10 Essential Small Business Systems Every Owner Needs

Small Business Systems provide the foundation for growth, efficiency, and sustainability. Many owners ask which systems will help them run operations smoothly and scale up. He or she may feel overwhelmed by daily tasks, struggle with role confusion, or face personal strain from burnout and inefficiency. Without a clear methodology, businesses often experience:
Operational chaos and wasted resources
Poor delegation and bottlenecks
Systematization saves time, reduces mistakes, and supports business goals. Even startups with limited resources can implement effective systems and achieve better outcomes.
Key Takeaways
Small business systems help owners save time, reduce errors, and support growth by organizing daily tasks and processes.
Financial management systems like bookkeeping, invoicing, and expense tracking keep money matters clear and improve cash flow.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) tools centralize customer data, automate tasks, and boost sales by building stronger relationships.
Inventory management systems track stock accurately, automate reordering, and maintain good supplier relationships to meet customer demand.
Human resources systems organize employee records, manage payroll, and track time to ensure legal compliance and fair pay.
Operations systems use workflows, SOPs, and project management tools to improve team efficiency and keep tasks on track.
Marketing systems like content planning, social media, and email campaigns help businesses reach the right audience and grow sales.
IT and security systems protect business data with strong access controls, cloud backups, and cybersecurity measures to prevent costly attacks.
Small Business Systems Overview
Small Business Systems form the backbone of successful organizations. These systems combine policies, personnel, equipment, and computer facilities to coordinate business activities and help companies reach their goals. Owners rely on these systems to manage daily operations, support growth, and maintain long-term sustainability. When implemented well, Small Business Systems allow businesses to adapt to changing demands and expand their supply of products, services, or processes.
Technology and strategic planning play a critical role in building scalable systems. Many companies, such as those working with systems and teams, have seen their clients achieve greater efficiency and growth by adopting structured approaches. Clients at systems and teams use integrated solutions to streamline workflows, monitor performance, and align their teams with business objectives. This approach helps them create value from customers, markets, and relationships while preparing for future expansion.
System Strategy
A strong system strategy guides business development and supports efficient operations. Owners set clear key performance indicators (KPIs) that align with project goals. They use advanced analytics tools to monitor progress and refine their strategies. Fostering a feedback culture encourages ongoing optimization and adaptation. Continuous improvement ensures that strategies remain relevant and yield the best outcomes.
Organizations that embed analytics into strategic planning outperform those that rely on intuition. Data-driven strategies provide real-time market insights, cost savings, demand forecasting, and precise performance tracking. Aligning data strategy with business goals leads to faster growth and smarter operations. Companies measure impact using KPIs, targets, and reporting tools, which supports investment decisions and drives innovation.
Benefits
Small Business Systems offer several key benefits:
Improved resource efficiency and investment capacity, measured by financial health indicators like net cash available.
Increased revenue growth, which guides strategic focus and supports long-term success.
Enhanced operational efficiency, identified through profitability ratios and balanced scorecards.
Better decision-making and operational optimization, thanks to effective data and analytics systems.
Centralized data and streamlined strategy tracking using analytics dashboards.
Stronger internal alignment and execution by engaging employees as strategic partners.
Adaptive and informed decision-making through market insights and competitor benchmarking.
These benefits help owners save time, reduce errors, and create a foundation for sustainable growth. By investing in Small Business Systems, companies position themselves for long-term success and scalability.
Financial Management

Bookkeeping
Bookkeeping forms the foundation of any small business’s financial management system. Accurate bookkeeping allows owners to track every dollar that enters or leaves the business. This process involves recording daily transactions, categorizing income and expenses, and reconciling accounts. Organized records help businesses prepare for tax season and avoid costly mistakes. Many owners choose to automate bookkeeping tasks to reduce errors and save time. Automation tools can log transactions, match receipts, and generate reports with minimal manual input. Even simple spreadsheets or basic bookkeeping software can provide a consistent and reliable system for tracking finances. Maintaining up-to-date records ensures that business owners always know their financial position and can make informed decisions.
Invoicing
Invoicing is a critical part of getting paid on time. A clear and efficient invoicing system helps businesses send bills to customers, track outstanding payments, and follow up on overdue accounts. Modern invoicing tools allow owners to create professional invoices, set payment terms, and accept multiple payment methods, including credit cards and online transfers. Many systems also offer features like automated reminders and recurring billing, which reduce the risk of missed payments. By streamlining the invoicing process, businesses can improve cash flow and build stronger relationships with their clients. Timely invoicing also supports accurate financial reporting and simplifies end-of-year accounting.
Expense Tracking
Expense tracking helps businesses control costs and identify areas for savings. Owners record every business expense, from office supplies to travel costs, and categorize them for easy analysis. Consistent expense tracking ensures that all deductions are captured for tax purposes and that spending stays within budget. Many financial management systems offer mobile apps that allow employees to snap photos of receipts and upload them instantly. Automated expense tracking tools can also flag unusual spending patterns and generate detailed reports. By monitoring expenses closely, businesses can make smarter purchasing decisions and avoid unnecessary costs.
Tip: Documenting financial processes—such as logging income, tracking expenses, and reconciling accounts—creates a strong foundation for financial health. Automation and organized records support timely tax filings and confident decision-making.
Accounting Software | Market Share / Popularity | Notes |
|---|---|---|
QuickBooks (Intuit) | Dominant player, widely used by small businesses | |
Xero | Widely used | Popular among fast-growing businesses |
Sage | Widely used | Known for mid-sized business solutions |
FreshBooks | Widely used | Preferred for service-based businesses |
Netsuite | Widely used | Scalable for larger SMBs and enterprises |
Small businesses often rely on accounting software to manage bookkeeping, invoicing, and expense tracking. QuickBooks leads the market in the US, while Xero, Sage, FreshBooks, and Netsuite also serve many small and growing companies. These tools automate key tasks, reduce manual errors, and provide valuable insights for better financial management.
Tools
Small businesses rely on the right tools to manage their finances efficiently. These tools help owners automate tasks, reduce errors, and gain insights into their financial health. Choosing the right software can make daily operations smoother and support long-term growth.
Popular Accounting Software
Many small businesses use accounting software to handle bookkeeping, invoicing, and expense tracking. The following table highlights some of the most widely used options:
Software | Key Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|
QuickBooks | Invoicing, payroll, reporting, tax tools | Most small businesses |
FreshBooks | Time tracking, invoicing, expense management | Service-based businesses |
Xero | Bank reconciliation, inventory, multi-currency | Growing businesses |
Zoho Books | Automation, client portal, integrations | Businesses needing customization |
Wave | Free invoicing, receipt scanning, basic accounting | Startups and freelancers |
Note: Each software offers a free trial. Owners can test features before making a commitment.
Expense Tracking Apps
Mobile apps help business owners track expenses on the go. Employees can upload receipts, categorize spending, and generate reports. Some popular apps include:
Expensify: Automates receipt scanning and expense approval.
Receipt Bank (now Dext): Captures and organizes receipts for easy bookkeeping.
Shoeboxed: Digitizes paper receipts and business cards.
Invoicing Tools
Efficient invoicing tools help businesses get paid faster. Many accounting platforms include built-in invoicing, but standalone tools also exist:
Invoice2go: Customizable invoices and payment tracking.
PayPal Invoicing: Simple invoicing with integrated payment options.
Integrations and Automation
Modern financial tools often integrate with other business systems. For example, accounting software can connect with point-of-sale (POS) systems, e-commerce platforms, and payroll providers. Automation reduces manual data entry and ensures records stay up to date.
Cloud-Based Solutions
Cloud-based tools allow owners to access financial data from anywhere. These solutions offer secure backups and real-time collaboration with accountants or team members. Cloud access also supports remote work and flexible business operations.
Tip: Owners should review their business needs before choosing a tool. Consider factors like budget, ease of use, and integration with existing systems.
Selecting the right financial management tools helps small businesses save time, reduce stress, and make better decisions. With the right setup, owners can focus more on growth and less on paperwork.
Customer Relationship Management
CRM Basics
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems help small businesses organize and manage their interactions with customers. A CRM acts as a central hub for storing customer information, tracking communication, and managing sales activities. With a CRM, businesses can keep all customer data in one place, making it easier to understand customer needs and deliver better service. CRM systems also help teams stay organized by tracking leads, managing follow-ups, and recording every interaction. This structure supports stronger relationships and helps businesses grow by turning prospects into loyal customers.
Features
Effective CRM systems offer a range of features that support small business growth and customer satisfaction. Key features include:
Centralized customer data: Stores all customer information for easy access and a complete view of each relationship.
Sales pipeline and lead management: Tracks leads through every stage, helping teams focus on the most valuable opportunities.
Workflow automation: Automates repetitive tasks like sending emails or reminders, saving time and ensuring consistency.
Multichannel customer interaction tracking: Monitors communication across phone, email, social media, and chat to deliver a personalized experience.
Customer support and service tools: Helps teams manage and resolve customer issues quickly and efficiently.
Customization: Adapts to unique business processes and needs.
Intuitive interface: Easy for employees to learn and use, which encourages adoption.
Flexibility and scalability: Grows with the business, supporting more users and data as needed.
Collaboration tools: Improves teamwork and communication within the company.
Integration capabilities: Connects with other business tools to streamline workflows.
Cloud-based access: Allows remote access to data and supports flexible work environments.
Enhanced reporting: Provides real-time insights with customizable dashboards.
Increased productivity: Automation reduces manual work, letting teams focus on important tasks.
Cost savings: Efficient processes lead to faster sales and higher revenue.
Better customer experience: Ensures no customer is overlooked, building loyalty and trust.
Tip: Choosing a CRM with strong automation and integration features can help small businesses save time and reduce errors.
Tools
Many CRM tools are available for small businesses, each offering different strengths. User satisfaction ratings help owners compare options and choose the best fit for their needs. The table below highlights some of the most recommended CRM tools and their ratings:
CRM Tool | User Satisfaction Rating | Notes on Suitability for Small Businesses |
|---|---|---|
Zoho Desk | 4.5 | Widely recognized as suitable for small to medium businesses |
Freshdesk Omni | 4.3 | Scalable and feature-rich, good for small businesses |
Zendesk for Service | 4.4 | Popular choice for small to medium businesses |
Esker Customer Service Suite | 4.8 | High rating, but less explicitly noted for small businesses |
Oracle Fusion Service | 4.7 | High rating, broad enterprise focus |
eGain Customer Engagement Suite | 4.6 | Strong user satisfaction, cloud-based |
Salesforce Service Cloud | 4.4 | Industry leader, scalable but often used by larger businesses |
Sugar Serve | 4.4 | Comprehensive CRM, suitable for various business sizes |
Emplifi Service Cloud | 4.2 | Unified platform, less specific to small businesses |
ServiceNow Customer Service | 4.3 | Cloud-based, enterprise focus |
Microsoft Dynamics 365 | 4.3 | Broad digital transformation focus |
Verint Channel Automation | 3.7 | Lower rating, enterprise focus |
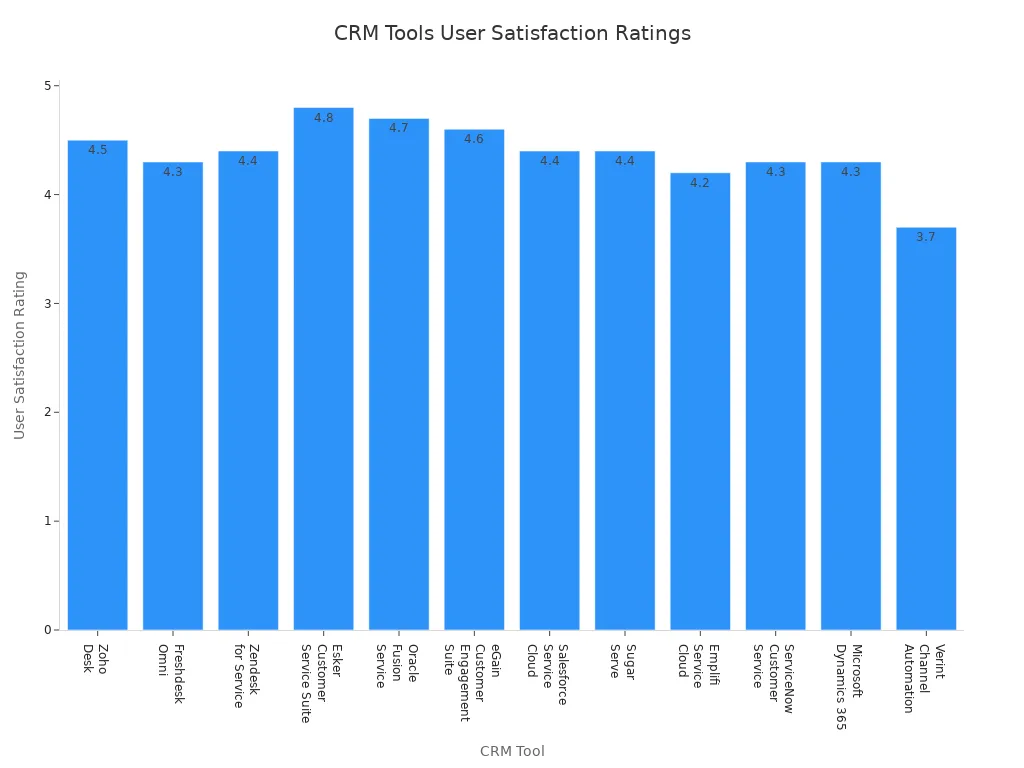
Small businesses should consider factors such as scalability, integration options, and ease of use when selecting a CRM. Many tools offer cloud-based access and mobile apps, making it easier for teams to manage customer relationships from anywhere. Automation and reporting features also help businesses track performance and improve customer service over time.
Inventory Management

Stock Tracking
Inventory management plays a vital role in small business success. Accurate stock tracking helps owners know what products they have, where items are stored, and how quickly inventory moves. Reliable records of products sold and stored support better decision-making. High inventory turnover often signals strong sales and healthy profit margins. Low turnover can indicate weak sales and reduced liquidity. Poor stock tracking leads to excess or obsolete inventory, tying up capital that could be used elsewhere. Owners who use inventory management software automate tracking, avoid overstocking, and ensure enough stock to meet demand. Good inventory practices support operational efficiency and help businesses meet customer needs.
Tip: Regular inventory audits help maintain accurate counts and prevent costly mistakes.
Small businesses benefit from tools that simplify stock tracking. Many solutions offer real-time updates, barcode scanning, and customizable reports. These features allow owners to monitor inventory levels and spot trends quickly.
Reordering
Reordering ensures that businesses always have the right products available for customers. Owners set minimum stock levels and receive alerts when inventory runs low. Automated reordering systems help avoid stockouts and reduce manual work. Strategic reordering supports stock rotation, such as first-in, first-out (FIFO), which keeps products fresh and prevents dead stock. Sales promotions, like discounts or flash sales, can help clear slow-moving inventory and improve cash flow. However, frequent promotions may erode profit margins and create customer dependency on discounts. Owners must calculate break-even points for promotions to ensure increased sales volume covers reduced margins.
Effective reordering reduces storage and depreciation costs. It also improves cash liquidity by converting stagnant inventory into cash. Businesses that plan reorders carefully avoid tying up funds in excess stock and maintain healthy cash flow.
Supplier Management
Supplier management helps businesses maintain strong relationships with vendors and ensures a steady supply of products. Owners track supplier performance, delivery times, and pricing to make informed choices. Reliable suppliers support consistent inventory levels and reduce the risk of stockouts. Businesses often use inventory management tools to monitor supplier orders and automate procurement.
The following table highlights popular inventory management tools for small businesses:
Tool Name | Best For | Key Features & Strengths | Pricing Highlights | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
BlueTally | All-around inventory & asset mgmt | Asset tracking with QR codes, maintenance logs, customizable reports, low stock alerts | Free plan available; Starter $59/mo | Powerful integrations, SOC 2 certified, responsive support | Free trial limited to 50 items |
inFlow Inventory | B2B and wholesale businesses | Multiple pricing schemes, bulk product updates | Pricing varies; responsive support | Comprehensive inventory mgmt, good support | Integration setup can be challenging |
Ordoro | Multichannel sellers | Order aggregation, kitting/bundling, shipping integrations | Advanced $349/mo, Premium $499/mo | Multi-channel & warehouse mgmt, dropshipping support | Hourly syncing issues |
Katana | Manufacturing businesses | Real-time stock updates, order prioritization, sales order fulfillment | Starter $179/mo, up to $1799/mo | Real-time mgmt, reorder automation, multi-currency | No dedicated mobile app |
Veeqo | Free inventory tool | Real-time syncing, automated stock rules, detailed reports | Free with unlimited orders/users | Ecommerce & shipping integrations, good support | Learning curve |
Finale Inventory | Mobile barcode scanning | Mobile barcode app, stock auditing, proactive procurement, financial reporting | Starter $99/mo to Platinum $949/mo | Global support, API support | Barcode app Android-only, auto logout inconvenience |
Fishbowl Inventory | QuickBooks users | QuickBooks integration, multi-location tracking, customizable reports | Starting $329/mo | Responsive support, comprehensive mgmt | Integration setup can be challenging |
Unleashed | Scaling up operations | Unlimited warehouses, BOM, comprehensive reporting | Medium $349/mo to Large Plus $999/mo | Accounting integration, dynamic reporting | Basic mobile app needs improvement |
Owners select inventory tools based on business size, product type, and integration needs. These solutions automate supplier management, streamline procurement, and support growth.
Note: Treating inventory purchases as regular expenses is a common mistake. Inventory needs change with demand, so careful planning is essential for profitability and cash flow.
Human Resources
Employee Records
Small businesses must keep accurate employee records to meet legal requirements and support daily operations. These records include personnel files, payroll documents, and medical files. Personnel files hold hiring documents, contact information, and performance reviews. Payroll files contain timesheets, W-4 and W-2 forms, and wage details. Medical files store health insurance applications, injury reports, and Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA) documentation. Form I-9s require separate storage to protect privacy and simplify audits.
Federal laws set specific retention periods for different types of records. Consistent organization, whether digital or paper, helps businesses stay compliant and efficient. The table below summarizes key legal requirements:
Type of Employee Record | Legal Requirement / Law | Retention Period |
|---|---|---|
Payroll Records | Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) | |
Wage Calculation Records (e.g., timecards) | FLSA | At least 2 years |
Benefit Plan Records | ERISA | Enrollment + 6 years |
Employee Benefit Plans | EEOC | While plan is active + 1 year |
Medical Records | OSHA | At least 30 years |
FMLA-related Records | FMLA | At least 3 years |
Employment Eligibility Verification (Form I-9) | Immigration regulations | 3 years after hire or 1 year after termination (whichever is later) |
Payroll Tax Records | IRS | At least 4 years |
Performance Reviews | Best practice | 2 years |
Termination Records | Best practice | 1 year from termination date |
Tip: Keeping records organized and secure protects both the business and its employees. Regular audits help ensure compliance with federal and state laws.
Payroll
Payroll systems help small businesses pay employees accurately and on time. These systems also handle tax calculations, deductions, and compliance with labor laws. Modern payroll solutions offer features that simplify payroll management and reduce errors. Many small businesses use software that automates payroll processing, tax filings, and year-end forms like W-2s and 1099s.
Common payroll solutions include:
Full-service automated payroll with tax calculations, filings, and payments
Built-in compliance updates for federal, state, and local regulations
Employee self-service portals and mobile apps for payroll access
HR tools for onboarding, benefits administration, and time tracking
Integration with accounting software and other business tools
Multistate tax compliance and new-hire reporting
Automated generation and delivery of year-end tax forms
The table below highlights popular payroll solutions and their compliance features:
Payroll Solution | Use Case | Key Compliance Features |
|---|---|---|
Gusto | Full-service payroll | Automated tax filings, year-end forms, PTO tracking, new-hire reporting |
Wave | Payroll add-on | Tax filing support, automated calculations |
OnPay | Payroll with HR compliance | Document storage, workers' comp, 401(k) tracking |
Rippling | Payroll with HR/IT integration | Automated processing, compliance updates, mobile payroll access |
Intuit QuickBooks | Contractor payroll | 1099 filings, direct deposit, accounting integration |
ADP | Scalable payroll | Multistate compliance, automated tax filing, onboarding |
Patriot Software | Affordable payroll | Tax filing, free setup, self-service options |
Paychex Flex | Payroll with HR support | Automated tax filings, self-service, household payroll options |
Payroll software helps small businesses stay compliant with tax laws and labor regulations. Automation reduces manual work and lowers the risk of costly mistakes.
Time Tracking
Time tracking systems record employee work hours, overtime, and absences. Accurate time tracking supports payroll accuracy and helps businesses comply with wage and hour laws. Many small businesses use digital time clocks, mobile apps, or integrated payroll software to track hours. These tools often include features like clock-in/out reminders, overtime alerts, and real-time reporting.
Reliable time tracking improves productivity and ensures fair compensation. It also provides documentation for audits and helps resolve disputes. Businesses that use automated time tracking reduce errors and save time on manual calculations.
⏰ Accurate time tracking protects both the business and its employees. It ensures everyone gets paid correctly and supports compliance with labor laws.
Operations
Workflow
Workflow systems help small businesses organize daily tasks and improve efficiency. These systems map out each step in a process, so every team member knows what to do and when to do it. Clear workflows reduce confusion and help everyone stay on track. When businesses use workflow software, they can assign roles, monitor progress, and quickly spot any problems.
Here are some ways workflow systems boost operational efficiency:
Mapping tasks clearly ensures every team member understands their responsibilities.
Assigning specific roles eliminates redundancy and clarifies accountability.
Monitoring progress with workflow software helps identify and resolve bottlenecks.
Customizable workflows allow businesses to cut unnecessary steps and improve communication.
Automating recurring tasks, such as approvals or invoice processing, reduces manual errors.
Centralized communication tools keep teams aligned, even when working remotely.
Continuous process optimization supports smooth growth and adaptation.
Tip: Businesses should regularly review their workflows to find areas for improvement and keep operations running smoothly.
SOPs
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) give businesses a set of clear instructions for routine tasks. SOPs help new employees learn faster and make sure everyone follows the same steps. This consistency reduces mistakes and saves time. Well-written SOPs also make it easier to train staff and maintain quality as the business grows.
SOPs should be easy to read and updated often. Owners can use checklists, flowcharts, or step-by-step guides. Digital SOPs stored in the cloud allow quick access for all team members. When everyone follows the same procedures, businesses see fewer errors and better results.
Note: Keeping SOPs up to date ensures that the team always uses the best methods for each task.
Project Management
Project management tools help small businesses plan, track, and complete projects on time. These tools organize tasks, set deadlines, and allow teams to share updates. Many tools also offer features like file sharing, real-time chat, and progress tracking. This makes it easier for teams to work together, even from different locations.
The table below shows some popular project management tools and their main advantages:
Tool | Main Advantages | Example Companies Using It |
|---|---|---|
Evernote | Organizes ideas, documents, workflows; team storage with shared access; multi-platform (web, desktop, mobile) | Migros (Swiss supermarket) |
Basecamp | All-in-one package: document storage, schedule management, real-time group chats, client collaboration | Groupon, Harvest |
Trello | Visual card system for project tracking; drag-and-drop ease; multi-tier pricing; integrates with many apps | National Geographic, Adobe, British Red Cross |
Slack | User-friendly integrations; manages email campaigns; archives conversations; fosters collaboration | NASA Jet Propulsion Labs, Zapier, Emma |
Flow | Simple UX; Kanban boards; resource management; integrates with Slack; supports project milestone sharing | Shopify, Bumble, TED |
Asana | Multiple workflow visualizations; project status at a glance; priority assignment; flexible pricing | New York Times, Deloitte, Red Bull, United Way |
Many small businesses also use tools like Microsoft Office 365 and Google Workplace for document sharing, scheduling, and communication. These platforms support teamwork and help keep projects organized.
Tip: Choosing the right project management tool depends on team size, budget, and the type of work. Testing a few options can help find the best fit for the business.
Marketing
Content Planning
Content planning helps small businesses organize their marketing messages and reach the right audience. A clear plan outlines what topics to cover, when to publish, and which channels to use. Many businesses start by identifying their target customers and the problems they want to solve. They then create a content calendar that schedules blog posts, videos, social media updates, and email campaigns. This approach keeps marketing efforts consistent and focused.
A good content plan includes a mix of formats. Blog articles educate customers, while videos and infographics grab attention quickly. Social media posts encourage engagement and sharing. Businesses often use tools like Google Calendar or Trello to manage their content schedules. Regular planning sessions help teams review what works and adjust their strategy for better results.
Tip: Consistent content builds trust and keeps customers coming back for more information.
Social Media
Social media platforms give small businesses a powerful way to connect with customers and promote their brand. Facebook stands out with its large user base and affordable ads. Businesses can target specific groups and interact directly with customers. Instagram works well for visual marketing. Many users discover new products there and feel inspired to make purchases after seeing posts.
Small businesses often use social media management tools to handle multiple platforms from one dashboard. These tools support Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, LinkedIn, Pinterest, and TikTok. Key features include automated content creation, scheduling, and analytics. AI-powered recommendations help businesses choose the best times to post and suggest effective hashtags. Unified inboxes allow teams to respond to messages quickly, while social listening tools track customer sentiment.
Social media management platforms offer:
Multi-channel content scheduling
AI-driven optimization and A/B testing
Analytics and reporting
Affordable pricing and scalability
Integration with tools like Google Analytics and Canva
Mobile apps for on-the-go management
These features help small businesses save time and improve their marketing results. Team collaboration tools make it easier to manage campaigns, even with limited staff.
Social media success depends on regular posting, quick responses, and adapting to trends.
Email Marketing
Email marketing remains one of the most effective tools for small businesses. It allows direct communication with customers and helps build lasting relationships. Businesses use email to share news, promote products, and offer special deals. Personalization increases open rates and encourages customers to take action.
For small businesses, email marketing delivers a strong return on investment. On average, every $1 spent on email marketing brings in about $38. This high ROI makes email a smart choice for reaching customers and driving sales. Many email platforms offer templates, automation, and analytics to help businesses create professional campaigns without much technical skill.
A simple email marketing process includes:
Building a subscriber list
Segmenting contacts based on interests or behavior
Creating engaging content and subject lines
Scheduling emails for optimal times
Tracking results and refining future campaigns
Note: Regularly reviewing email performance helps businesses improve their messages and increase engagement.
Sales
Lead Generation
Small businesses rely on effective lead generation strategies to grow their customer base and increase sales. Owners use a variety of methods to attract and convert leads. The following table highlights some of the most successful approaches:
Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
Irresistible Opt-in Offers | Exclusive downloadable content such as eBooks or templates encourage prospects to share contact details. |
Local SEO | Optimizing business profiles and website content improves visibility in local searches. |
Email Marketing Campaigns | Personalized emails with clear calls-to-action nurture leads and drive conversions. |
Social Media Platforms | Engaging posts and targeted ads on LinkedIn, Facebook, and Twitter reach new audiences. |
Hosting Webinars and Events | Online and local events establish authority and generate qualified leads. |
AI Tools and Automation | Automated outreach and personalized messaging increase efficiency and lead quality. |
Content Marketing | Blogs, case studies, and repurposed content support SEO and educate potential customers. |
Multi-channel Approaches | Combining direct mail, PPC ads, and other channels broadens lead capture. |
Owners also participate in local events, host webinars, and use play-on-demand sessions to attract prospects. They develop content marketing strategies with ebooks, case studies, and templates to educate leads. Social media marketing focuses on platforms where the target audience is active, using both organic posts and paid ads. Email campaigns use segmentation and automation to deliver compelling messages. SEO techniques, including keyword research and local optimization, help increase organic traffic and lead quality.
Tip: Combining several lead generation methods increases reach and improves the chances of finding high-quality prospects.
Pipeline
A well-structured sales pipeline helps small businesses manage leads from initial contact to final sale. Pipeline management tools organize the sales process, prioritize high-value opportunities, and automate follow-ups. Owners use these tools to identify promising prospects and allocate resources effectively. Automated reminders and follow-up cadences ensure consistent communication, which is critical for converting leads.
Studies show that companies with a defined sales process generate 18% more revenue than those without. Businesses that optimize pipeline management grow 28% faster than their peers. Pipeline features such as AI-driven analytics and CRM integrations provide real-time visibility, identify bottlenecks, and support accurate forecasting. Sales teams use these insights to focus on deals likely to close and tailor interactions to customer needs.
Sales pipeline management tools help shorten sales cycles, improve coordination, and increase conversion rates.
Closing
Closing sales requires skill, preparation, and a customer-focused approach. Owners build rapport by engaging in honest conversations and showing empathy. They listen actively to customer needs and offer personalized solutions. Effective closing techniques guide prospects toward a decision without pressure. Common methods include the assumptive close, alternative close, scarcity close, takeaway close, and summary close.
Sales teams use meeting management tools to schedule and follow up on sales meetings. Deal progression tools help align purchase criteria and advance opportunities. Multi-threading strategies engage multiple stakeholders, while opportunity management tools prioritize actions and identify risks. After closing, owners thank customers, fulfill promises, and maintain communication to encourage repeat business. They ask for feedback and referrals to expand their customer base.
Best practices for closing sales:
Build trust and show genuine interest in customer needs.
Handle objections by understanding product strengths and weaknesses.
Use a formalized sales playbook for demos and objection handling.
Leverage technology to track interactions and improve efficiency.
Follow up after closing to ensure satisfaction and foster future sales.
Successful closing depends on listening, understanding, and providing value. Owners who master these skills create loyal customers and drive business growth.
Customer Service
Support Channels
Small businesses rely on multiple customer service channels to meet customer needs and resolve issues quickly. Each channel offers unique benefits and fits different situations. The table below highlights the most common support channels and their descriptions:
Customer Service Channel | Description |
|---|---|
Live Chat | Real-time online communication with customer service representatives for fast and efficient issue resolution. |
AI-Powered Assistants | Chatbots handling simple queries 24/7, freeing human agents for complex tasks. |
Text Messaging | SMS communication for quick updates and customer engagement. |
Customer interaction via email with timely responses and clear CTAs. | |
Web Forms | Structured forms to collect and manage customer inquiries efficiently. |
FAQ Pages | Self-service pages answering common questions to empower customers and reduce support load. |
Self-Service Tools | Platforms including knowledge bases, FAQs, and community forums for customer empowerment. |
Social Media | Real-time customer engagement on social platforms to provide assistance and build relationships. |
In-Person Assistance | Physical store support including product demos and events to enhance customer experience. |
Live chat and AI-powered assistants provide instant answers. Email and web forms allow for detailed communication and record-keeping. FAQ pages and self-service tools help customers solve problems independently. Social media and text messaging offer quick, personal engagement. In-person assistance remains important for businesses with physical locations.
Businesses that offer multiple support channels increase customer satisfaction and build trust.
Feedback
Collecting customer feedback helps small businesses improve service quality and adapt to customer needs. Feedback comes from surveys, reviews, and social media. Each method provides direct insights into customer expectations and experiences.
Customer reviews reveal what works well and highlight areas needing improvement.
Negative reviews identify problems and give businesses a chance to resolve issues, showing commitment to service.
Prompt responses to feedback can turn negative experiences into positive outcomes.
Reviews and surveys guide improvements in products, services, and processes.
Engaging with feedback builds trust and strengthens customer loyalty.
Loyal customers often return and recommend the business to others, boosting reputation and reducing marketing costs.
Positive reviews influence new customers and improve local search rankings.
Regular analysis of feedback enables informed decisions and fosters a customer-focused culture. Implementing changes based on feedback signals to customers that their opinions matter.
Collecting and acting on feedback leads to better service and stronger customer relationships.
Templates
Customer service templates help support teams respond quickly and consistently. Effective templates save time and ensure a professional tone, but they should always allow for personalization. The most useful templates include:
Instant support responses that acknowledge customer issues and set clear expectations for updates.
Follow-up messages requesting feedback to improve service quality.
Proactive welcome emails to new customers, building rapport from the start.
Templates for handling upset customers with empathy and a focus on resolution.
Inbox management apps that let teams share templates, ensuring consistent communication across remote staff.
Best practices for using templates:
Evaluate each customer request to understand the situation and avoid repetitive exchanges.
Show empathy by acknowledging customer feelings and avoiding confrontation.
Provide detailed answers and up-to-date resources.
Anticipate follow-up questions and include answers proactively.
Personalize responses by using customer names and tailoring language to each issue.
Templates should reflect the brand’s voice and support meaningful interactions. They serve as tools to help staff deliver excellent service, not as replacements for genuine communication.
Well-designed templates improve response times and help teams deliver consistent, high-quality support.
IT & Security
Data Security
Small businesses face many cybersecurity threats that can disrupt operations and put sensitive data at risk. Common threats include malware, ransomware, phishing, password hacking, and social engineering attacks. Malware comes in several forms, such as trojan horses, viruses, and worms. Ransomware attacks can lock important business data and demand payment for its release. Phishing uses fake emails or messages to steal information, often leading to business email compromise. Weak passwords make accounts easy targets for hackers. Many small businesses lack strong security measures, making them attractive to attackers.
Nearly 70% of small businesses experience cyber attacks, and 60% of those attacked close within six months if they do not have a cybersecurity plan.
Other risks include data breaches, website hacking, and denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks. Employees at small businesses face more social engineering attacks than those at larger companies. Most small businesses hold customer data, such as credit card numbers and social security numbers, which increases the impact of a breach. Regular security training, strong password policies, and up-to-date software help reduce these risks.
Cloud Solutions
Cloud solutions offer secure, affordable options for small business IT needs. These services provide remote access to data, user-friendly interfaces, and automated backup management. Cloud platforms enable quick disaster recovery, helping businesses maintain continuity during unexpected events. Flexible storage options allow companies to scale as they grow, while also reducing costs.
Many cloud solutions include advanced security features. SD-WAN technology offers reliable and secure networking with backup connections. Unified communications platforms use end-to-end encryption and multifactor authentication to protect business communications. Cloud-based cybersecurity tools, such as Zero-Trust Network Access (ZTNA), Security Service Edge (SSE), and Secure Access Service Edge (SASE), add extra layers of protection.
Cloud Backup Solution | Key Security Features | Affordability & Suitability for SMBs |
|---|---|---|
Microsoft Azure | Compliance-focused, secure integration with Microsoft 365 | Scalable storage, good for businesses using Microsoft tools |
Oracle Cloud | Enterprise-grade security, regulatory compliance | Cost-effective plans for SMBs |
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) | Secure storage, global data centers | Upfront pricing, free credits for testing |
Acronis Cyber Backup | Advanced encryption, ransomware protection | Unlimited storage, flexible server locations |
MSP360 | Custom encryption, GDPR and HIPAA compliance | Highly affordable, free plan available |
Vultr | Robust security protocols | Competitive pricing, scalable hosting |
Vinchin Backup & Recovery | End-to-end encryption, immutable backups | Cost-effective, easy to use with 24/7 support |
Cloud solutions help small businesses protect valuable data and support remote work.
Access Control
Access control systems protect both digital and physical resources. Best practices start with defining role-based permissions, so employees only access what they need for their jobs. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds another layer of security. Businesses should conduct regular access audits to remove outdated permissions and align access with current roles.
Enforce multi-factor authentication on critical systems.
Conduct routine access audits to update permissions.
Automate onboarding and offboarding to reduce errors.
Use centralized Identity and Access Management (IAM) solutions.
Integrate endpoint security to allow only compliant devices.
Monitor access in real time to detect suspicious activity.
Adopt a Zero Trust policy, verifying every login.
Apply the principle of least privilege, granting only necessary access.
Employee training on access control and security awareness strengthens the overall defense of the business.
Compliance & Legal
Licenses
Small businesses in the United States must follow many compliance rules to operate legally. Owners need to secure and maintain the right licenses and permits at the federal, state, and local levels. These requirements depend on the business type and location. Common licenses include general business licenses, health permits, and industry-specific certifications. Failure to renew or update these licenses can lead to fines or even business closure.
Key compliance requirements for small businesses include:
Following federal labor laws such as the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), which covers minimum wage, overtime pay, and child labor standards.
Complying with environmental regulations from the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), which address air and water quality, hazardous waste, and toxic substances.
Paying all federal and state taxes on time.
Renewing business licenses and local permits as required.
Maintaining and renewing any industry-specific licenses, permits, or certifications.
Owners should check with local and state agencies to confirm which licenses apply to their business. Regular reviews help avoid costly mistakes.
Document Management
Proper document management supports compliance and protects the business during audits or legal disputes. Owners must keep records such as bylaws, operating agreements, stock or membership transfers, and meeting minutes. Corporations and LLCs must hold required meetings and maintain accurate records. Organized records make it easier to file annual or biennial reports and pay state fees.
Many small businesses use digital tools to manage legal documents. Services like LegalZoom offer registered agent services, annual report filing, and business license search tools. These platforms provide legal document templates for consulting agreements, employment contracts, non-disclosure agreements, and more. Electronic signature tools and secure cloud storage help keep documents safe and accessible.
Keeping documents organized and up to date reduces stress and supports smooth business operations.
Deadlines
Meeting compliance deadlines is critical for small businesses. Missing a deadline can result in penalties, loss of good standing, or legal trouble. Owners must track important dates such as tax payments, license renewals, and report filings.
A simple checklist for compliance deadlines includes:
Renew business licenses and permits before they expire.
File annual or biennial reports with the state and pay associated fees.
Complete federal requirements like Affordable Care Act reporting if the business has 50 or more employees.
Maintain compliance with marketing, advertising, workplace safety, and disability laws.
Legal service providers often send reminders for upcoming deadlines. Using compliance kits, document templates, and digital calendars helps owners stay organized and avoid missing important dates.
Staying ahead of deadlines protects the business and builds trust with customers, employees, and regulators.
Small Business Systems drive long-term success by saving time, reducing stress, and enabling growth. Research shows that leadership support, expert guidance, and clear communication boost success rates for system implementation.
Factor/Statistic | Description | Impact on Small Business Success |
|---|---|---|
Success Rate with Consultant | 85% success rate when hiring software consultants for ERP implementation | Indicates external expertise significantly improves success rates |
Leadership Support | 77% of companies cite institutional leadership support as critical | Highlights importance of CEO/leadership involvement |
Communication | 60% identify effective communication with stakeholders as key | Emphasizes need for clear communication for success |
Implementation Duration | Small/midsize businesses complete ERP in 3-9 months | Shows feasibility of timely implementation for small businesses |
Implementation Approach | Over 50% use phased approach rather than 'big bang' | Suggests phased implementation reduces risk and improves outcomes |
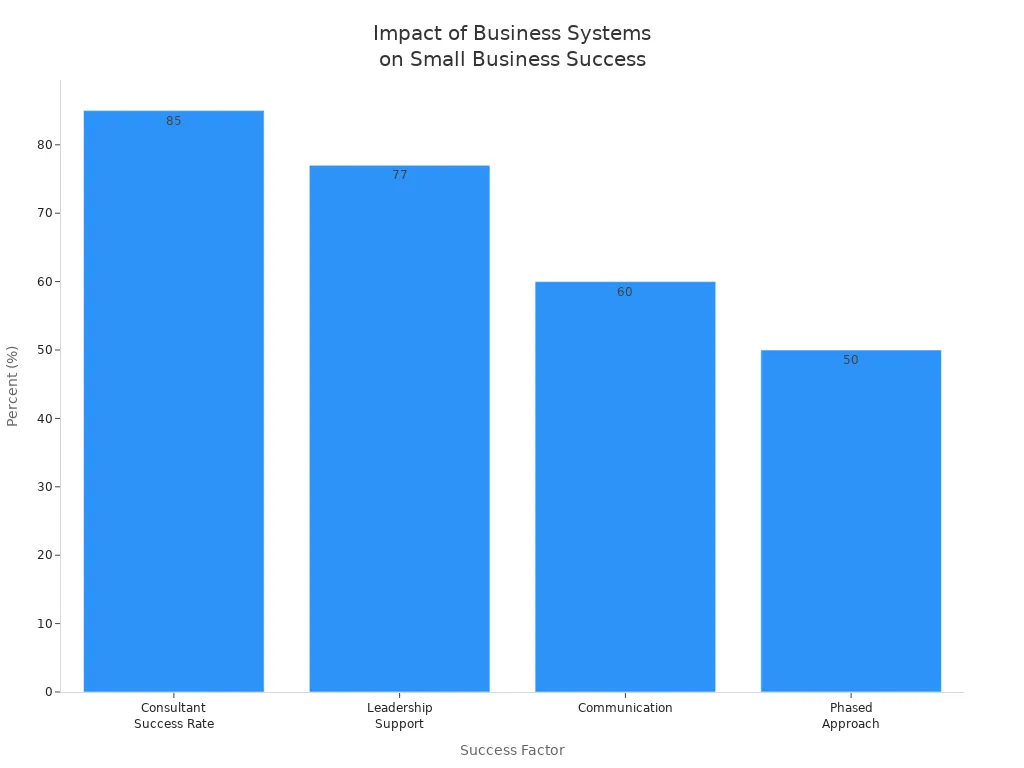
Owners can start by following these steps:
Identify important processes to systematize.
Create clear, easy-to-follow procedures.
Adopting even one or two systems can make a difference. For those seeking guidance, systems and teams can help optimize business systems. Share your progress or reach out for more resources.
FAQ
What is a small business system?
A small business system is a set of organized processes, tools, or software that helps a company manage daily tasks. These systems improve efficiency, reduce errors, and support business growth.
Why do small businesses need systems?
Systems help small businesses save time, reduce mistakes, and ensure consistency. They allow owners to focus on growth instead of daily problems. Systems also make it easier to train new employees.
How can a business choose the right system?
A business should assess its needs, budget, and goals. Owners can compare features, read reviews, and test free trials. Choosing tools that integrate with current processes helps ensure a smooth transition.
Are these systems expensive to implement?
Many systems offer affordable plans for small businesses. Some tools provide free versions with basic features. Owners can start small and upgrade as the business grows.
Can systems help with remote work?
Yes, many systems support remote work. Cloud-based tools allow teams to access data, communicate, and collaborate from any location. This flexibility helps businesses adapt to changing work environments.
How often should systems be updated?
Businesses should review systems regularly, at least once a year. Updates keep systems secure and efficient. Owners should also gather feedback from employees to find areas for improvement.
What is the biggest mistake when setting up systems?
The biggest mistake is not documenting processes clearly. Without clear instructions, employees may become confused. Proper documentation ensures everyone follows the same steps and maintains quality.



