction with Six Sigma
Delivering Consistent Quality
Meeting customer expectations through reliable processes
Six Sigma ensures consistent quality by reducing process variations and maintaining high standards. Organizations use the DMAIC framework to identify inefficiencies, implement improvements, and sustain results. This structured approach guarantees that customers receive reliable products and services every time. By focusing on predictable outcomes and minimizing defects, businesses can meet or exceed customer expectations.
Metrics like First Pass Yield (FPY) and Defects Per Unit (DPU) highlight the impact of Six Sigma on quality. FPY measures the percentage of units passing inspection on the first attempt, while DPU tracks the average number of defects per unit. Both metrics reflect the effectiveness of Six Sigma techniques in delivering consistent results. Additionally, monitoring the Cost of Poor Quality (COPQ) helps organizations reduce financial losses caused by defects, further enhancing customer satisfaction.
Metric | Description |
|---|---|
First Pass Yield (FPY) | Measures the percentage of units passing inspection on the first attempt, indicating process quality. |
Defects Per Unit (DPU) | Average number of defects per unit, lower values indicate higher quality. |
Cost of Poor Quality (COPQ) | Financial impact of defects, reducing it increases profitability and customer satisfaction. |
Example: Ensuring consistent product quality in food production
In the food production industry, Six Sigma tools have been instrumental in maintaining consistent quality. Teams use DMAIC to analyze production processes, identify sources of variability, and implement corrective actions. For example, by standardizing ingredient measurements and cooking times, food manufacturers ensure uniform taste and texture across batches. This consistency builds customer trust and loyalty, as consumers can rely on the same high-quality experience with every purchase.
Adapting to Customer Needs
Using Six Sigma tools to respond to changing demands
Six Sigma tools enable organizations to adapt processes to evolving customer needs. By leveraging data-driven insights, businesses can understand customer preferences and tailor their offerings accordingly. The DMAIC framework plays a crucial role in this adaptation. Teams define customer requirements, measure current performance, and analyze gaps. They then implement improvements and establish controls to sustain the changes.
Streamlined processes enhance responsiveness and efficiency, allowing businesses to address customer demands more effectively. Proactive issue identification prevents dissatisfaction, demonstrating a commitment to quality. Additionally, fostering a customer-centric culture encourages employees to engage in continuous improvement, further boosting satisfaction.
Key benefits of adapting to customer needs:
Improved product reliability increases customer trust.
Tailored services enhance customer experiences.
Faster problem resolution reduces wait times and frustration.
Example: Enhancing service delivery in the hospitality industry
The hospitality industry has successfully applied Six Sigma techniques to improve service delivery. Hotels use DMAIC to analyze guest feedback, identify pain points, and implement targeted improvements. For instance, by streamlining check-in processes and optimizing room cleaning schedules, hotels reduce wait times and enhance guest satisfaction. This customer-focused approach ensures that services align with evolving expectations, creating memorable experiences for guests.
By delivering consistent quality and adapting to customer needs, Six Sigma methodology empowers organizations to achieve higher satisfaction levels. Its focus on data-driven decision-making and continuous improvement makes it an invaluable tool for businesses striving to exceed customer expectations.
Building a Culture of Continuous Improvement with Six Sigma

Empowering Teams Through Training
Providing Six Sigma certifications to foster expertise
Six Sigma certifications play a vital role in fostering expertise among employees. These certifications equip teams with the knowledge and skills needed to apply Six Sigma tools effectively. Organizations often invest in training programs to ensure employees understand the DMAIC framework and other Six Sigma techniques. Certified professionals can identify inefficiencies, implement solutions, and sustain improvements, contributing to continuous process improvement.
For example, companies like Motorola and General Electric have prioritized Six Sigma certification programs to enhance employee capabilities. These initiatives have led to optimized processes, improved operational excellence, and increased employee engagement. By empowering teams with certifications, businesses create a culture of continuous improvement that drives long-term success.
Organization | Implementation Focus | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
Motorola | HR processes | Improved efficiency, cost savings, enhanced employee satisfaction |
General Electric | Recruitment and performance management | Enhanced operational excellence and reputation |
Various Industries | HR processes | Optimized processes, improved employee engagement, operational excellence |
Example: Employee-led quality improvement initiatives
Employee-led initiatives often emerge as a result of Six Sigma certifications. Certified employees take ownership of quality management strategies, leading projects that address inefficiencies and improve outcomes. For instance, teams may use Six Sigma tools like Pareto charts and control charts to identify and resolve recurring issues. These initiatives not only enhance process efficiency but also foster a sense of accountability and collaboration among employees.
Encouraging Data-Driven Decision Making
Shifting from intuition to evidence-based strategies
Six Sigma promotes a shift from intuition-based decision-making to evidence-based strategies. This data-driven methodology relies on empirical evidence and statistical analysis to guide business decisions. Evidence-Based Management (EBM) integrates scientific principles into decision-making processes, improving accuracy and effectiveness. Organizations use Six Sigma tools to analyze data, identify trends, and implement solutions that align with business goals.
Benefits of Data-Driven Decision Making:
Faster decision-making through objective data analysis.
Increased efficiency by identifying waste and streamlining operations.
Enhanced customer satisfaction by aligning changes with customer needs.
Example: Using statistical tools to guide business decisions
Organizations across industries use statistical tools to make informed decisions. Manufacturing companies monitor critical processes using Statistical Process Control (SPC) charts to detect and correct deviations. Hospitals analyze patient satisfaction surveys to identify areas for improvement and address root causes of dissatisfaction. Marketing teams conduct A/B testing to compare campaign effectiveness and select strategies with higher conversion rates. These examples demonstrate how Six Sigma techniques enable businesses to achieve measurable improvements through data-driven methodologies.
By empowering teams through Six Sigma certifications and encouraging evidence-based decision-making, organizations build a culture of continuous improvement. This approach not only enhances operational efficiency but also fosters innovation and collaboration, ensuring sustainable growth.
Reducing Costs While Maintaining Quality Using Six Sigma
Lowering Operational Costs
Reducing waste and rework through process improvements
Six sigma helps organizations lower operational costs by reducing waste and rework. By identifying inefficiencies and eliminating non-value-added activities, businesses can streamline their processes. This approach minimizes errors and ensures resources are used effectively. Tools like Value Stream Mapping and Root Cause Analysis allow teams to pinpoint areas of waste and implement targeted improvements.
For example, companies in the electronics manufacturing industry have used six sigma to optimize production lines. By analyzing defect rates and addressing root causes, they reduced rework and scrap materials. This not only lowered costs but also improved production efficiency.
Company | Cost Reduction (%) | Annual Savings ($) |
|---|---|---|
GE | Nearly $1 billion | |
Motorola | N/A | $17 billion over a decade |
Honeywell | N/A | Exceeding $600 million |
The table above highlights the significant cost savings achieved by companies that implemented six sigma. These results demonstrate the methodology's effectiveness in reducing operational expenses while maintaining high-quality standards.
Example: Cost savings in electronics manufacturing
Electronics manufacturers have successfully applied six sigma to achieve cost savings. By using tools like Statistical Process Control (SPC), they monitored production processes and identified variations. Corrective actions reduced defects and improved first-pass yields. This approach not only saved money but also enhanced product reliability, leading to increased customer satisfaction.
Preventing Costly Failures
Proactively addressing potential issues before escalation
Six sigma emphasizes proactive strategies to prevent costly failures. Proper planning, continuous monitoring, and employee training are essential components of this approach. Control plans help maintain improvements and mitigate risks. Regular audits ensure processes remain efficient and effective over time.
Key Practices for Preventing Failures:
Develop control plans to sustain improvements.
Conduct regular audits to identify potential risks.
Train employees to recognize and address issues early.
By addressing potential problems before they escalate, organizations can avoid significant financial losses. This proactive approach ensures processes remain stable and reliable, reducing the likelihood of failures.
Example: Avoiding product recalls in consumer goods
Consumer goods companies have used six sigma to prevent product recalls. By implementing robust quality control measures, they identified defects early in the production process. For instance, teams used Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) to assess risks and prioritize corrective actions. This approach minimized the chances of defective products reaching customers, saving companies from costly recalls and reputational damage.
By reducing waste, rework, and failures, six sigma enables organizations to achieve cost savings without compromising quality. Its data-driven approach ensures processes remain efficient and reliable, making it a valuable tool for businesses across industries.
Adapting Six Sigma Methodology Across Industries
Applications in Manufacturing
Reducing defects and improving production efficiency
Manufacturing industries have embraced six sigma to reduce defects and enhance production efficiency. By focusing on data-driven decision-making, manufacturers can identify inefficiencies and implement targeted improvements. This approach minimizes variability, leading to fewer reworks and higher customer satisfaction. Lean six sigma principles, which combine waste reduction with process optimization, have proven particularly effective in achieving these goals.
Key benefits of six sigma in manufacturing:
Enhanced product quality by reducing variability and defects.
Increased process efficiency, allowing faster production and higher output.
Significant cost savings through reduced waste and operational expenses.
For example, Company A reduced product defects from 15% to 2% and cut production time by 30% after adopting six sigma. Similarly, Company B achieved a 20% reduction in operational costs and a 50% increase in customer satisfaction. These results highlight the transformative impact of six sigma on manufacturing processes.
Example: Lean Six Sigma in automotive production
The automotive industry has successfully implemented lean six sigma to improve production quality and efficiency. By analyzing assembly line processes, manufacturers identified bottlenecks and eliminated non-value-added activities. This approach reduced production time and improved first-pass yields. For instance, a leading car manufacturer used lean six sigma to streamline its operations, achieving a 99% reduction in defects and boosting customer satisfaction. These improvements not only enhanced product reliability but also strengthened the company’s competitive edge.
Applications in Service Sectors
Enhancing customer experiences and service delivery
Service industries have adopted six sigma to enhance customer experiences and improve service delivery. By focusing on customer-centric processes, organizations can meet or exceed expectations. Lean six sigma tools help identify critical-to-quality factors, ensuring services align with customer needs. This methodology also reduces errors, improving reliability and consistency.
Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
Meet Customer Expectations | Delivering quality goods and services promptly helps in meeting or exceeding customer expectations. |
Reduce Defects | Aiming for near perfection minimizes errors and flaws in service processes. |
Quality | Enhancing reliability, consistency, and overall quality of outputs is the end goal of six sigma. |
Focus on the Customer | Utilizing customer feedback through surveys and social media helps define Critical-to-Quality factors. |
Organizations increasingly integrate customer feedback into lean six sigma initiatives. This practice helps identify areas for improvement that directly impact satisfaction. For example, structured questionnaires and online feedback platforms allow businesses to measure satisfaction and prioritize enhancements.
Example: Six Sigma in financial services for error reduction
Financial services have leveraged six sigma to minimize errors and improve operational efficiency. By analyzing transaction processes, banks and insurance companies identified recurring issues and implemented corrective actions. For instance, a major bank used six sigma to reduce loan processing errors, cutting approval times by 40%. This improvement not only enhanced customer satisfaction but also increased trust in the institution’s services. Such examples demonstrate how six sigma drives excellence in service delivery.
The six sigma methodology offers a structured and data-driven approach to improving quality. It reduces defects, enhances efficiency, and boosts customer satisfaction. By emphasizing continuous improvement, it helps organizations adapt to changing demands while maintaining high standards. Lean six sigma combines waste reduction with process optimization, making it a versatile tool across industries. Businesses adopting six sigma achieve measurable improvements in quality, cost savings, and overall performance. Its focus on evidence-based strategies ensures long-term success and operational excellence.
FAQ
What is Six Sigma methodology?
Six Sigma is a data-driven approach that improves quality by reducing defects and variability in processes. It uses tools like the DMAIC framework to identify inefficiencies and implement solutions.
How does Six Sigma differ from Lean methodology?
Six Sigma focuses on reducing defects and variability, while Lean emphasizes eliminating waste and improving flow. Both methodologies complement each other when combined as Lean Six Sigma.
Can Six Sigma be applied outside manufacturing?
Yes, Six Sigma is versatile. Service industries like healthcare, finance, and hospitality use it to enhance customer satisfaction, reduce errors, and improve operational efficiency.
What are the key tools used in Six Sigma?
Common tools include Value Stream Mapping, Fishbone Diagrams, Control Charts, and Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA). These tools help teams analyze and improve processes.
How does Six Sigma improve customer satisfaction?
Six Sigma ensures consistent quality by reducing defects and meeting customer expectations. It adapts processes to changing demands, enhancing reliability and trust.
Is Six Sigma suitable for small businesses?
Small businesses can benefit from Six Sigma by optimizing processes, reducing costs, and improving quality. Its scalability makes it accessible to organizations of all sizes.
What certifications are available for Six Sigma?
Certifications include Yellow Belt, Green Belt, Black Belt, and Master Black Belt. Each level provides expertise in Six Sigma tools and techniques.
How long does it take to see results from Six Sigma?
Results vary by project scope and complexity. Many organizations see measurable improvements within months of implementation.



